, Corinna Eleni Psomadakis2 and Bobby Buka3
(1)
Department of Family Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine Attending Mount Sinai Doctors/Beth Israel Medical Group-Williamsburg, Brooklyn, NY, USA
(2)
School of Medicine Imperial College London, London, UK
(3)
Department of Dermatology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Keywords
AbscessBacterial infectionBacteriaPustuleErythema Staphylococcus aureus Staph Streptococcus StrepInfectionCellulitisSkin and soft tissue infectionSSTIFluctuantPurulentPusI&DIncision and drainageAntibioticsOral antibioticsMRSA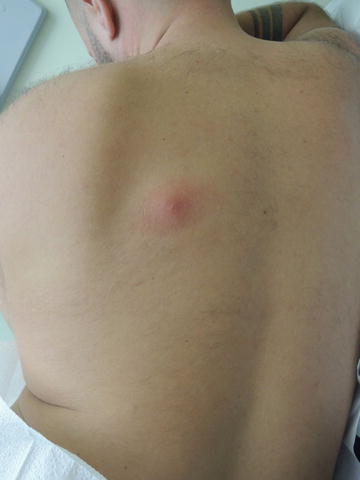
Fig. 47.1
Tender fluctuant ballotable subcutaneous nodule that is tender to touch
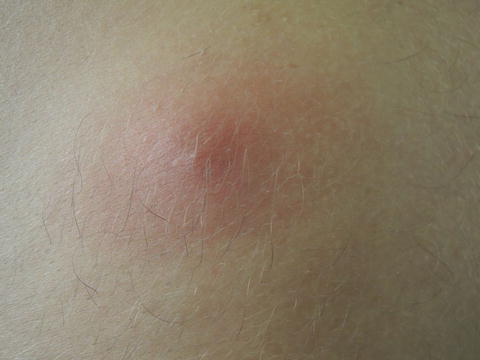
Fig. 47.2
A central pustule is occasionally discernable overlying this lesion
Primary Care Visit Report
A 29-year-old male with past medical history of depression, anxiety, and ADD (on citalopram and Adderall) presented with a “pimple” on his back. He said it started 3 weeks prior to this visit, while he was in Tanzania volunteering. Recently, the bump became larger and more irritated and he subsequently found it painful to lie on his back. He denied any fever, chills, or systemic symptoms.
Vitals were normal. On exam, on his back, there was a 4 cm × 3.5 cm area of erythema, a 2 cm × 1.5 cm area of induration, and a 1 mm white central papule.
The lesion was treated as an abscess. The abscess was not fluctuant , and therefore it was not ready to be incised and drained. The patient was advised to apply warm compresses twice daily. The area of erythema on the patient’s back was marked with a permanent marker, and he was given a prescription for Bactrim DS twice daily with instructions to initiate antibiotics only if the area of erythema spread beyond the marked borders.
Discussion from Dermatology Clinic
Differential Dx
Abscess
Ruptured epidermal inclusion cyst
Foreign body reaction
Furuncle
Carbuncle
Hidradenitis suppurativa
Favored Dx
The dome-shaped, tender nodule with central white pustule and surrounding erythema is consistent with an abscess.
Overview
Skin abscesses are collections of pus in the dermis or subcutaneous tissue that result from an inflammatory response to bacterial infection . Infection can occur following any trauma or break in the skin, or following occlusion of hair follicles. Abscesses that involve hair follicles are called furuncles . Furuncles are an example of deep folliculitis, and carbuncles are groups of furuncles that are interconnected subcutaneously.
Skin abscesses are one of the most common dermatological complaints managed by primary care and emergency physicians [1]. The most frequently implicated pathogens are S. aureus and streptococci. Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) account for 3 % of emergency department visits in the United States, and one third of those visits are due to abscesses [2]. The incidence of abscesses overall is increasing, and it is thought to mirror the increased incidence of MRSA infections [2–4]. It is estimated that over 50 % of abscesses are caused by community-associated MRSA [1, 3].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








