, Corinna Eleni Psomadakis2 and Bobby Buka3
(1)
Department of Family Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine Attending Mount Sinai Doctors/Beth Israel Medical Group-Williamsburg, Brooklyn, NY, USA
(2)
School of Medicine Imperial College London, London, UK
(3)
Department of Dermatology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Keywords
PsoriasisPenisPlaquesGenitalImmuneInflammationPruritusCorticosteroids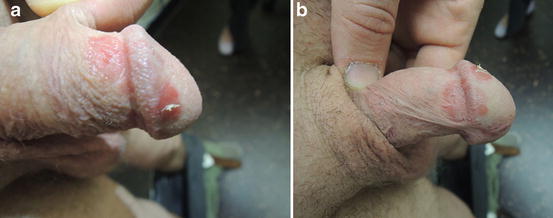
Fig. 30.1
(a and b) Scaly erythematous plaques on the penile coronal
Primary Care Visit Report
A 31-year-old male with no past medical history presented with a rash on his penis that had been present for 1 week. There was no pain, no discharge, and no dysuria. The patient had multiple sexual partners and said he had never had STD testing.
Vitals were normal. On exam, there were multiple 2–3 cm erythematous raised plaques over the meatus and glans with irregular borders and scaling. There was no pus, and no penile discharge. The penis was circumcised. The patient had no other rashes on his body.
The patient was tested for HIV, syphilis, and gonorrhea/chlamydia. The patient was advised to use bacitracin ointment on the penile lesions and, if no improvement, to then try over-the-counter lotrimin cream and aquaphor lotion.
The patient was found to be positive for Chlamydia and was treated with 1 g azithromycin.
Four weeks later, the lesions on his penis persisted despite lotrimin and aquaphor. A mild Class VI steroid cream was started (desonide 0.05 % twice daily) to treat for potential psoriasis on his penis .
Discussion from Dermatology Clinic
Differential Dx
Penile psoriasis
Lichen planus
Candida
Seborrheic dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Squamous cell carcinoma
Zoon’s balanitis
Favored Dx
Family history, and the examination of extensor surfaces of elbows and knees, scalp, lumbosacral region, and nails for signs of psoriatic plaques and nail pitting can help in making a diagnosis of psoriasis. Psoriatic plaques can present in isolation, however, and the penis may sometimes be the first site of onset of psoriasis. The red, scaly appearance of the lesions in this patient suggests psoriasis.
Overview
Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, or salmon-colored scaly plaques. Psoriasis is the most common noninfectious dermatosis that occurs on the glans penis [1]. Chronic plaque psoriasis affects approximately 2 % of the population [2, 3] with up to 40 % of those patients experiencing genital involvement [3]. Psoriasis can occur at any age. There are two peak ages of onset observed, at 16–22 years, and 57–60 years old [3]. It is most common in Caucasians [4].
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








