, Corinna Eleni Psomadakis2 and Bobby Buka3
(1)
Department of Family Medicine, Mount Sinai School of Medicine Attending Mount Sinai Doctors/Beth Israel Medical Group-Williamsburg, Brooklyn, NY, USA
(2)
School of Medicine Imperial College London, London, UK
(3)
Department of Dermatology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA
Keywords
FolliculitisBacterial folliculitisPilosebaceous unitHair follicle Staphylococcus aureas Pseudomonas aeruginosa Hot tub folliculitisTopical antibioticOral antibioticMupirocin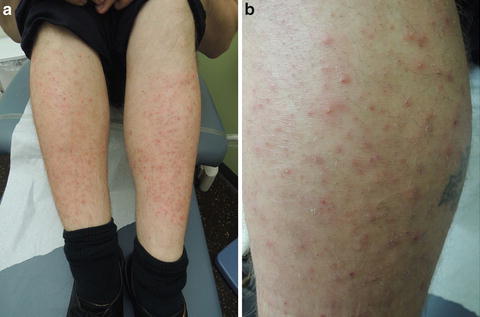
Fig. 24.1
(a and b) Pretibial legs with innumerable perifollicular papules and pustules
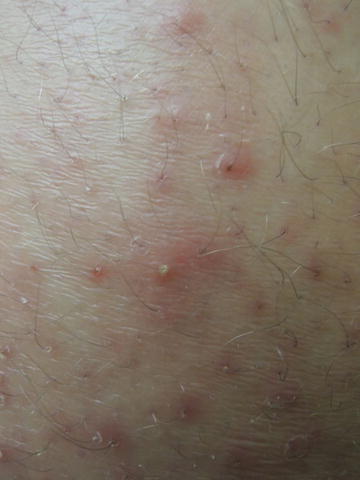
Fig. 24.2
Perifollicular pustules on erythematous base
Primary Care Visit Report
A 33-year-old male with no past medical history presented with itchy bumps on his legs, torso and arms, present for over 1 year. He had seen a primary care doctor the prior year, where he was diagnosed with folliculitis and given 2 weeks of oral antibiotics (he could not recall which one). He said the treatment made the whiteheads go away but that the bumps remained. The patient reported improvement in cooler weather and almost complete resolution in winter. With humid weather, the rash returned. He noted the rash got worse immediately after showering. Over the past few weeks, he’d noticed that each morning he was waking up with more lesions on his legs. He ran, played tennis, and surfed 2–3 times per week. He had been using over-the-counter hydrocortisone 1 % cream with little effect.
Vitals were normal. On exam, there were multiple 4–5 mm erythematous papules, some with pustules, scattered diffusely over the bilateral anterior lower extremities, and less diffusely on the posterior lower extremities . There were scattered 4–5 mm erythematous papules on the lower forearms and abdomen as well.
This appeared to be folliculitis. Given the severity, duration, and failure to resolve on 2 weeks of oral antibiotics , the patient was referred to dermatology for further evaluation.
Discussion from Dermatology Clinic
Differential Dx
Bacterial folliculitis
Fungal folliculitis
Pityrosporum folliculitis
Pseudomonas folliculitis (AKA “hot tub” folliculitis )
Eosinophilic folliculitis of HIV
Acne
Keratosis pilaris
Favored Dx
Erythematous papules and pustules that occur at the openings of hair follicles are consistent with common bacterial folliculitis . This particular patient’s history, with no recent exposure to whirlpools or hot tubs and no predisposing conditions, and the appearance of his lesions also indicate common bacterial folliculitis .
Overview
Folliculitis describes a common inflammation of the pilosebaceous unit —which includes the hair shaft, hair follicle , sebaceous gland, and erector pili muscle. It can occur due to infection (bacterial, fungal, viral, parasitic), irritation, trauma, some medications, and certain diseases. Folliculitis is classified as superficial or deep depending on which parts of the hair follicle are affected. The most common type of folliculitis is superficial bacterial folliculitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus [1–3]. S. epidermidis and Streptococcus species have also been implicated [3].
There are several variants of folliculitis, each associated with different pathogens or predisposing conditions. Approximately 4 % of patients on long-term antibiotic treatment for acne may develop peri-oral gram-negative folliculitis, frequently caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa [1, 4]. P. aeruginosa is also involved in “hot tub” folliculitis [2, 4]. Other gram-negative bacteria involved in the pathogenesis of folliculitis are Klebsiella, Proteus, Escherichia, Enterobacter, and Citrobacter species [1, 4, 5]. Fungal folliculitis may be caused by dermatophytes (most frequently Malassezia and T. rubrum), pityrosporum yeasts, and Candida [4]. Candida species are implicated in folliculitis of immunocompromised people and heroin abusers [2, 3]. Herpes simplex virus and herpes zoster virus are two common causes of viral folliculitis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








