![]() Clinical suspicion of patellar dislocation
Clinical suspicion of patellar dislocation
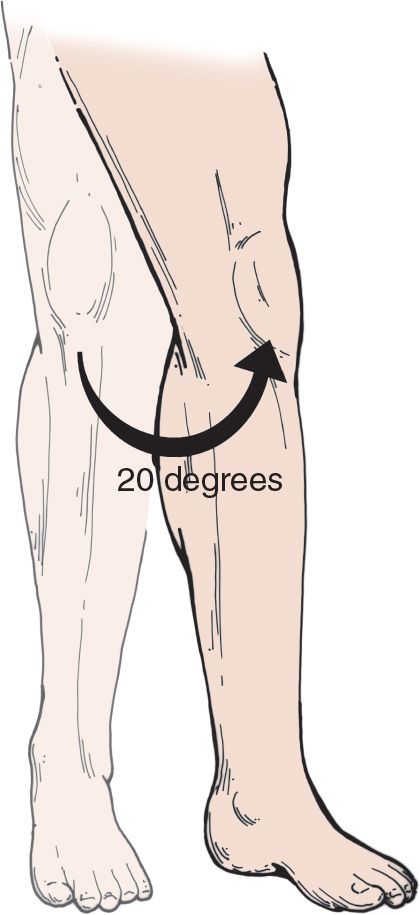
![]() The knee is held in 20 to 30 degrees of flexion
The knee is held in 20 to 30 degrees of flexion
![]() An obvious deformity is typically seen
An obvious deformity is typically seen
![]() Dislocated patella on x-ray (anteroposterior [AP] or sunrise views; lateral view less helpful)
Dislocated patella on x-ray (anteroposterior [AP] or sunrise views; lateral view less helpful)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Fracture
Fracture
![]() Effusion (hemarthrosis)
Effusion (hemarthrosis)
TECHNIQUE
![]() Patellar dislocations frequently relocate spontaneously before the patient seeks treatment
Patellar dislocations frequently relocate spontaneously before the patient seeks treatment
![]() Intravenous Sedation and Muscle Relaxation
Intravenous Sedation and Muscle Relaxation
![]() Often the procedure may be accomplished without use of sedation or muscle relaxation
Often the procedure may be accomplished without use of sedation or muscle relaxation
![]() Reduction Procedure
Reduction Procedure
![]() Reduction is performed by manually applying pressure to the patella in an anteromedial direction while extending the extremity
Reduction is performed by manually applying pressure to the patella in an anteromedial direction while extending the extremity
![]() A palpable relocation should be felt and confirmed by relief of the patient’s symptoms
A palpable relocation should be felt and confirmed by relief of the patient’s symptoms
![]() Reduction may be difficult due to the medial patellar facet being locked on to the lateral femoral condyle
Reduction may be difficult due to the medial patellar facet being locked on to the lateral femoral condyle
![]() In these cases, apply downward pressure to the lateral patella which creates the external rotational force needed to unlock the facet (FIGURE 64.1). Continue with the standard reduction technique.
In these cases, apply downward pressure to the lateral patella which creates the external rotational force needed to unlock the facet (FIGURE 64.1). Continue with the standard reduction technique.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree