Fig. 7.1
Anatomy of the facial nerve. (1) Facial nerve, (2) auriculotemporal nerve, (3) superficial temporal branches, (4) parotid plexus, (5) temporal branches, (6) zygomaticotemporal branch of the zygomatic nerve, (7) zygomaticofacial branch of the zygomatic nerve, (8) buccal branches of the facial nerve (Reproduced with permission from Danilo Jankovic)
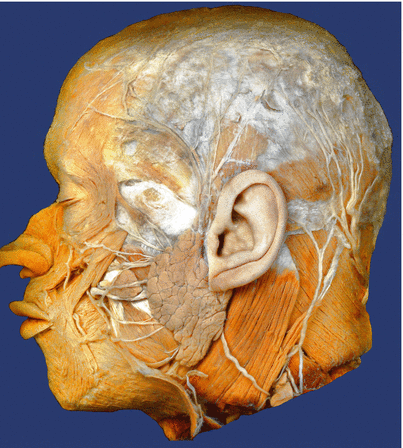
Fig. 7.2
Facial nerve. Anatomic specimen (Reproduced with permission from Danilo Jankovic)
The seventh cranial nerve carries motor fibers for the muscles of facial expression and—in the intermediate nerve, a nerve fascicle emerging separately from the brain stem—gustatory fibers and visceral efferent secretory (parasympathetic) fibers. Both sections of the nerve pass through the internal acoustic meatus and emerge as a neural trunk in the facial canal. The geniculate ganglion is located at the bend in the nerves in the petrous bone. The facial canal then courses via the tympanic cavity and turns caudally toward the stylomastoid foramen, through which the nerve exits from the skull. In the parotid gland, it divides into its end branches (parotid plexus). Before entering the parotid gland, the facial nerve gives off the posterior auricular nerve and branches to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and to the stylohyoid muscle. From the parotid plexus emerge the temporal branches, zygomatic branches, buccal branches, and marginal mandibular branch and the cervical branch to the platysma. These branches supply the muscles of facial expression.
Block Techniques
The facial nerve can be blocked using various techniques along its course to the orbit.
Van Lint Method [5] (Fig. 7.3)

Fig. 7.3
Block for eyelid anesthesia. Van Lint method (Reproduced with permission from Danilo Jankovic)
The injection is carried out temporally from the exterior margin of the eyelid or classically just below it temporally. A 23-G needle 30–40 mm long is initially introduced until bone contact is made. After careful aspiration, the injection is carried out medially and downward and then medially and upward. Fan-shaped injection is carried out as the needle is advanced (dosage, 1.5–2 mL local anesthetic).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








