Fig. 34.1
Chest X-ray at initial presentation showing multifocal bilateral alveolar opacities
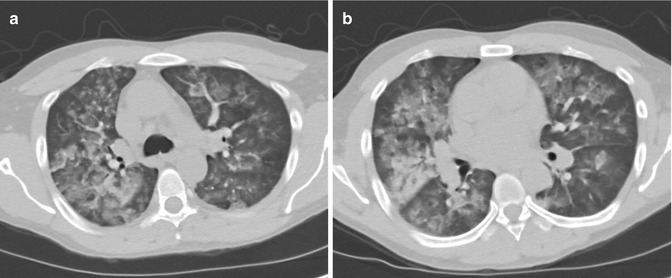
Fig. 34.2
(a, b) Chest CT images performed after hemodialysis showing diffuse bilateral alveolar opacities
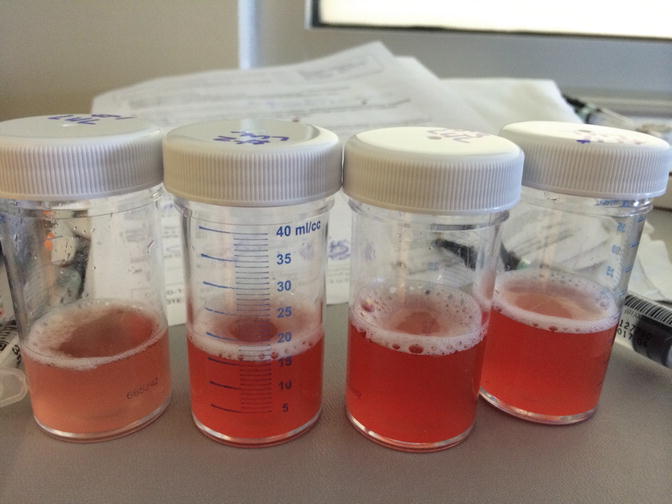

Fig. 34.3
Sequential bronchoalveolar lavages starting left to right showing progressively bloody return
Question
What is the diagnosis?
Answer
Capillaritis with diffuse alveolar hemorrhage
This patient presented with hemoptysis confirmed to be diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and chronic renal failure. The initial suspected etiology was volume overload due to missed dialysis sessions due to the elevated BNP level. The patient was treated conservatively with dialysis and while his reported hemoptysis improved, his chest x-ray showed persistent alveolar infiltrates. The serologic analysis that confirmed the diagnosis included Antinuclear Antibody of 1:360, P-ANCA positivity, and antibody to Myeloperoxidase of greater than 8.0 units. The constellation of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, renal involvement, and p-ANCA/MPO positivity confirmed a diagnosis of Microscopic Polyangiitis. Imaging of the sinuses showed no signs of inflammation of the upper respiratory tract. The patient was treated with prednisone and cyclophosphamide pulse dosing for six doses. He had one subsequent episode of hemoptysis requiring hospitalization 1 month after initial presentation. In general, he responded well to treatment and was weaned from corticosteroids over the next 3 months after completion of cyclophosphamide with improvement on chest imaging (Fig. 34.4).
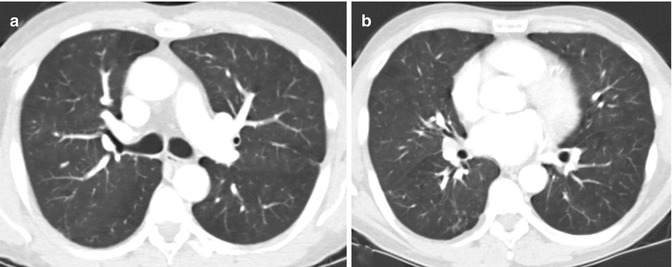

Fig. 34.4
(a, b) Chest CT images performed after 1 year of immunosuppressive treatment showing resolution of alveolar opacities
Principles of Management
Differential Diagnosis
The differential diagnosis for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage can be quite extensive ranging from autoimmune to coagulopathy to medications. Three characteristic patterns have been identified: Capillaritis, ‘Bland’ pulmonary hemorrhage, and alveolar bleeding due to another process [1, 2]. Capillaritis is the most common cause of DAH and is typically a result of antibody-mediated cell damage. Autoimmune conditions associated with DAH include antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) associated vasculitides, Goodpasture Syndrome, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Table 34.1). Initial evaluation of a patient with hemoptysis and suspected diffuse alveolar hemorrhage typically includes fiberoptic bronchoscopy to identify a source of bleeding, identification of potential infectious etiologies, and serologic workup for autoimmune conditions.
Table 34.1
Causes of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage
Capillaritis |
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) |
Churg-Strauss syndrome |
Microscopic polyangiitis (MPA) |
Isolated pauci-immune pulmonary capillaritis |
Idiopathic pauci-immune glomerulonephritis |
Primary immune complex-mediated vasculitis |
Goodpasture’s syndrome |
Henoch-Schonlein purpura |
Systemic lupus erythematosus |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome |
Mixed connective tissue disease |
Polymyositis/dermatomyositis |
Essential cryoglobulinemia |
Behcet’s disease |
Acute lung transplantation rejection |
Autologous bone marrow transplantation |
Bland Pulmonary Hemorrhage |
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis |
Coagulopathy: anticoagulants, anti-platelet, thrombolytics, DIC |
Mitral stenosis, pulmonary veno-occlusive disease |
Infection: human immunodeficiency virus infection, infective endocarditis |
Toxin or inhalation injury: isocyanates, crack cocaine, retinoic acid |
Drug-associated disease: propylthiouracil, diphenylhydantoin, amiodarone, mitomycin, |
D-penicillamine, sirolimus, methotrexate, haloperidol, nitrofurantoin, gold, |
all-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA), bleomycin, montelukast, zafirlukast, infliximab |
Alveolar bleeding due to another condition |
Diffuse alveolar damage |
Pulmonary embolism |
Sarcoidosis |
High-altitude pulmonary edema, barotrauma |
Infection: invasive aspergillosis, cytomegalovirus infection, legionellosis, herpes simplex virus infection,
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|




