![]() Presentation of the infant buttocks or feet before the head
Presentation of the infant buttocks or feet before the head
![]() Considered a high-risk delivery even among seasoned obstetricians
Considered a high-risk delivery even among seasoned obstetricians
PRESENTATION TYPES
![]() Frank breech—fetus with bilateral hip flexion and knees extended with feet opposite the head
Frank breech—fetus with bilateral hip flexion and knees extended with feet opposite the head
![]() Footling (incomplete) breech—one or both hips or knees extended and presenting before buttocks
Footling (incomplete) breech—one or both hips or knees extended and presenting before buttocks
![]() Complete breech—bilateral hip and knee flexion with feet opposite the trunk (FIGURE 42.1)
Complete breech—bilateral hip and knee flexion with feet opposite the trunk (FIGURE 42.1)
INDICATIONS
![]() Imminent vaginal delivery without obstetrical backup and buttocks or feet of the fetus appear at the vulva
Imminent vaginal delivery without obstetrical backup and buttocks or feet of the fetus appear at the vulva
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Placenta previa
Placenta previa
![]() Spontaneous arrest of labor
Spontaneous arrest of labor
![]() Immediate availability of obstetric services
Immediate availability of obstetric services
CONSENT
![]() Obtain informed consent if possible and time permits
Obtain informed consent if possible and time permits
RISKS
![]() Peripartum fetal and maternal morbidity or mortality
Peripartum fetal and maternal morbidity or mortality
![]() Maternal bleeding and pain
Maternal bleeding and pain
![]() Breech position may result from underlying fetal or uterine abnormalities
Breech position may result from underlying fetal or uterine abnormalities
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Examine for presenting part
Examine for presenting part
![]() Place the mother in lithotomy position
Place the mother in lithotomy position
![]() Allow natural delivery of baby as much as possible; assist without excessive traction
Allow natural delivery of baby as much as possible; assist without excessive traction
![]() Flex baby’s head to assist with delivery
Flex baby’s head to assist with delivery
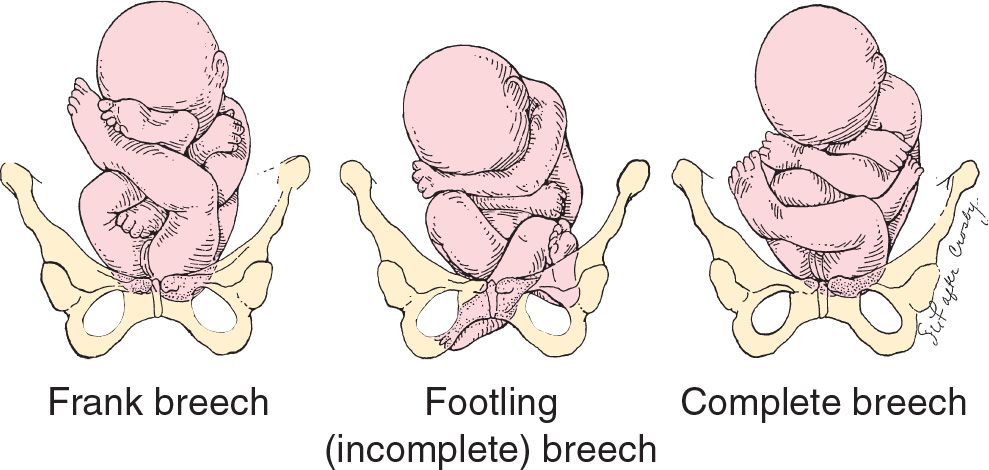
FIGURE 42.1 Fetal attitude in frank, incomplete, and complete breech presentations. (From Cruikshank DP. Breech, other malpresentations, and umbilical cord complications. In: Scott JR, Gibbs RS, Karlan BY, et al, eds. Danforth’s Obstetrics and Gynecology. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003:382, with permission.)
TECHNIQUES
![]() Examine the vagina to determine the presenting part
Examine the vagina to determine the presenting part
![]() Use ultrasonography or Leopold maneuver to determine fetal lie
Use ultrasonography or Leopold maneuver to determine fetal lie
![]() Consult obstetrics emergently
Consult obstetrics emergently
![]() Prepare for possible cesarean section
Prepare for possible cesarean section
![]() Place the mother in the lithotomy position with a wedge under her buttocks
Place the mother in the lithotomy position with a wedge under her buttocks
![]() Consider episiotomy once the fetal anus has appeared at the vulva
Consider episiotomy once the fetal anus has appeared at the vulva
![]() Allow maternal effort to spontaneously deliver the fetal buttocks, flexed knees, and lower limbs
Allow maternal effort to spontaneously deliver the fetal buttocks, flexed knees, and lower limbs
![]() Avoid excessive premature traction of the fetus, which can cause undesirable positioning of the head, resulting in head and nuchal arm entrapment
Avoid excessive premature traction of the fetus, which can cause undesirable positioning of the head, resulting in head and nuchal arm entrapment
![]() If knees are extended, the physician may flex each knee (Pinard maneuver—see FIGURE 42.2) to facilitate delivery
If knees are extended, the physician may flex each knee (Pinard maneuver—see FIGURE 42.2) to facilitate delivery
![]() Grasp the infant’s bony pelvis during vaginal delivery
Grasp the infant’s bony pelvis during vaginal delivery
![]() Rotate the fetus in the anteroposterior plane to deliver each shoulder
Rotate the fetus in the anteroposterior plane to deliver each shoulder
![]() Shoulder delivery may be expedited by flexing the fetal elbow or adducting the extended elbow by placing a finger in the antecubital fossa
Shoulder delivery may be expedited by flexing the fetal elbow or adducting the extended elbow by placing a finger in the antecubital fossa
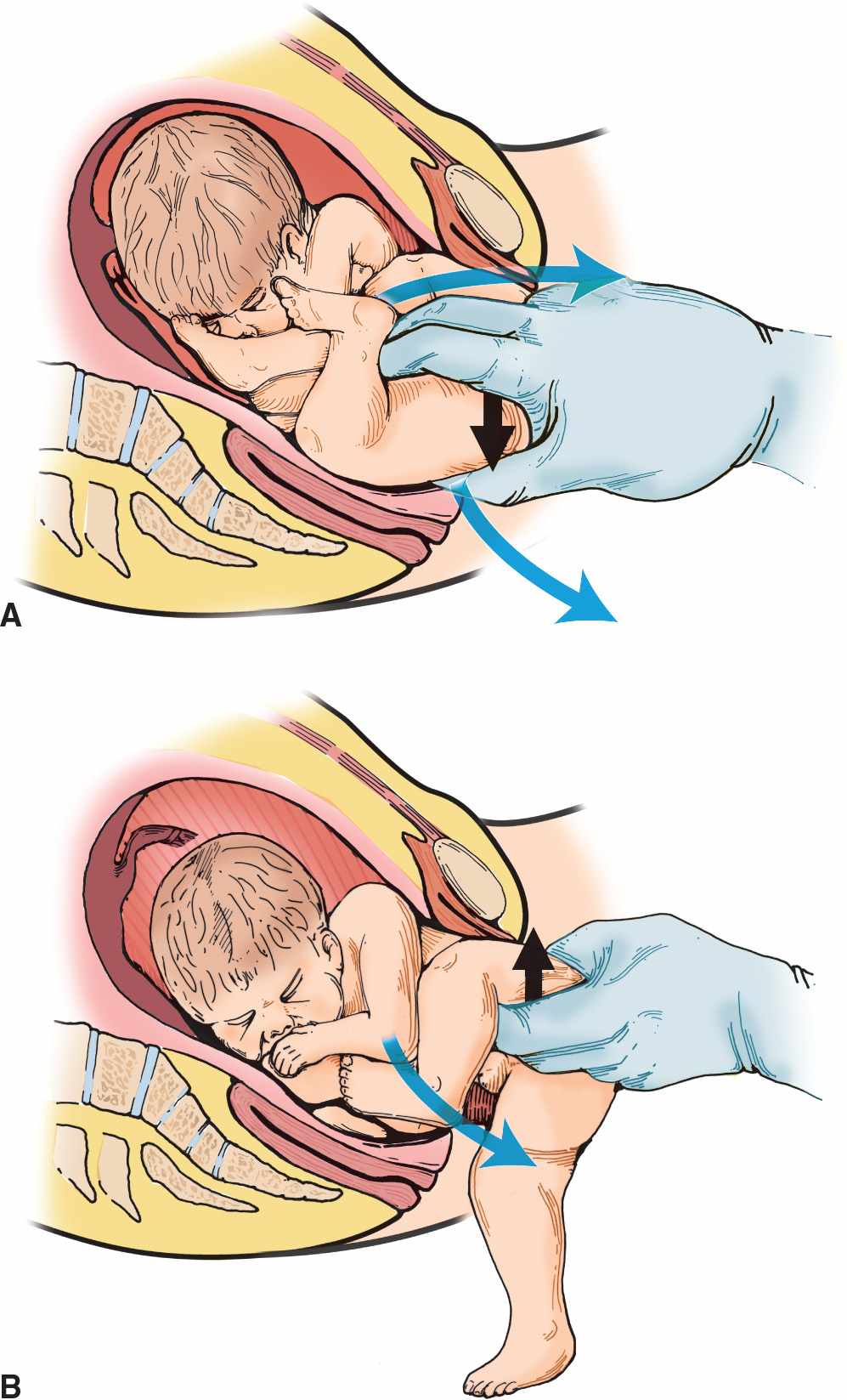
![]() When delivering the head, attempt to flex the neck by holding the chin and applying suprapubic pressure (FIGURE 42.3) or use the Mauriceau maneuver
When delivering the head, attempt to flex the neck by holding the chin and applying suprapubic pressure (FIGURE 42.3) or use the Mauriceau maneuver
![]() The index and middle fingers are placed over the infant’s maxillary bones (not in the infant’s mouth) to help keep the head flexed. This should allow the mother to expel the fetus.
The index and middle fingers are placed over the infant’s maxillary bones (not in the infant’s mouth) to help keep the head flexed. This should allow the mother to expel the fetus.
![]() Use forceps if needed
Use forceps if needed
![]() Consider symphysiotomy as a last resort
Consider symphysiotomy as a last resort
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree