Fig. 59.1
Ultrasound view of the groin area at the level of the inguinal crease
Figure 59.1 image is obtained from a patient (80yo M, 60 kg) in the PACU after a repeat femoral peripheral nerve block for postoperative pain of a knee arthroplasty. The patient received a total of 30 cc of 0.5% bupivacaine and 20 cc of 0.5% ropivacaine. Patient is complaining of persistent pain in the area of the surgery.
Questions
- 1.
What are the structures labeled a, b, and c?
- 2.
What are the possible causes of persistent postoperative pain?
- 3.
Would you repeat the block?
- 4.
If the patient develops seizures how would you treat him?
- 5.
If the patient develops hypotension and asystole how would you treat him?
- 6.
What other options are available to treat this patient’s pain?
Answers
- 1.
a, femoral vein; b, femoral artery; c, femoral nerve.
- 2.
Persistent pain might be due to:
- (a)
Inadequate distribution of the local anesthetic in the correct plane, possibly due to difficult and distorted anatomy after multiple attempts
- (b)
Lack of coverage of the sciatic nerve area on the back of the knee or the obturator nerve on the medial aspect of the thigh
- (a)
- 3.
This patient has received a large amount of local anesthetic after the two attempts; a repeat one is inadvisable as we are over the maximum safe dose for local anesthetic.
In this patient, the maximum safe dose of ropivacaine (3.5 mg/kg) is 280 mg and bupivacaine (2 mg/kg) is 160 mg.
In the case of combined local anesthetics, the proportional maximum dose of each agent should be calculated, and the sum should not exceed 100%.
This patient has received 100 mg of ropivacaine and 150 mg of bupivacaine.
The proportion of the maximum safe dose per agent is calculated as follows:
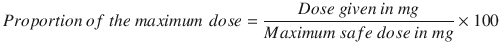
In this patient the proportion for each agent is calculated as follows: