![]() Trephination: To create a fistula through the nail to the hematoma
Trephination: To create a fistula through the nail to the hematoma
![]() Decompression, drainage, and pain relief of small subungual hematomas
Decompression, drainage, and pain relief of small subungual hematomas
![]() Nail removal and nail bed laceration repair
Nail removal and nail bed laceration repair
![]() Large hematomas and nail bed lacerations
Large hematomas and nail bed lacerations
![]() Partial nail avulsion or subluxation with nail instability or nail fold disruption
Partial nail avulsion or subluxation with nail instability or nail fold disruption
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Significant crush injuries or missing/destroyed nail matrix warrant specialty consultation
Significant crush injuries or missing/destroyed nail matrix warrant specialty consultation
RISKS/CONSENT ISSUES
![]() Germinal matrix injuries and open tuft fractures should be documented and referred to a specialist to ensure optimal outcome
Germinal matrix injuries and open tuft fractures should be documented and referred to a specialist to ensure optimal outcome
LANDMARKS
![]() Hematomas typically collect on the sterile matrix under the nail
Hematomas typically collect on the sterile matrix under the nail
![]() Germinal matrix
Germinal matrix
![]() Region where new nail is formed
Region where new nail is formed
![]() Avoid injury during the procedure
Avoid injury during the procedure
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() X-ray digit if fracture possible
X-ray digit if fracture possible
![]() Prepare patient
Prepare patient
![]() Consider anesthesia
Consider anesthesia
![]() Perform procedure (FIGURE 73.1)
Perform procedure (FIGURE 73.1)
![]() Trephination
Trephination
![]() Goal is to form a hole through the nail of sufficient size to drain the hematoma
Goal is to form a hole through the nail of sufficient size to drain the hematoma
![]() Personal protection (including an eye shield) as blood may spurt out when released
Personal protection (including an eye shield) as blood may spurt out when released
![]() Needle or scalpel method: Apply gentle pressure with the tip of the instrument perpendicular to the surface of the nail, twisting until blood is released
Needle or scalpel method: Apply gentle pressure with the tip of the instrument perpendicular to the surface of the nail, twisting until blood is released
![]() Heated paper clip method: Creates a wider hole but may tattoo the nail bed
Heated paper clip method: Creates a wider hole but may tattoo the nail bed
![]() Disposable electrocautery device method: Quick and effective (FIGURE 73.2)
Disposable electrocautery device method: Quick and effective (FIGURE 73.2)
![]() Discharge instructions are to soak the finger in warm water twice a day for 7 days to allow the blood to continue to drain
Discharge instructions are to soak the finger in warm water twice a day for 7 days to allow the blood to continue to drain
![]() Nail Bed Laceration Repair
Nail Bed Laceration Repair
![]() Supplies: Iris scissors, hemostats, and suture set with fine absorbable sutures (5-0 to 7-0 chromic or Vicryl)
Supplies: Iris scissors, hemostats, and suture set with fine absorbable sutures (5-0 to 7-0 chromic or Vicryl)
![]() Perform digital block under sterile conditions
Perform digital block under sterile conditions
![]() Apply tourniquet for hemostasis
Apply tourniquet for hemostasis
![]() Remove the nail from the nail bed matrix
Remove the nail from the nail bed matrix
![]() Insert closed Iris scissors horizontally under the nail
Insert closed Iris scissors horizontally under the nail
![]() Gently spread scissors and advance in repeated movements, gradually progressing to the nail root and separating the entire nail from the nail bed
Gently spread scissors and advance in repeated movements, gradually progressing to the nail root and separating the entire nail from the nail bed
![]() Once the nail is free from the nail bed and eponychium, grasp with hemostat and gently pull longitudinally to free the nail
Once the nail is free from the nail bed and eponychium, grasp with hemostat and gently pull longitudinally to free the nail
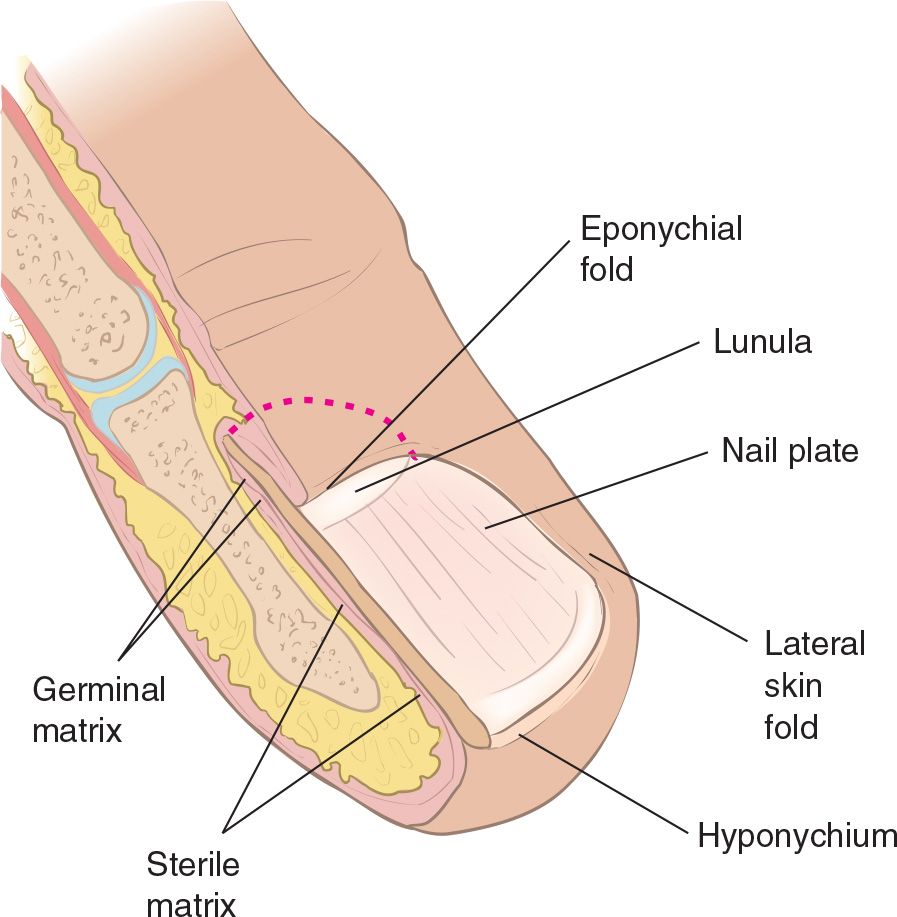
FIGURE 73.1 Anatomy of the finger and nail bed. (From Eberlein R. Hand and finger injuries. In: Henretig FM, King C, eds. Textbook of Pediatric Emergency Procedures. Philadelphia, PA: Williams & Wilkins; 1997:1048, with permission.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


