Fig. 69.1
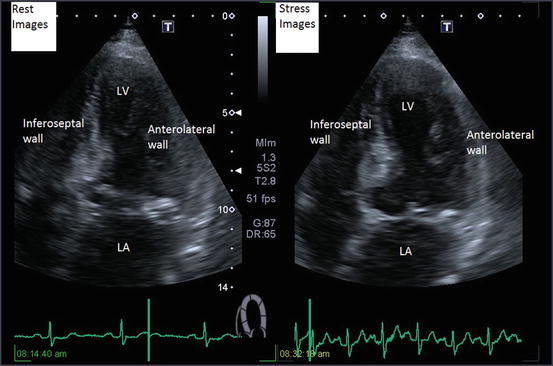
Fig. 69.2
Questions
- 1.
What do the images demonstrate?
- 2.
What is the pathophysiologic basis of stress testing?
- 3.
What factors influence the choice of stress testing?
- 4.
What is the role of stress testing in the preoperative setting?
Answers
- 1.
Patient underwent a dobutamine stress echocardiogram. Figures show still frames of the left ventricle in end systole, at rest, and at peak stress (Figs. 69.1 and 69.2). Findings are consistent with stress-induced wall motion abnormality involving the left anterior descending coronary artery distribution (anterior and anterolateral myocardium).
- 2.
Functional stress testing is the test of choice for detecting myocardial ischemia. Stress testing is based on the principle of “the ischemic cascade”; according to which, as the severity of ischemia increases, the ischemic manifestations worsen progressively from diastolic dysfunction, reduced epicardial perfusion, regional wall motion abnormalities, global systolic dysfunction, and finally EKG changes [1].
The aim of a stress test is to activate the ischemic cascade with either exercise or drugs and demonstrate the resulting ischemic manifestations via EKG, echocardiography, myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI), or magnetic resonance imaging.
Exercise stress is preferred over pharmacological stress because of the higher physiological stress levels achieved via exercise. Exercise stress also provides additional prognostic information like functional capacity. However, not all patients are candidate for exercise stress testing, especially those who have significant disabilities or disabling comorbidities.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




