80. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Definition
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) is a hypersensitivity disorder mediated by immune-complex formation. It is a potentially fatal systemic disorder that is a severe type of erythema multiforme. SJS is also known as “erythema multiforme major.”
Incidence
The frequency of SJS is estimated to be about 1.2:1,000,000 to 6:1,000,000. This disorder has been reported in all racial and ethnic groups and affects both sexes about equally over all age groups.
Etiology
Stevens-Johnson syndrome is classified into four categories (see box below). Approximately half of all cases of SJS have been linked to ingestion of a medication. To date, more than 100 different medications have been linked to the development of SJS (see box on pp. 321-322). The second most common cause result from infectious agents/vectors (see box on p. 321). As many as 25% of SJS cases are deemed idiopathic, while the smallest number of SJS cases have been associated with some form of carcinoma and/or lymphoma.
Four Etiologic Categories of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
1. Infectious
2. Drug-induced
3. Malignancy-related
4. Idiopathic
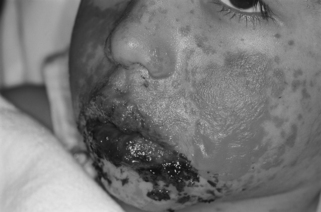 |
| Stevens-Johnson Syndrome. Severe oral and skin involvement. |
Infectious Causes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
• Adenoviruses
• Calmette-Guérin virus
• Deep fungal infections
• Enterobacter species
• Enteroviruses
• Herpes simplex virus
• Influenza
• Measles
• Mumps
• Mycobacterium pneumoniae
• Mycobacterium tuberculosis
• Streptococcus pneumoniae
• Syphilis
• Typhoid fever
Drugs Associated with the Development of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
Sulfonamides
• Pyrimethamine-sulfadoxine (Fansidar)
• Sulfadiazine (Coptin)
• Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine)
• Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Anticonvulsants
• Carbamazepine
• Phenobarbital
• Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Others
• Acetaminophen
• Allopurinol (Aloprim, Zyloprim)
• Aminopenicillins
• Amithiozone
• Amoxapine (Asendin)
• Barbiturates
• Cephalosporins
• Chlormezanone (Trancopal)
• Clobazam
• Diclofenac
• Fluvoxamine (Luvox)
• Hydantoins
• Imidazole antifungals
• Indapamide (Lozol)
• Lamotrigine (Lamictal)
• Macrolides
• Mianserin
• Oxicam
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (piroxicam, tenoxicam)
• Propionic NSAIDs
• Propranolol (Inderal, InnoPran XL)
• Pyrazolone derivatives (i.e., dipyrone)
• Quinolones
• Salicylates
• Sertraline (Zoloft)
• Tetracycline
• Tiapride
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





