![]() Impaction of the infant shoulders in the pelvic outlet occurring after delivery of the head during a vertex vaginal delivery
Impaction of the infant shoulders in the pelvic outlet occurring after delivery of the head during a vertex vaginal delivery
PROCEDURAL DEFINITION
![]() Maneuvers intended to disimpact the shoulders by adducting the shoulders, either by direct pressure or by rotating the infant’s trunk
Maneuvers intended to disimpact the shoulders by adducting the shoulders, either by direct pressure or by rotating the infant’s trunk
INDICATIONS
![]() Failure of delivery of anterior shoulder with usual downward traction after delivery of infant head
Failure of delivery of anterior shoulder with usual downward traction after delivery of infant head
![]() “Turtle Sign”—Retraction of fetal head back into maternal perineum after initial delivery
“Turtle Sign”—Retraction of fetal head back into maternal perineum after initial delivery
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Immediate availability of obstetric services for cesarean section
Immediate availability of obstetric services for cesarean section
CONSENT
![]() None. Considered an obstetrical emergency since fetal demise can occur if the procedure is indicated and not performed.
None. Considered an obstetrical emergency since fetal demise can occur if the procedure is indicated and not performed.
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Recognize shoulder dystocia
Recognize shoulder dystocia
![]() Call for help immediately (including emergency department personnel and appropriate consulting services)
Call for help immediately (including emergency department personnel and appropriate consulting services)
![]() Prepare patient
Prepare patient
![]() IV, oxygen, and maternal and fetal monitor must be available
IV, oxygen, and maternal and fetal monitor must be available
![]() Call for assistance and obstetric, anesthesia, and pediatric backup
Call for assistance and obstetric, anesthesia, and pediatric backup
![]() Drain bladder if distended
Drain bladder if distended
![]() Avoid maternal pushing while attempts are made to reposition fetus
Avoid maternal pushing while attempts are made to reposition fetus
![]() Avoid excessive head and neck traction or uterine fundal pressure
Avoid excessive head and neck traction or uterine fundal pressure
![]() Apply maneuvers to facilitate delivery (may need to attempt multiple maneuvers)
Apply maneuvers to facilitate delivery (may need to attempt multiple maneuvers)
TECHNIQUES
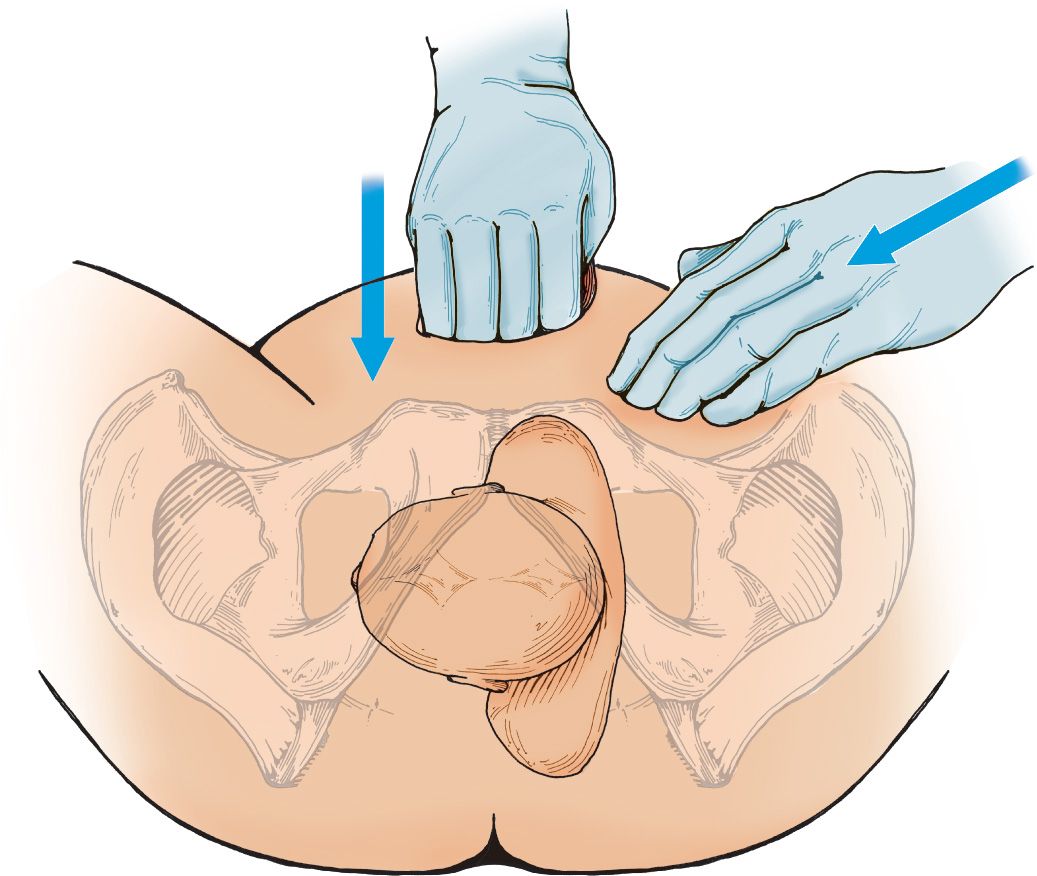
![]() Mazzanti Maneuver (FIGURE 41.1)
Mazzanti Maneuver (FIGURE 41.1)
![]() Adduct shoulders by applying downward or oblique suprapubic pressure to dislodge anterior shoulder from pubic symphysis
Adduct shoulders by applying downward or oblique suprapubic pressure to dislodge anterior shoulder from pubic symphysis
![]() Avoid applying fundal pressure, which may cause further fetal injury
Avoid applying fundal pressure, which may cause further fetal injury
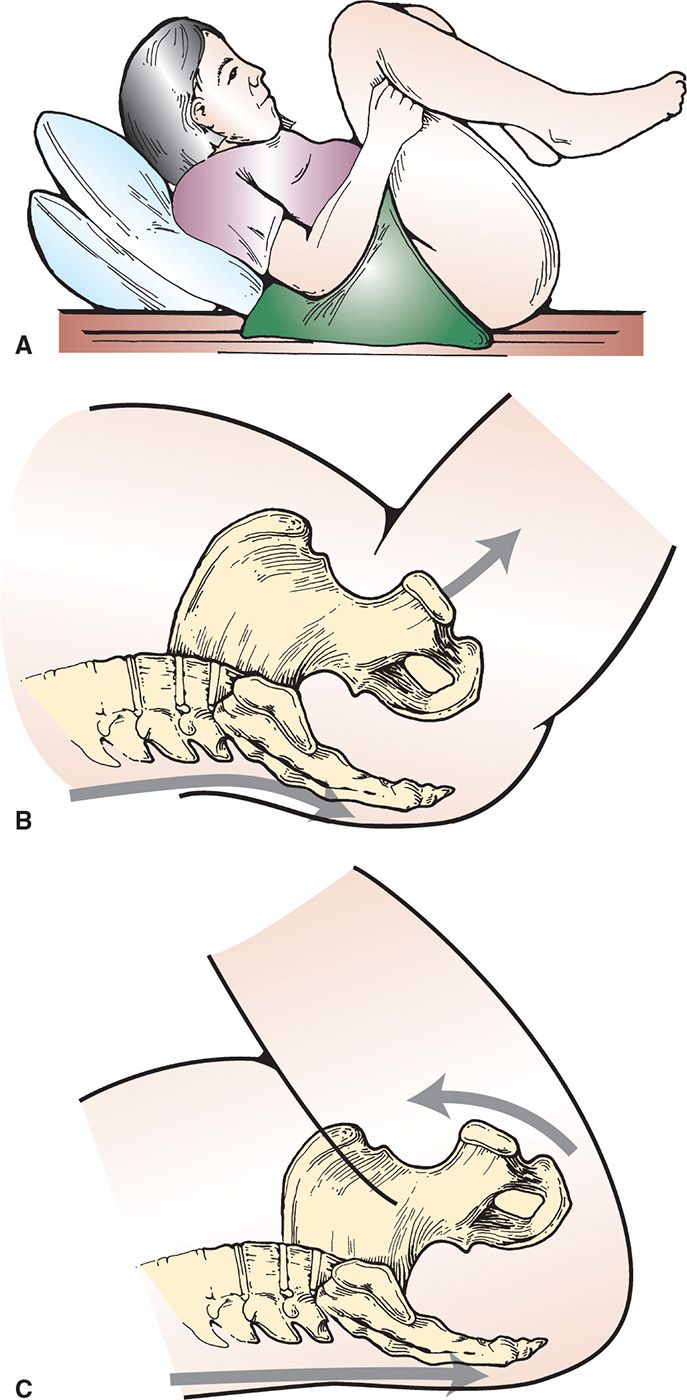
![]() McRoberts Maneuver (FIGURE 41.2)
McRoberts Maneuver (FIGURE 41.2)
![]() Hyperflex maternal hips to a knee-to-chest position
Hyperflex maternal hips to a knee-to-chest position
![]() This flattens the lumbar spine and rotates the pelvis toward the head, which frees the impacted anterior shoulder
This flattens the lumbar spine and rotates the pelvis toward the head, which frees the impacted anterior shoulder
![]() Woods Screw Maneuver (FIGURE 41.3)
Woods Screw Maneuver (FIGURE 41.3)
![]() Rotate the fetus 180 degrees by applying pressure to the clavicular surface of the posterior shoulder in an attempt to dislodge anterior shoulder
Rotate the fetus 180 degrees by applying pressure to the clavicular surface of the posterior shoulder in an attempt to dislodge anterior shoulder
![]() Do not twist the head and neck
Do not twist the head and neck
![]() Rubin Maneuver (FIGURE 41.4)
Rubin Maneuver (FIGURE 41.4)
![]() Place one hand behind the posterior shoulder and adduct shoulder while rotating it anteriorly
Place one hand behind the posterior shoulder and adduct shoulder while rotating it anteriorly
![]() Gaskin Maneuver
Gaskin Maneuver
![]() Mother is repositioned on her hands and knees (on “all fours”) and gentle downward traction is applied to posterior shoulder or upward traction applied to the anterior shoulder
Mother is repositioned on her hands and knees (on “all fours”) and gentle downward traction is applied to posterior shoulder or upward traction applied to the anterior shoulder
![]() Delivery of the Posterior Arm (FIGURE 41.5)
Delivery of the Posterior Arm (FIGURE 41.5)
![]() Locate the posterior arm in the vagina
Locate the posterior arm in the vagina
![]() Apply pressure to the antecubital fossa to flex the elbow and bring the forearm across chest
Apply pressure to the antecubital fossa to flex the elbow and bring the forearm across chest
![]() Locate the forearm and hand and pull through the vagina to deliver the posterior shoulder
Locate the forearm and hand and pull through the vagina to deliver the posterior shoulder
![]() Clavicular Fracture
Clavicular Fracture
![]() Fracture the clavicle intentionally to decrease bisacromial diameter by pulling the anterior clavicle outward away from the lung to avoid causing a pneumothorax
Fracture the clavicle intentionally to decrease bisacromial diameter by pulling the anterior clavicle outward away from the lung to avoid causing a pneumothorax
![]() Zavanelli Maneuver (FIGURE 41.6)
Zavanelli Maneuver (FIGURE 41.6)
![]() Reverse the cardinal movements of labor and take the patient to the operating room (OR) for cesarean section
Reverse the cardinal movements of labor and take the patient to the operating room (OR) for cesarean section
![]() Relax the uterus with terbutaline (0.25 mg SC (subcutaneously)) or nitroglycerin (50–200 µg/min IV)
Relax the uterus with terbutaline (0.25 mg SC (subcutaneously)) or nitroglycerin (50–200 µg/min IV)
![]() Rotate fetal head to occiput anterior position
Rotate fetal head to occiput anterior position
![]() Flex fetal neck and apply gentle cephalad pressure to fetal head to replace the fetus back into the pelvis
Flex fetal neck and apply gentle cephalad pressure to fetal head to replace the fetus back into the pelvis
![]() Prepare for cesarean section
Prepare for cesarean section
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree