![]() To evacuate abnormal collections of fluid from the joint space for synovial fluid analysis, especially in the investigation of the following conditions:
To evacuate abnormal collections of fluid from the joint space for synovial fluid analysis, especially in the investigation of the following conditions:
![]() Septic arthritis
Septic arthritis
![]() Crystal arthropathy
Crystal arthropathy
![]() Hemarthrosis
Hemarthrosis
![]() Inflammatory processes
Inflammatory processes
![]() To diagnose occult fracture or ligamentous injury
To diagnose occult fracture or ligamentous injury
![]() To decrease/relieve pressure in the joint for pain relief
To decrease/relieve pressure in the joint for pain relief
![]() To assess whether an overlying laceration extends into the joint space using methylene blue
To assess whether an overlying laceration extends into the joint space using methylene blue
![]() To instill medication for treatment and pain relief
To instill medication for treatment and pain relief
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Absolute Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
![]() Abscess/cellulitis in the tissue overlying the puncture site
Abscess/cellulitis in the tissue overlying the puncture site
![]() Relative Contraindications
Relative Contraindications
![]() Known bacteremia
Known bacteremia
![]() Bleeding diathesis or anticoagulant therapy
Bleeding diathesis or anticoagulant therapy
![]() Prosthetic joint
Prosthetic joint
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Patient preparation
Patient preparation
![]() Sterile technique
Sterile technique
![]() Analgesia
Analgesia
![]() Aspiration
Aspiration
LANDMARKS
![]() Anterior Approach
Anterior Approach
![]() Coracoid process and head of the humerus
Coracoid process and head of the humerus
![]() Posterior Approach
Posterior Approach
![]() Posterolateral edge of the acromion
Posterolateral edge of the acromion
SUPPLIES
![]() Povidone–iodine or other antiseptic solution, drapes
Povidone–iodine or other antiseptic solution, drapes
![]() Lidocaine with epinephrine
Lidocaine with epinephrine
![]() 25- and 18-gauge needles, 20-mL syringe
25- and 18-gauge needles, 20-mL syringe
![]() Gauze pads, adhesive tape
Gauze pads, adhesive tape
TECHNIQUE
![]() Patient Preparation
Patient Preparation
![]() The patient should sit upright with arm in slight external rotation
The patient should sit upright with arm in slight external rotation
![]() Confirm landmarks and, if needed, mark the needle insertion point
Confirm landmarks and, if needed, mark the needle insertion point
![]() Sterilize the needle insertion area with povidone–iodine solution or comparable skin antiseptic
Sterilize the needle insertion area with povidone–iodine solution or comparable skin antiseptic
![]() Wipe injection site with alcohol to avoid introduction of iodine into synovium
Wipe injection site with alcohol to avoid introduction of iodine into synovium
![]() Drape the area with sterile towels
Drape the area with sterile towels
![]() Analgesia
Analgesia
![]() Use a 25-gauge needle to raise a wheal of anesthetic
Use a 25-gauge needle to raise a wheal of anesthetic
![]() Inject lidocaine with epinephrine at the puncture site
Inject lidocaine with epinephrine at the puncture site
![]() Anesthetize the subcutaneous tissue and a track toward the joint
Anesthetize the subcutaneous tissue and a track toward the joint
![]() Avoid entering the joint space at this point if synovial fluid analysis is desired
Avoid entering the joint space at this point if synovial fluid analysis is desired
![]() Aspiration
Aspiration
![]() Anterior Approach
Anterior Approach
![]() Insert an 18-gauge needle attached to a 20-mL syringe just below and lateral to the coracoid process, medial to the head of the humerus
Insert an 18-gauge needle attached to a 20-mL syringe just below and lateral to the coracoid process, medial to the head of the humerus
![]() Point the needle posterolaterally to avoid the joint capsule
Point the needle posterolaterally to avoid the joint capsule
![]() Gently aspirate while advancing the needle. The needle should be advanced approximately 3 cm or until fluid is aspirated (FIGURE 58.1).
Gently aspirate while advancing the needle. The needle should be advanced approximately 3 cm or until fluid is aspirated (FIGURE 58.1).
![]() Posterior Approach
Posterior Approach
![]() Insert an 18-gauge needle attached to a 20-mL syringe 1 cm below and 1 cm medial to the posterolateral edge of the acromion
Insert an 18-gauge needle attached to a 20-mL syringe 1 cm below and 1 cm medial to the posterolateral edge of the acromion
![]() Aim the needle anteriorly toward the coracoid process
Aim the needle anteriorly toward the coracoid process
![]() Gently aspirate while advancing the needle. The needle should be advanced approximately 3 cm or until fluid is aspirated (FIGURE 58.2).
Gently aspirate while advancing the needle. The needle should be advanced approximately 3 cm or until fluid is aspirated (FIGURE 58.2).
![]() Once the required amount of fluid is obtained, withdraw the needle
Once the required amount of fluid is obtained, withdraw the needle
![]() Apply pressure over the area of insertion for 30 seconds or until bleeding stops
Apply pressure over the area of insertion for 30 seconds or until bleeding stops
![]() Wipe off all excess povidone–iodine on the skin
Wipe off all excess povidone–iodine on the skin
![]() Apply clean dressing
Apply clean dressing
COMPLICATIONS
![]() Iatrogenic infection
Iatrogenic infection
![]() Excessive pain during procedure
Excessive pain during procedure
![]() Localized bleeding
Localized bleeding
![]() Reaccumulation of fluid
Reaccumulation of fluid
![]() Injury to articular cartilage
Injury to articular cartilage
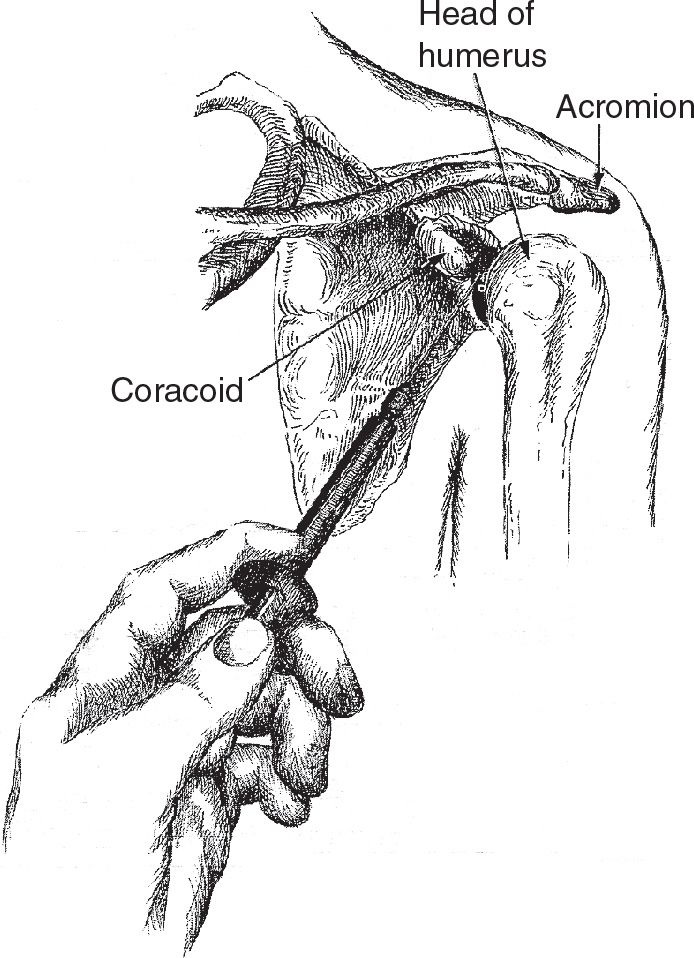
FIGURE 58.1 Anterior approach. (From Simon RR, Brenner BE. Emergency Procedures and Techniques. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002:242, with permission.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


