Chapter 34 Sexually Transmitted Infections
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are a major public health care concern. Women as well as infants are at a great risk of bearing the long-term consequences of STIs. The effective assessment and management of these diseases are key in the emergency department (ED). The emergency nurse must be able to assess and provide care for this population as they present to the ED.1–3 This chapter places a primary focus on female patients who present to the ED seeking treatment for gynecological problems.
The adolescent population has the highest reported incidence of STIs.3 Adolescence is a time of sexual exploration through experimentation. Therefore the emergency nurse must learn to establish a trusting relationship rapidly to garner information pertinent to the care of adolescents. This is accomplished by being nonjudgmental and allowing for confidentiality as well as respect.1,3
Patient History and Assessment
Additional information to obtain:
If the patient presents with a gynecological complaint, the emergency nurse should:
Selected Emergencies
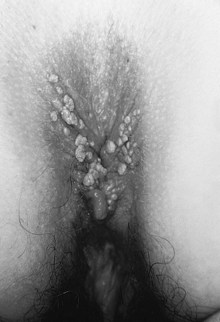
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most prevalent STI in both adolescents and adult women. HPV is usually asymptomatic but can cause benign warts or certain types of cancer.5,6 There are more than 40 types of HPV that can infect both men and women.
Signs and Symptoms
• Genital warts (Condylomata acuminata): can occur on the vulva, perianal area, vaginal walls, and cervix (Fig. 34-1); can also occur in male patients
Therapeutic Interventions
• In the absence of genital warts no treatment is recommended.
• Topical medication (Podofilox 0.5% gel or Imiquimod 5% cream) as ordered if external warts are identified.
• Educate patient on treatment and prevention related to spreading the virus.
• HPV vaccine starting at age 11 or 12 years.
• Instruct patient to notify her obstetrician of HPV if pregnant, as HPV can worsen during pregnancy.
• Encourage routine Pap testing; HPV is associated with cervical dysplasia.
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a viral illness that is transmitted through oral, vaginal, and rectal intercourse. HSV is a chronic infection with remissions and exacerbations. It has been estimated that up to 70% of people with HSV are asymptomatic.2,6
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, the second most common STI in the United States, is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, a gram-negative diplococcus. Women under the age of 25 years are at greatest risk.6 Gonorrhea is the leading cause of cervicitis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) in female patients and of urethritis in male patients.6 Men will present symptomatically whereas women can remain asymptomatic. Untreated gonorrhea can lead to infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain.6,10