| SIRS Criteria ( | |
|---|---|
| Fever or hypothermia | <36°C (96.8°F) or >38°C (100.4°F) |
| Tachycardia | HR >90 bpm |
| Tachypnea | RR >20 or PaCO2 <32 mmHg |
| Leukocytosis/leukopenia | <4000/microliter, >12 000/microliter, or >10% bands |
Critical presentation
- Hypotension: systolic blood pressure <90 mmHg or mean arterial pressure <65 mmHg.
- Beware of relative hypotension in patients with chronic hypertension.
- Encephalopathy and altered mental status.
- Acute kidney injury presenting as oliguria or anuria.
- Cardiogenic shock: decreased left ventricular ejection fraction on echocardiogram, troponin leak.
- Lung injury or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
Diagnosis and evaluation
Step 1: Confirm the diagnosis and determine the severity of illness.
- Basic metabolic panel:
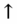 creatinine (acute kidney injury),
creatinine (acute kidney injury), 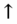 glucose (increased insulin resistance).
glucose (increased insulin resistance).
- CBC with differential: WBC <4000/microliter or >12 000/microliter (SIRS),
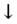 platelets (DIC).
platelets (DIC).
- Coagulation profile:
 PT/INR/PTT (DIC).
PT/INR/PTT (DIC).
- Lactate:
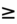 4 mmol/L (evidence of cellular anaerobic respiration and threshold to initiate EGDT).
4 mmol/L (evidence of cellular anaerobic respiration and threshold to initiate EGDT).
- Arterial blood gas:
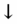 pH (metabolic acidosis).
pH (metabolic acidosis).
- Liver function tests:
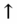 AST,
AST, 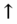 ALT,
ALT, 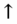 bilirubin (shock liver).
bilirubin (shock liver).
- Cardiac markers:
 troponin (cardiac injury).
troponin (cardiac injury).
Step 2: Determine the etiology.
- Chest radiograph to evaluate for pulmonary processes.
- Urine analysis to rule out a urinary tract infection.
- Lumbar puncture if symptoms are concerning for meningitis.
- Cultures:
- Blood (two different sites + one from each chronically indwelling catheter).
- Urine.
- Sputum if there is a suspicion for pneumonia.
- Cerebrospinal fluid if clinically indicated.
- Blood (two different sites + one from each chronically indwelling catheter).
- Imaging as indicated by symptoms (computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis, ultrasound, etc.).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree




