![]() Relief of urinary retention
Relief of urinary retention
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() No true emergency exists
No true emergency exists
![]() Successful, blind insertion of Foley catheter
Successful, blind insertion of Foley catheter
![]() Physiologic (i.e., normal) phimosis especially in younger boys (<3 years old)
Physiologic (i.e., normal) phimosis especially in younger boys (<3 years old)
![]() Preferred treatment may be medical (local skin care, topical steroids) or surgical but non–emergent (dilation or circumcision by a urologist)
Preferred treatment may be medical (local skin care, topical steroids) or surgical but non–emergent (dilation or circumcision by a urologist)
![]() It is uncommon that phimosis needs to be treated emergently in the emergency department (ED); inability to reduce the prepuce is not in itself an indication for emergent surgical intervention
It is uncommon that phimosis needs to be treated emergently in the emergency department (ED); inability to reduce the prepuce is not in itself an indication for emergent surgical intervention
![]() Coagulopathy (relative contraindication)
Coagulopathy (relative contraindication)
RISKS/CONSENT ISSUES
![]() Pain (local anesthesia will be given)
Pain (local anesthesia will be given)
![]() Local bleeding
Local bleeding
![]() Infection (sterile technique will be used)
Infection (sterile technique will be used)
![]() Scarring at the site of incision/dilation (though definitive treatment will likely include circumcision, removing the scarred tissue)
Scarring at the site of incision/dilation (though definitive treatment will likely include circumcision, removing the scarred tissue)
![]() Damage to glans penis and urethral meatus
Damage to glans penis and urethral meatus
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Patient preparation
Patient preparation
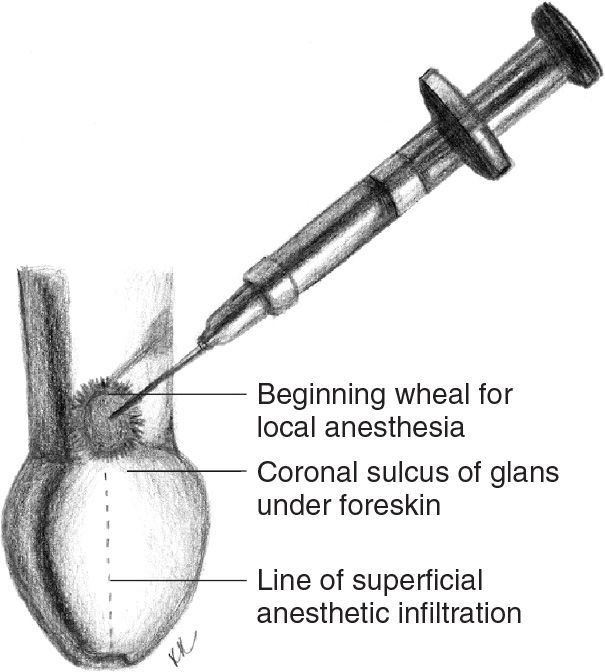
![]() Anesthesia
Anesthesia
![]() Dilation or dorsal slit
Dilation or dorsal slit
![]() Dressing
Dressing
SUPPLIES
![]() Povidone–iodine or chlorhexidine
Povidone–iodine or chlorhexidine
![]() 1% Lidocaine without epinephrine
1% Lidocaine without epinephrine
![]() 5-mL syringe
5-mL syringe
![]() 27-gauge needle
27-gauge needle
![]() Sterile field supplies
Sterile field supplies
![]() Sterile gloves
Sterile gloves
![]() Straight hemostat
Straight hemostat
![]() Straight scissors
Straight scissors
![]() Topical antibiotic ointment
Topical antibiotic ointment
![]() Gauze
Gauze
![]() Paper tape
Paper tape
TECHNIQUE
![]() Patient Preparation
Patient Preparation
![]() Position: Supine with legs slightly abducted
Position: Supine with legs slightly abducted
![]() Clean penis and surrounding region with antiseptic solution
Clean penis and surrounding region with antiseptic solution
![]() Sterile drape revealing only the genital region
Sterile drape revealing only the genital region
![]() Consider light procedural sedation as well
Consider light procedural sedation as well
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree