![]() To drain infection of the soft tissue surrounding the rectum, which is caused by obstruction of the anal crypts and ducts
To drain infection of the soft tissue surrounding the rectum, which is caused by obstruction of the anal crypts and ducts
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Perianal abscesses with fistula-in-ano should be drained in the operating room (OR)
Perianal abscesses with fistula-in-ano should be drained in the operating room (OR)
LANDMARKS
![]() Most perianal abscesses form in the soft tissue adjacent to the anal sphincter
Most perianal abscesses form in the soft tissue adjacent to the anal sphincter
![]() Ischiorectal, intersphincteric, external sphincter, and supralevator abscesses form internally underneath the subcutaneous tissue adjacent to the rectum (FIGURE 70.1)
Ischiorectal, intersphincteric, external sphincter, and supralevator abscesses form internally underneath the subcutaneous tissue adjacent to the rectum (FIGURE 70.1)
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Analgesia
Analgesia
![]() Incision
Incision
![]() Blunt dissection
Blunt dissection
![]() Packing and dressing
Packing and dressing
TECHNIQUE
![]() Supplies
Supplies
![]() Adhesive tape
Adhesive tape
![]() 1% Lidocaine with epinephrine (1:100,000)
1% Lidocaine with epinephrine (1:100,000)
![]() 25- and 22-guage needles, 10-mL syringes
25- and 22-guage needles, 10-mL syringes
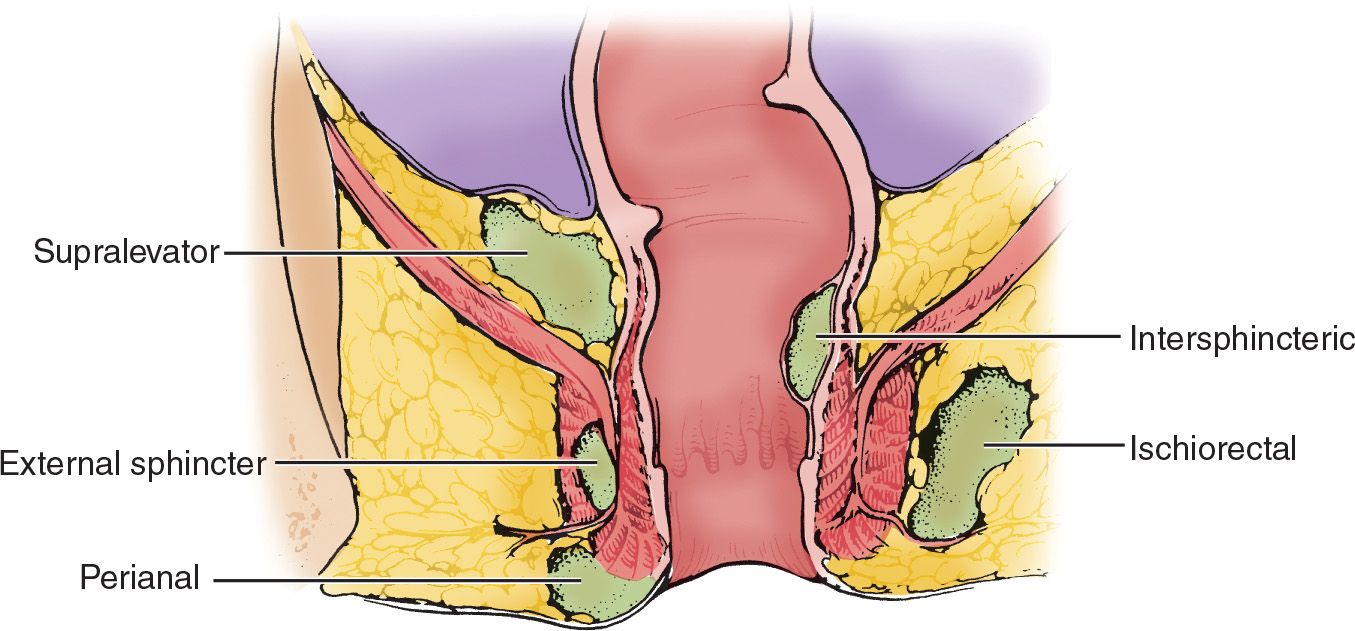
FIGURE 70.1 Anorectal abscesses. (From Coates WC. Perianal, rectal, and anal diseases. In: Wolfson AB, ed. Harwood-Nuss’ Clinical Practice of Emergency Medicine. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2014:609, with permission.)
![]() No. 11 scalpel blade
No. 11 scalpel blade
![]() Hemostat
Hemostat
![]() Saline
Saline
![]() Sterile packing
Sterile packing
![]() 4 × 4 gauze pads
4 × 4 gauze pads
![]() Preparation
Preparation
![]() Consider mild oral sedative or anxiolytic for the patient before procedure
Consider mild oral sedative or anxiolytic for the patient before procedure
![]() Place patient in the prone position
Place patient in the prone position
![]() Separate buttocks with adhesive tape to the lateral aspect of the hip (FIGURE 70.2)
Separate buttocks with adhesive tape to the lateral aspect of the hip (FIGURE 70.2)
![]() Analgesia
Analgesia
![]() Infiltrate area around the abscess with 1% lidocaine with epinephrine (1:100,000)
Infiltrate area around the abscess with 1% lidocaine with epinephrine (1:100,000)
![]() Incision
Incision
![]() Using a no.11 blade, a linear or elliptical incision is made over the most fluctuant part of the abscess
Using a no.11 blade, a linear or elliptical incision is made over the most fluctuant part of the abscess
![]() Express as much as possible from the abscess with gentle squeezing pressure (FIGURE 70.3)
Express as much as possible from the abscess with gentle squeezing pressure (FIGURE 70.3)
![]() Blunt Dissection
Blunt Dissection
![]() Explore abscess with a hemostat to break loculations
Explore abscess with a hemostat to break loculations
![]() Irrigate the abscess with normal saline (FIGURE 70.4)
Irrigate the abscess with normal saline (FIGURE 70.4)
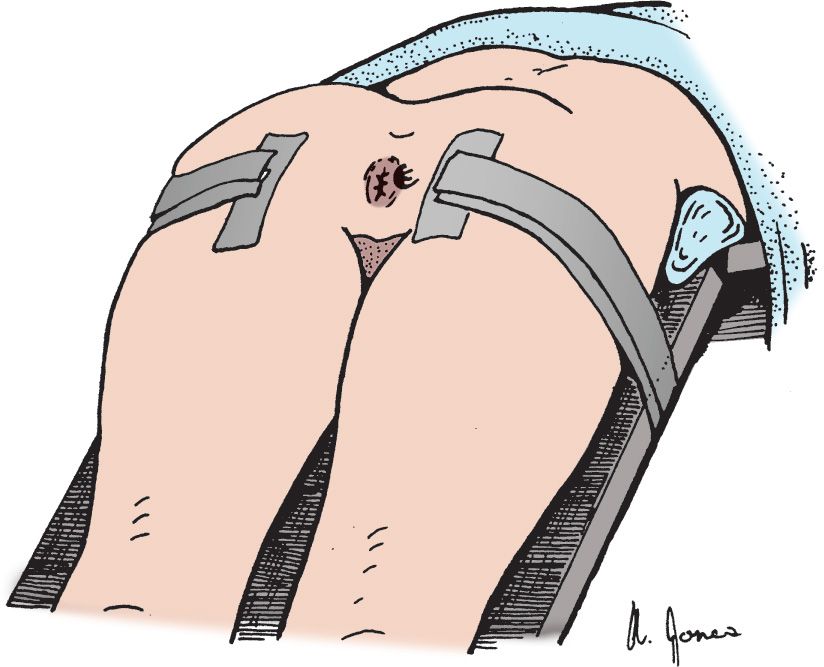
FIGURE 70.2 When excising a thrombosed external hemorrhoid or performing incision and drainage of an anal abscess, separate the buttocks by using 3-inch adhesive tape, as shown, to provide optimal exposure. (From Simon RR, Brenner BE. Emergency Procedures and Techniques. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002:33, with permission.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


