64. Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome
Definition
Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome (OWRS) is an autosomal dominant, inherited disorder characterized by telangiectases, recurrent epistaxis, and first-degree relative(s) positive for the disorder. Telangiectases are lesions produced by telangiectasia. They may present as a coarse or fine, red line or may appear as a punctum with radiating arms (spider-like appearance). Osler-Weber-Rendu syndrome is also known as hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT).
Incidence
The incidence of OWRS is 1:100,000 to 2:100,000. It is reported in all racial groups and almost all ethnic groups without predilection for either gender.
Curaçao Criteria for Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome
• Epistaxis: Spontaneous and recurrent
• Family history: First-degree relative positive for hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
• Telangiectases: Multiple at various characteristic sites (lips, oral cavity, fingers, nose)
• Visceral lesions: Gastrointestinal telangiectasia, pulmonary AVM, hepatic AVM, central AVM, or spinal AVM
AVM, Arteriovenous malformation.
Etiology
There are four types of HHT: (1) HHT type 1, (2) HHT type 2, (3) JPHT, and (4) HHT type 3. Genetic loci have been identified for three types of the disease. HHT type 1 results from defects in the long arm of chromosome 9 (9q33-34). HHT type 2 is derived from defects on the long arm of chromosome 12 (12q13). JPHT appears to result from mutations on the long arm of chromosome 5 (5q31.1-32). HHT type 3 appears to follow pathways similar to the three other types, but a specific gene locus has not been identified.
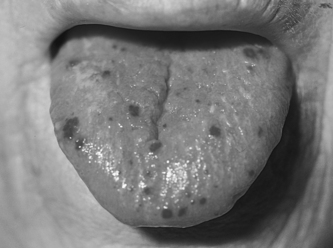 |
| Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome. Note the telangiectatic lesions. |
Signs and Symptoms
• Anemia
• Arteriovenous malformations (AVM) at multiple sites, notably the brain and lungs
• Clubbing
• Continuous thoracic bruit
• Cyanosis
• Dyspnea on exertion
• Easy fatigability
• Epistaxis
• Hemoptysis
• Hepatomegaly
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





