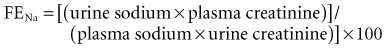11 Oliguria
 Definitions and Epidemiology
Definitions and Epidemiology
A number of definitions for oliguria can be found in the literature. Oliguria is often defined as urine output less than 200 to 500 mL per 24 hours. In order to standardize the use of the term across different studies and populations, the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) recently adopted a definition of oliguria as urine output of less than 0.3 mL/kg/h for at least 24 hrs (www.ADQI.net). For all practical purposes, however, urine output under 0.5 mL/kg/h is usually considered inadequate for most critically ill patients.
Given the lack of consensus over definitions, it has been difficult to determine the incidence of oliguria. Some studies have estimated that up to 18% of medical and surgical intensive care unit (ICU) patients with intact renal function exhibit episodes of oliguria.1 Furthermore, 69% of ICU patients who develop acute kidney injury (AKI) are oliguric.2 Overall, AKI in the ICU has a poor prognosis (mortality rates range from 30%-70%), and oliguric renal failure is associated with worse outcome compared to nonoliguric renal failure, although this distinction is less clear for AKI. It is essential to understand the physiologic derangements leading to this exceedingly common problem.
 Pathophysiology
Pathophysiology
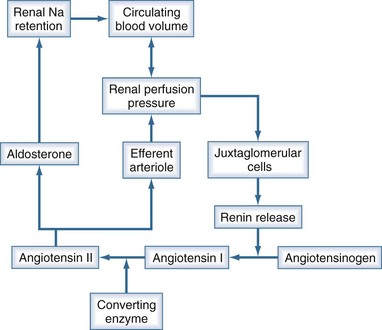
Urine output is a function of glomerular filtration, tubular secretion, and tubular reabsorption. Glomerular filtration is directly dependent on intravascular volume and renal perfusion. Renal perfusion in turn is a function of arterial pressure and renal vascular resistance. The intrarenal vasculature is capable of preserving glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in the face of varying systemic pressure through important neurohumoral autoregulating mechanisms that affect the afferent and efferent arterioles. The most important of these neurohumoral mechanisms is the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (Figure 11-1). Oliguria can be due to decreased GFR, increased tubular reabsorption of filtrate, or a combination of both. Oliguria also can be caused by mechanical obstruction to urine flow. In any case, oliguria is an insensitive clinical manifestation of AKI.
Reduction in glomerular filtration rate
Oliguria secondary to a decrease in GFR is usually related to one of the following conditions:
 Diagnostic Approach to Oliguria
Diagnostic Approach to Oliguria
Rule out Urinary Obstruction
The first step in diagnosis is to rule out urinary obstruction. A prior history of prostatic hypertrophy may provide some clues to the presence of distal obstruction. However, in the ICU setting, distal obstruction presenting as oliguria is commonly due to obstruction of the urinary catheter (especially in male patients). Hence, in patients with new-onset oliguria, the urinary catheter must be flushed or changed in order to rule out obstruction. Although uncommon in the acute setting, complete or severe partial bilateral ureteral obstruction may also lead to acute, “acute on chronic,” or chronic renal failure. Early diagnosis of urinary tract obstruction (UTO) is important, since many cases can be corrected, and a delay in therapy can lead to irreversible renal injury. Renal ultrasonography is usually the test of choice to exclude UTO.4 It is noninvasive, can be performed by the bedside, and also carries the advantage of avoiding the potential allergic and toxic complications of radiocontrast media. In the majority of affected patients, ultrasonography can establish the diagnosis of hydronephrosis and often establish its cause. Ultrasonography also can be useful for detecting other causes of renal disease such as polycystic kidney disease. However, under some circumstances, renal ultrasound may not yield good results. For example, in early obstruction or obstruction associated with severe dehydration, hydronephrosis may not be seen on the initial ultrasound examination but may appear later in the course of the disease. Computed tomography (CT) scanning should be performed if the ultrasound results are equivocal or if the kidneys are not well visualized. CT also is indicated if the cause of the obstruction cannot be identified by ultrasonography.
Laboratory Indices
Although most authorities advocate examining the urine sediment, the yield of urine microscopy in the ICU is very low. Urine sediment is typically bland or reveals hyaline and fine granular casts in a prerenal state. By contrast, ATN is often associated with coarse granular casts and tubular epithelial casts. However, the discrimination of these findings is limited, and AKI may be present in the absence of changes in urinary sediment, particularly with sepsis-induced AKI. The main utility of examining the urine sediment is in the detection of red cell casts, which indicate primary glomerular disease. The urine sediment in postrenal failure is often very bland; casts or sediment typically are absent. Occasionally a few red cells and white cells may be seen. Eosinophilia, eosinophiluria, and hypocomplementemia, if present (although insensitive and nonspecific), point to the diagnosis of atheroembolic etiology of acute oliguria.5
Table 11-1 lists laboratory values that can be useful for distinguishing prerenal from intrarenal causes of oliguria. The fractional excretion of filtered sodium (FENa) is calculated according to the following formula:
TABLE 11-1 Biochemical Indices Useful to Distinguish Prerenal from Intrarenal Acute Renal Failure
| Prerenal | Renal | |
|---|---|---|
| Osm u (mOsm/kg) | >500 | <400 |
| Na u (mmol/L or meq/L) | <20 | >40 |
| Urea/creatinine | >0.1 | <0.05 |
| U/S creatinine | >40 | <20 |
| U/S osmolality | >1.5 | >1 |
| FENa (%)* | <1 | >2 |
| FEurea (%) | <25 | >25 |
ARF, acute renal failure; S, serum; U, urine.
* ((u Na / s Na) / (u creat / s creat)) × 100
If the calculated FENa is less than 1%, a prerenal cause of oliguria should be suspected. Importantly, interpretation of the FENa is difficult or impossible if the patient has received diuretic or natriuretic agents (including dopamine and/or mannitol). Interpretation of the FENa also can be confounded by the presence of large amounts of endogenous osmotically active substances in the urine, such as glucose or urea. Drugs that interfere with the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone axis, such as ACE inhibitors or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory agents, also can confound the interpretation of FENa.
Several nephrotoxic factors, such as aminoglycosides, cyclosporine, and contrast media, are associated with FENa values below 1%, mimicking prerenal azotemia. Furthermore, sepsis may result in urine chemistries that resemble prerenal physiology even when renal blood flow is normal or increased.6
A low fractional excretion of urea (FEurea) (<35%) has been proposed to be more sensitive and specific than FENa in differentiating between prerenal and renal causes of AKI, especially when diuretics have been administered.7 The diagnostic accuracy of FENa versus FEurea was recently compared in 99 patients hospitalized at a tertiary care center; study subjects had developed a 30% increase in SCr concentration from baseline within 1 week.8 Patients were classified as having prerenal azotemia if the rise in SCr was transient and consistent with the clinical context. Each group also was subdivided according to exposure to diuretics. FEurea of 35% or less and FENa of 1% or less were then analyzed for their ability to predict prerenal azotemia. Sensitivity, specificity, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were generated for each index. Sensitivity and specificity of FEurea were 48% and 75%, respectively, in patients who did not receive diuretics, and 79% and 33%, respectively, in patients who received diuretics. Sensitivity and specificity of FENa were 78% and 75%, respectively, in patients not administered diuretics, and 58% and 81%, respectively, in those who received diuretics. ROC curves did not identify better diagnostic cutoff values for FEurea or FENa. Unfortunately, the study did not examine the combination of these indices, so neither test provides a level of diagnostic accuracy that can be relied on in clinical practice.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree