BASICS
![]() Unilateral (sometimes bilateral) motor dysfunction of cranial nerve (CN) VII
Unilateral (sometimes bilateral) motor dysfunction of cranial nerve (CN) VII
ETIOLOGY
![]() Associated with pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, trauma, infection, neoplasm, Lyme disease, herpes simplex virus
Associated with pregnancy, diabetes mellitus, trauma, infection, neoplasm, Lyme disease, herpes simplex virus
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Abrupt onset of symptoms
Abrupt onset of symptoms
![]() Unilateral face paralysis of forehead and lower face
Unilateral face paralysis of forehead and lower face
• Cannot close eye, raise eyebrow, smile on affected side
• Central lesions (i.e., stroke) spare the forehead
![]() May include pain in ipsilateral ear, hyperacusis, impaired taste, lacrimation
May include pain in ipsilateral ear, hyperacusis, impaired taste, lacrimation
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical exam finding
Clinical exam finding
![]() Consider head CT or MRI if risk factors for CVA or symptoms atypical
Consider head CT or MRI if risk factors for CVA or symptoms atypical
TREATMENT
![]() Most resolve spontaneously
Most resolve spontaneously
![]() Treat with oral prednisone
Treat with oral prednisone
![]() Consider acyclovir
Consider acyclovir
Transection (Segmental) Syndrome
![]() Loss of all sensation, weakness below affected level
Loss of all sensation, weakness below affected level
![]() Bladder dysfunction
Bladder dysfunction
![]() Trauma, hemorrhage, abscess, transverse myelitis, metastatic lesions
Trauma, hemorrhage, abscess, transverse myelitis, metastatic lesions
![]() Bilateral symptoms, including corticospinal tracts, central autonomic tracts to bladder
Bilateral symptoms, including corticospinal tracts, central autonomic tracts to bladder
![]() Gait ataxia, weakness, muscle flaccidity hyperreflexia
Gait ataxia, weakness, muscle flaccidity hyperreflexia
![]() Ventral two-third of spinal cord, includes corticospinal tracts, spinothalamic tracts, descending autonomic tracts to bladder control
Ventral two-third of spinal cord, includes corticospinal tracts, spinothalamic tracts, descending autonomic tracts to bladder control
![]() Muscle weakness and reflex changes, urinary incontinence
Muscle weakness and reflex changes, urinary incontinence
![]() Focal to level of injury, do not ascend or descend
Focal to level of injury, do not ascend or descend
![]() Loss of pain and temperature
Loss of pain and temperature
![]() Syringomyelia, tumor
Syringomyelia, tumor
![]() Aka hemi cord
Aka hemi cord
![]() Lateral hemisection injury (trauma, bullet, stabbing) that affects the ipsilateral part of your body
Lateral hemisection injury (trauma, bullet, stabbing) that affects the ipsilateral part of your body
![]() Weakness, loss of proprioception, pain, temperature, and vibration
Weakness, loss of proprioception, pain, temperature, and vibration
![]() Only weakness no sensory changes
Only weakness no sensory changes
![]() Upper motor neuronal injury = hyperreflexia, extensor plantar responses
Upper motor neuronal injury = hyperreflexia, extensor plantar responses
![]() Lower motor neuron injury = muscle atrophy and fasciculations
Lower motor neuron injury = muscle atrophy and fasciculations
![]() Chronic myelopathies
Chronic myelopathies
![]() Lesions at L2
Lesions at L2
![]() Early and significant urine/bowel incontinence
Early and significant urine/bowel incontinence
![]() Saddle anesthesia (S3 to S5)
Saddle anesthesia (S3 to S5)
![]() Tumors, disc herniation, fracture
Tumors, disc herniation, fracture
BASICS
![]() Chronic and progressive decline of function that interferes with independence and daily function
Chronic and progressive decline of function that interferes with independence and daily function
![]() Nonreversible
Nonreversible
![]() Alzheimer disease is most common
Alzheimer disease is most common
ETIOLOGY
![]() Reduced cerebral production of choline acetyl transferase, which leads to a decrease in acetylcholine synthesis and impaired function
Reduced cerebral production of choline acetyl transferase, which leads to a decrease in acetylcholine synthesis and impaired function
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Impairment in learning, reasoning, memory, handling complex tasks, spatial ability and orientation, language, learning and retaining new information
Impairment in learning, reasoning, memory, handling complex tasks, spatial ability and orientation, language, learning and retaining new information
![]() Aphasia, apraxia, agnosia, impaired executive function
Aphasia, apraxia, agnosia, impaired executive function
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() History and physical exam
History and physical exam
![]() History from family members is particularly beneficial
History from family members is particularly beneficial
![]() Screening for B12 deficiency and thyroid disorders
Screening for B12 deficiency and thyroid disorders
![]() Cognitive testing
Cognitive testing
![]() Mini-mental status exam
Mini-mental status exam
![]() Structural imaging with MRI or CT to rule out other etiologies
Structural imaging with MRI or CT to rule out other etiologies
TREATMENT
![]() Symptomatic: treatment of behavioral disturbances, environmental manipulations to support function, and counseling
Symptomatic: treatment of behavioral disturbances, environmental manipulations to support function, and counseling
![]() Cholinesterase inhibitors, such as tacrine, rivastigmine, galantamine
Cholinesterase inhibitors, such as tacrine, rivastigmine, galantamine
![]() Memantine for moderate to severe Alzheimer dementia
Memantine for moderate to severe Alzheimer dementia
BASICS
![]() Acute, rapid, transient disturbance of consciousness
Acute, rapid, transient disturbance of consciousness
ETIOLOGY
![]() Fluid and electrolyte disorders, infections, drug or alcohol toxicity or withdrawal, metabolic disorders, low perfusion states, postoperative states
Fluid and electrolyte disorders, infections, drug or alcohol toxicity or withdrawal, metabolic disorders, low perfusion states, postoperative states
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Decreased ability to focus and change in level of awareness
Decreased ability to focus and change in level of awareness
![]() Sleep impairment, hallucinations, distractible
Sleep impairment, hallucinations, distractible
![]() Emotional disturbances, such as fear, depression, euphoria
Emotional disturbances, such as fear, depression, euphoria
DIAGNOSIS
![]() History and physical exam, mental status exam
History and physical exam, mental status exam
![]() Lab testing and imaging to identify underlying etiology
Lab testing and imaging to identify underlying etiology
TREATMENT
![]() Correct underlying medical disorder
Correct underlying medical disorder
![]() Antipsychotics for impulsive, violent, or unpredictable patients
Antipsychotics for impulsive, violent, or unpredictable patients
BASICS
![]() Acute immune-mediated polyneuropathy, progressing over about 2 weeks
Acute immune-mediated polyneuropathy, progressing over about 2 weeks
ETIOLOGY
![]() Exact cause is unknown
Exact cause is unknown
![]() Sixty percent caused by a preceding infection
Sixty percent caused by a preceding infection
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Progressive, symmetric muscle weakness, usually ascending
Progressive, symmetric muscle weakness, usually ascending
![]() Weakness can be mild to nearly complete paralysis of all extremities, facial, respiratory, and bulbar muscles
Weakness can be mild to nearly complete paralysis of all extremities, facial, respiratory, and bulbar muscles
![]() Decreased DTRs, respiratory muscle weakness and depression, back and extremity pain, paresthesias
Decreased DTRs, respiratory muscle weakness and depression, back and extremity pain, paresthesias
DIAGNOSIS
![]() Cerebrospinal fluid from lumbar puncture (LP) reveals elevated protein with normal WBC
Cerebrospinal fluid from lumbar puncture (LP) reveals elevated protein with normal WBC
![]() Electromyography and nerve conduction studies
Electromyography and nerve conduction studies
TREATMENT
![]() Plasmapheresis
Plasmapheresis
![]() IV immunoglobulin
IV immunoglobulin
![]() Subdural, epidural, subarachnoid
Subdural, epidural, subarachnoid
• See specific section
![]() Infections (meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess)
Infections (meningitis, encephalitis, brain abscess)
• See specific section
![]() Vascular:
Vascular:
• Malignant hypertension (HTN), vertebral dissection (associated with exertion, chiropractor), thrombosis, cerebral aneurysm
![]() Temporal arteritis:
Temporal arteritis:
• Unilateral frontotemporal severe headache (HA), tender to palpation of temporal artery
• Diagnosis: erythrocyte sedimentation rate >50
• Treatment: prednisone
![]() Age >50, rapid onset, severe intensity, no prior HA, fever, trauma, vision changes, immunosuppression, HTN, neuro deficits, altered mental status (AMS)
Age >50, rapid onset, severe intensity, no prior HA, fever, trauma, vision changes, immunosuppression, HTN, neuro deficits, altered mental status (AMS)
![]() Tension
Tension
• Band-like, aching (nonpulsatile), bilateral, lacking secondary symptoms (nausea, vomiting, photophobia)
• No focal neuro deficits
• Tenderness to posterior cervical and temporal muscles
• Precipitated by stress, sleep deprivation, hunger, eyestrain, alcohol
• Treatment: supportive, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, Tylenol, muscle relaxants
![]() Cluster
Cluster
• Severe, burning/pulsating, unilateral, periorbital HA with associated ipsilateral lacrimation, conjunctival injection, nasal congestion, myosis, ptosis
• Short duration occurring several times per day for weeks
• Most commonly in male >30 years
• Treatment: high-flow O2, IM/intranasal triptans
![]() Migraine
Migraine
• Unilateral, severe, throbbing, associated photophobia, phonophobia, nausea, vomiting, aura (visual, auditory, smell)
• Common in women near menses, family history
• Treat with analgesia/antiemetics (Tylenol, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chlorpromazine, Reglan)
![]() Adjust environment (quiet/dark room)
Adjust environment (quiet/dark room)
![]() Caffeine
Caffeine
![]() Triptans
Triptans
![]() Ergotamines (do not use ergotamine within 24 hours of triptan use due to vasoconstrictive effect)
Ergotamines (do not use ergotamine within 24 hours of triptan use due to vasoconstrictive effect)
• Prophylaxis propanolol, amitriptyline, fluoxetine, Topamax, Neurontin, valproate
BASICS
![]() Autoimmune neuro muscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness
Autoimmune neuro muscular disorder characterized by muscle weakness
ETIOLOGY
![]() Antibodies block acetylcholine receptor in the postsynaptic membrane
Antibodies block acetylcholine receptor in the postsynaptic membrane
![]() Onset in the second and third decades (females predominantly) or sixth to eighth decade (males)
Onset in the second and third decades (females predominantly) or sixth to eighth decade (males)
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Features fluctuating muscle weakness and fatigue, tends to be worse later in the day and with repetitive activity
Features fluctuating muscle weakness and fatigue, tends to be worse later in the day and with repetitive activity
![]() Diplopia, ptosis, dysarthria, dysphagia, loss of facial muscles, “loss of smile”
Diplopia, ptosis, dysarthria, dysphagia, loss of facial muscles, “loss of smile”
![]() Respiratory muscle weakness is most serious, can cause respiratory failure, or “myasthenic crisis”
Respiratory muscle weakness is most serious, can cause respiratory failure, or “myasthenic crisis”
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical diagnosis by history and physical
Clinical diagnosis by history and physical
![]() Tensilon test: administering an anticholinesterase drug which will temporarily relieve muscle weakness
Tensilon test: administering an anticholinesterase drug which will temporarily relieve muscle weakness
![]() Serologic test for antibodies
Serologic test for antibodies
![]() Electromyography to detect impaired muscle to nerve transmission
Electromyography to detect impaired muscle to nerve transmission
![]() CT or MRI to rule out thymoma (present in 10% to 15% of patients with MG)
CT or MRI to rule out thymoma (present in 10% to 15% of patients with MG)
TREATMENT
![]() Symptom control by anticholinesterase drugs such as neostigmine or pyridostigmine
Symptom control by anticholinesterase drugs such as neostigmine or pyridostigmine
![]() Steroids and immunosuppressive drugs such as prednisone and tacrolimus to suppress production of antibodies
Steroids and immunosuppressive drugs such as prednisone and tacrolimus to suppress production of antibodies
BASICS
![]() Damage to the peripheral nervous system
Damage to the peripheral nervous system
![]() May affect sensation, movement, organ function
May affect sensation, movement, organ function
ETIOLOGY
![]() Metabolic (diabetes, hypothyroid, liver failure)
Metabolic (diabetes, hypothyroid, liver failure)
![]() Vitamin deficiency
Vitamin deficiency
![]() Medication (chemotherapy)
Medication (chemotherapy)
![]() Traumatic injury
Traumatic injury
![]() Excessive alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption
![]() Immune system disease or infection (Guillain–Barré, lupus, leprosy, multiple sclerosis, Lyme disease)
Immune system disease or infection (Guillain–Barré, lupus, leprosy, multiple sclerosis, Lyme disease)
![]() Shingles
Shingles
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Gradual onset of numbness and tingling in hands and feet
Gradual onset of numbness and tingling in hands and feet
![]() Burning, sharp, electric-like pain
Burning, sharp, electric-like pain
![]() Extreme sensitivity to touch and heat intolerance
Extreme sensitivity to touch and heat intolerance
![]() Muscle weakness if motor nerves are affected
Muscle weakness if motor nerves are affected
![]() Ankle jerk reflex is classically absent in peripheral neuropathy
Ankle jerk reflex is classically absent in peripheral neuropathy
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() History and physical, including neurologic exam
History and physical, including neurologic exam
![]() Lab testing: CT, MRI, LP to exclude other causes
Lab testing: CT, MRI, LP to exclude other causes
![]() Electromyography
Electromyography
TREATMENT
![]() There is no cure
There is no cure
![]() Depends on the cause and is focused on treating symptoms
Depends on the cause and is focused on treating symptoms
![]() Antiseizure medications, including Gabapentin (Figure 10.1)
Antiseizure medications, including Gabapentin (Figure 10.1)
![]() SEIZURE AND STATUS EPILEPTICUS
SEIZURE AND STATUS EPILEPTICUS
BASICS
![]() Partial:
Partial:
• Simple
![]() Consciousness preserved
Consciousness preserved
![]() Isolated limb jerking or “Jacksonian march”—motor symptoms that start in one part of body and march down the rest
Isolated limb jerking or “Jacksonian march”—motor symptoms that start in one part of body and march down the rest
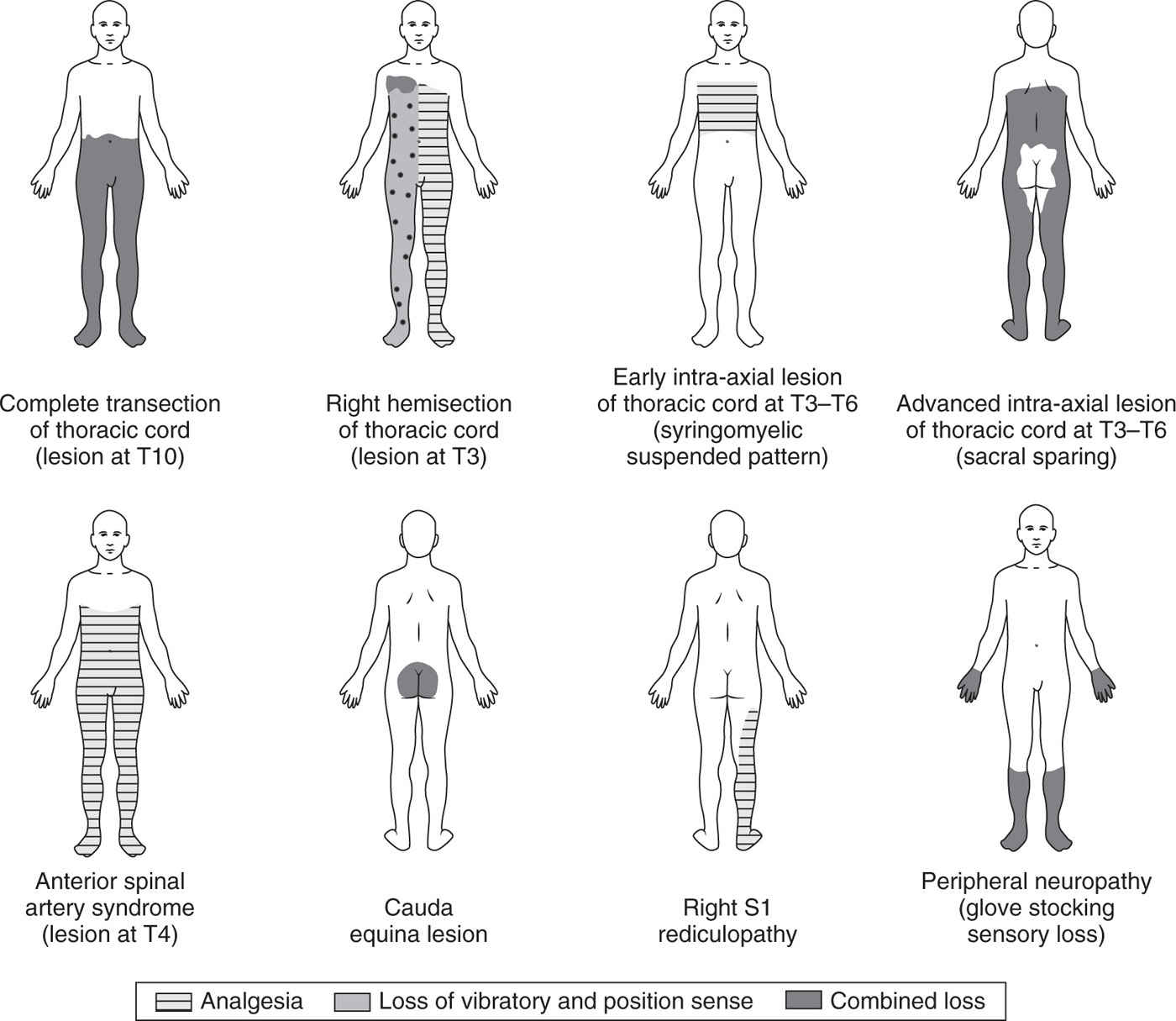
FIGURE 10.1. Characteristic sensory disturbances found in various spinal cord lesions in comparison with peripheral neuropathy. (From Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J, Mazziotta JC, eds. Bradley’s Neurology in Clinical Practice. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier; 2012. Figure 24.2 MD Consult.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








