BASICS
![]() A rapid increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine
A rapid increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine
ETIOLOGY
![]() Prerenal
Prerenal
• Volume depletion, heart failure, liver failure, sepsis, burns, bilateral renal artery stenosis, drugs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor)
![]() Postrenal
Postrenal
• Obstruction (benign prostatic hyperplasia, calculi, tumors)
![]() Intrinsic
Intrinsic
• Renal ischemia
• Nephrotoxin exposures
• Acute tubular necrosis
![]() Most common
Most common
![]() Caused by renal ischemia secondary to trauma, sepsis, rhabdomyolysis (Table 14.1)
Caused by renal ischemia secondary to trauma, sepsis, rhabdomyolysis (Table 14.1)
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Nausea, vomiting, oliguria
Nausea, vomiting, oliguria
![]() Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia
![]() Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis
DIAGNOSTICS
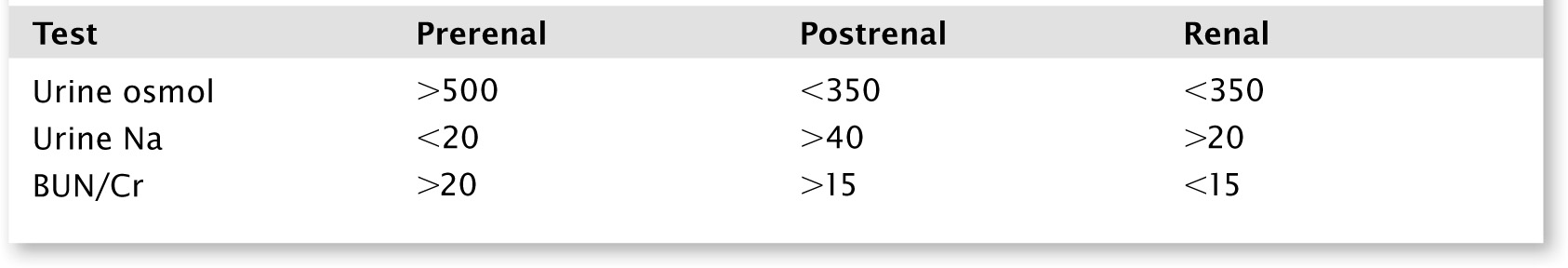
![]() Laboratory testing, including basic metabolic panel, urine electrolytes
Laboratory testing, including basic metabolic panel, urine electrolytes
TREATMENT
![]() IVFs
IVFs
![]() Diuresis to prevent volume overload
Diuresis to prevent volume overload
![]() Monitor electrolytes
Monitor electrolytes
![]() Dialysis if:
Dialysis if:
• Critical electrolyte abnormalities
• Unresponsive metabolic acidosis
• Uremia
• Toxic ingestion
BASICS
![]() A stone formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals
A stone formed in the kidneys from dietary minerals
ETIOLOGY
![]() Eighty percent Ca (others:uric acid, struvite)
Eighty percent Ca (others:uric acid, struvite)
![]() Risk factors:
Risk factors:
• Previous stones
• Male gender
• Family history
• History of gastric bypass
• Medications (hydrochlorothiazide, allopurinol)
• Diabetes
• Gout
• Dehydration
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Flank pain, can radiate to the groin
Flank pain, can radiate to the groin
![]() Colicky, waxing, and waning pain
Colicky, waxing, and waning pain
![]() Restless
Restless
![]() Hematuria (70% to 90%)
Hematuria (70% to 90%)
![]() Nausea, vomiting, urinary urgency, dysuria
Nausea, vomiting, urinary urgency, dysuria
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Lab tests, including urinalysis, basic metabolic panel
Lab tests, including urinalysis, basic metabolic panel
![]() Imaging:
Imaging:
• Noncontrast CT scan is test of choice
![]() Ureterovesicular junction is most common site to see stones as it is the most narrow
Ureterovesicular junction is most common site to see stones as it is the most narrow
• Kidney, ureter, and bladder x-ray (can miss stones and does not show hydronephrosis)
• Ultrasound
TREATMENT
![]() IV fluids, pain medication (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opiates)
IV fluids, pain medication (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and opiates)
![]() Urology consult for acute renal failure, urosepsis, unrelenting pain, stone >10 mm
Urology consult for acute renal failure, urosepsis, unrelenting pain, stone >10 mm
![]() Stone passage: smaller, more distal stones more likely to pass (most <5 mm pass spontaneously, then the percentage drops proportionally to the increasing size of the stone)
Stone passage: smaller, more distal stones more likely to pass (most <5 mm pass spontaneously, then the percentage drops proportionally to the increasing size of the stone)
![]() α-Blockers help facilitate the passage of the stone
α-Blockers help facilitate the passage of the stone
BASICS
![]() Inability to retract foreskin over glans (distally)
Inability to retract foreskin over glans (distally)
ETIOLOGY
![]() Uncircumcised males
Uncircumcised males
![]() Failure to return foreskin after exam, cleaning, catheter
Failure to return foreskin after exam, cleaning, catheter
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Pain, edema with constricting skin around glans
Pain, edema with constricting skin around glans
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical exam findings
Clinical exam findings
TREATMENT
![]() Manual reduction of the prepuce
Manual reduction of the prepuce
• Thumbs are placed on the glans, and the skin is rolled over the glans
![]() If unsuccessful, obtain urology consult for a dorsal slit
If unsuccessful, obtain urology consult for a dorsal slit
![]() Preventative interval circumcision
Preventative interval circumcision
BASICS
![]() Inability to retract foreskin over glans (proximally)
Inability to retract foreskin over glans (proximally)
ETIOLOGY
![]() Abnormal stricture of distal foreskin secondary to infections or inflammation
Abnormal stricture of distal foreskin secondary to infections or inflammation
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Pain and inability to retract foreskin
Pain and inability to retract foreskin
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical exam findings
Clinical exam findings
TREATMENT
![]() Manual retraction, then thorough cleaning and proper hygiene
Manual retraction, then thorough cleaning and proper hygiene
![]() If unsuccessful, obtain urology consult
If unsuccessful, obtain urology consult
BASICS
![]() Pathologic erection lasting >4 hours
Pathologic erection lasting >4 hours
ETIOLOGY
![]() Idiopathic, sickle cell disease, drugs (Viagra, hypertensives cocaine), spinal cord injury
Idiopathic, sickle cell disease, drugs (Viagra, hypertensives cocaine), spinal cord injury
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Erection can be painful
Erection can be painful
![]() End result can cause ischemia, necrosis, urinary retention, impotence
End result can cause ischemia, necrosis, urinary retention, impotence
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical exam findings
Clinical exam findings
TREATMENT
![]() Phenylephrine and terbutaline injections
Phenylephrine and terbutaline injections
![]() Needle aspiration of corpora cavernosa
Needle aspiration of corpora cavernosa
![]() Ice packs, pressure dressing
Ice packs, pressure dressing
![]() Recurrent episodes may require surgery
Recurrent episodes may require surgery
![]() PYELONEPHRITIS, URINARY TRACT INFECTION, UROSEPSIS, PERINEPHRIC ABSCESS
PYELONEPHRITIS, URINARY TRACT INFECTION, UROSEPSIS, PERINEPHRIC ABSCESS
BASICS
![]() An inflammation and infection of the kidney
An inflammation and infection of the kidney
![]() Women more common than men
Women more common than men
ETIOLOGY
![]() Most commonly caused by E. coli, followed by Proteus, Klebsiella
Most commonly caused by E. coli, followed by Proteus, Klebsiella
![]() The bacterial infection spreads up the urinary tract to the kidneys
The bacterial infection spreads up the urinary tract to the kidneys
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Dysuria, frequency, urgency, hematuria, fever, flank pain, vomiting
Dysuria, frequency, urgency, hematuria, fever, flank pain, vomiting
![]() Costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness
Costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Physical exam findings consisting of CVA tenderness, fever
Physical exam findings consisting of CVA tenderness, fever
![]() Urinalysis, urine culture
Urinalysis, urine culture
![]() Image if:
Image if:
• Persistent symptoms after 48 to 72 hours
• Kidney stones or abscess suspected
• Immunosuppression
![]() CT is the choice to assess for stone, gas-forming infections, hemorrhage, renal abscess
CT is the choice to assess for stone, gas-forming infections, hemorrhage, renal abscess
TREATMENT
![]() Based on prior culture data
Based on prior culture data
![]() Cephalosporins or fluoroquinolones for 10 to 14 days
Cephalosporins or fluoroquinolones for 10 to 14 days
![]() Admit if:
Admit if:
• Complicated/comorbidities
• Patient not tolerating orals
• Pregnant
• Renal transplant, single kidney
• Abscess
BASICS
![]() Infection in any part of urinary system, most commonly bladder or urethra
Infection in any part of urinary system, most commonly bladder or urethra
![]() Affects women more than men
Affects women more than men
ETIOLOGY
![]() Common microbes: E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
Common microbes: E. coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacter
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Lower abdominal pain, dysuria, urinary frequency
Lower abdominal pain, dysuria, urinary frequency
![]() Foul-smelling urine
Foul-smelling urine
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Urinalysis
Urinalysis
TREATMENT
![]() Tailor to presumed microbes
Tailor to presumed microbes
![]() Antibiogram dependent, but often Bactrim and Keflex are first line
Antibiogram dependent, but often Bactrim and Keflex are first line
![]() Macrobid 100 mg bid for 5 days for pregnant patients
Macrobid 100 mg bid for 5 days for pregnant patients
![]() Men must be treated for 14 days
Men must be treated for 14 days
BASICS
![]() Severe illness that occurs when an infection starts in the urinary tract and spreads into the bloodstream
Severe illness that occurs when an infection starts in the urinary tract and spreads into the bloodstream
![]() Can be life-threatening if it is not treated immediately
Can be life-threatening if it is not treated immediately
ETIOLOGY
![]() Caused by bacteria from urinary tract infections (UTIs) and pyelonephritis
Caused by bacteria from urinary tract infections (UTIs) and pyelonephritis
![]() Risk factors: elderly patients, HIV, transplant recipients, diabetics, and immunosuppressed patients
Risk factors: elderly patients, HIV, transplant recipients, diabetics, and immunosuppressed patients
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Fever, weakness, hypotension, flank pain
Fever, weakness, hypotension, flank pain
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Urinalysis, urine culture
Urinalysis, urine culture
![]() Lab testing, including complete blood count, lactate, blood cultures
Lab testing, including complete blood count, lactate, blood cultures
![]() Consider imaging, including ultrasound, chest x-ray
Consider imaging, including ultrasound, chest x-ray
TREATMENT
![]() ABCs, supportive
ABCs, supportive
![]() IV fluids, antibiotics
IV fluids, antibiotics
![]() Consider ICU admission if patient persistently hypotensive, hypoxic, on pressors
Consider ICU admission if patient persistently hypotensive, hypoxic, on pressors
BASICS
![]() Abscess in perinephric space
Abscess in perinephric space
ETIOLOGY
![]() Usually from obstructed pyelonephritis
Usually from obstructed pyelonephritis
![]() Risk factors: stones, diabetes mellitus, bacteremia
Risk factors: stones, diabetes mellitus, bacteremia
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Symptoms similar to severe pyelonephritis
Symptoms similar to severe pyelonephritis
![]() Few symptoms in the elderly, neuropathy, diabetes mellitus, alcoholics
Few symptoms in the elderly, neuropathy, diabetes mellitus, alcoholics
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Must have high clinical suspicion
Must have high clinical suspicion
![]() Urinalysis may be normal if no communication with the collecting system
Urinalysis may be normal if no communication with the collecting system
![]() Ultrasound or CT scan
Ultrasound or CT scan
TREATMENT
![]() IV antibiotics for 2 to 3 weeks, drainage, and relief of any urologic obstruction
IV antibiotics for 2 to 3 weeks, drainage, and relief of any urologic obstruction
![]() Renal abscess >5 cm = percutaneous drainage and antibiotics
Renal abscess >5 cm = percutaneous drainage and antibiotics
![]() Renal abscess <5 cm = antibiotics initially and if no response can consider drainage
Renal abscess <5 cm = antibiotics initially and if no response can consider drainage
![]() Perinephric abscess should be drained for diagnostic and therapeutic options
Perinephric abscess should be drained for diagnostic and therapeutic options
![]() SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTIONS
ETIOLOGY
![]() Transmitted from sexual intercourse, usually herpes simplex virus type 2
Transmitted from sexual intercourse, usually herpes simplex virus type 2
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Prodrome of hyperesthesia, parasthesia, or itching in area of peritoneum or genitals prior to outbreak
Prodrome of hyperesthesia, parasthesia, or itching in area of peritoneum or genitals prior to outbreak
![]() Occasional flu-like symptoms, inguinal lymphadenopathy, and fever
Occasional flu-like symptoms, inguinal lymphadenopathy, and fever
![]() Exquisitely tender vesicles on erythematous base
Exquisitely tender vesicles on erythematous base
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical exam findings
Clinical exam findings
![]() Tzanck smear
Tzanck smear
TREATMENT
![]() Vesicles are self-limiting and last 1 to 2 weeks
Vesicles are self-limiting and last 1 to 2 weeks
![]() Oral antiviral therapy (acyclovir, or valacyclovir) can shorten the outbreak
Oral antiviral therapy (acyclovir, or valacyclovir) can shorten the outbreak
![]() Advise patient that the virus can be transmitted even when there are no symptoms
Advise patient that the virus can be transmitted even when there are no symptoms
ETIOLOGY
![]() Treponema pallidum
Treponema pallidum
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Primary syphilis:
Primary syphilis:
• Usually with a chancre, a painless ulcer
![]() Secondary syphilis:
Secondary syphilis:
• Various cutaneous lesions which are usually pink papules or macules often seen on palms and soles
• Sore throat and fever
![]() Tertiary syphilis:
Tertiary syphilis:
• Neurology manifestations
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical exam findings
Clinical exam findings
![]() Polymerase chain reaction
Polymerase chain reaction
TREATMENT
![]() Primary and secondary should be treated with benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units by intramuscular (IM) injection
Primary and secondary should be treated with benzathine penicillin G 2.4 million units by intramuscular (IM) injection
ETIOLOGY
![]() Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydia trachomatis
![]() Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Men: asymptomatic or present with dysuria
Men: asymptomatic or present with dysuria
![]() Females: dysuria, vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, cervicitis
Females: dysuria, vaginal discharge, pelvic pain, cervicitis
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Direct swab or collect urine/urethral swab
Direct swab or collect urine/urethral swab
TREATMENT
![]() Chlamydia:
Chlamydia:
• Azithromycin 1,000 mg po or doxycycline 100 mg po bid for 7 days
![]() Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea
• Ceftriaxone 250 mg IM
• If penicillin or cephalosporin allergy, may give double dose of azithromycin
ETIOLOGY
![]() Human papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Fleshy warts appearing like cauliflower on the external genitalia
Fleshy warts appearing like cauliflower on the external genitalia
TREATMENT
![]() Freeze or remove the warts
Freeze or remove the warts
![]() Immunization for preexposure prophylaxis
Immunization for preexposure prophylaxis
BASICS
![]() A surgical emergency that may result in the loss of the affected testicle if not treated promptly
A surgical emergency that may result in the loss of the affected testicle if not treated promptly
ETIOLOGY
![]() Twisting of the spermatic cord constricts blood supply, which if left untreated can cause testicle necrosis
Twisting of the spermatic cord constricts blood supply, which if left untreated can cause testicle necrosis
![]() More common in children and young adults
More common in children and young adults
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Acute onset of pain and scrotal swelling
Acute onset of pain and scrotal swelling
![]() Occasional nausea and vomiting
Occasional nausea and vomiting
![]() The involved testis may be swollen or have a palpable torsed section
The involved testis may be swollen or have a palpable torsed section
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Ultrasound to evaluate blood flow
Ultrasound to evaluate blood flow
TREATMENT
![]() Occasional attempt at emergent manual reduction and emergent urologic consultation for surgical intervention
Occasional attempt at emergent manual reduction and emergent urologic consultation for surgical intervention
BASICS
![]() Inflammation of the testicles
Inflammation of the testicles
ETIOLOGY
![]() Usually secondary to viral illness, mumps, or sexually transmitted infection
Usually secondary to viral illness, mumps, or sexually transmitted infection
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Pain and swelling of the testicle
Pain and swelling of the testicle
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Ultrasound helpful to distinguish it from other pathology
Ultrasound helpful to distinguish it from other pathology
TREATMENT
![]() Symptomatic treatment
Symptomatic treatment
![]() Treat the underlying etiology if suspected infectious cause
Treat the underlying etiology if suspected infectious cause
BASICS
![]() Inflammation of the epididymis
Inflammation of the epididymis
ETIOLOGY
![]() Epididymal swelling caused by infection, trauma, or idiopathic
Epididymal swelling caused by infection, trauma, or idiopathic
![]() Common causes: C. trachomatis and gonorrhea in young men who are sexually active; E. coli, Pseudomonas, and Enterobacter species in older men
Common causes: C. trachomatis and gonorrhea in young men who are sexually active; E. coli, Pseudomonas, and Enterobacter species in older men
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Gradual onset of unilateral pain and swelling over a few hours
Gradual onset of unilateral pain and swelling over a few hours
![]() Epididymis and scrotum can be swollen and tender
Epididymis and scrotum can be swollen and tender
![]() May also have signs of UTI, but not consistent
May also have signs of UTI, but not consistent
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Urinalysis
Urinalysis
![]() Ultrasound
Ultrasound
TREATMENT
![]() If age <35:
If age <35:
• Treat for both C. trachomatis and gonorrhea with ceftriaxone 250 mg IM and doxycycline 100 mg bid
![]() If age >35:
If age >35:
• Assume enteric pathogen and treat with Cipro for 10 days
![]() Pain control and close urology follow-up
Pain control and close urology follow-up
BASICS
![]() Necrotizing fasciitis of perineal, genital, or perianal regions
Necrotizing fasciitis of perineal, genital, or perianal regions
ETIOLOGY
![]() Polymicrobial
Polymicrobial
![]() High rate of mortality
High rate of mortality
![]() Most patients have diabetes
Most patients have diabetes
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Edema, erythema tenderness in groin and genitals
Edema, erythema tenderness in groin and genitals
![]() Necrosis, crepitus of skin and subcutaneous tissue
Necrosis, crepitus of skin and subcutaneous tissue
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Clinical exam findings
Clinical exam findings
![]() Labs for leukocytosis
Labs for leukocytosis
![]() X-ray or CT scan may show subcutaneous gas
X-ray or CT scan may show subcutaneous gas
TREATMENT
![]() ABCs, supportive, IV fluid, antibiotics
ABCs, supportive, IV fluid, antibiotics
![]() Surgery and/or urology consult for consideration of surgical debridement
Surgery and/or urology consult for consideration of surgical debridement