BASICS
![]() Compression of lumbar and sacral nerve
Compression of lumbar and sacral nerve
ETIOLOGY
![]() Most commonly from tumor or disc herniation
Most commonly from tumor or disc herniation
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Back pain
Back pain
![]() Bowel or bladder dysfunction (urinary retention, overflow incontinence, loss of bowel or bladder control)
Bowel or bladder dysfunction (urinary retention, overflow incontinence, loss of bowel or bladder control)
![]() Saddle paresthesias
Saddle paresthesias
![]() Leg weakness
Leg weakness
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() MRI
MRI
TREATMENT
![]() Pain control
Pain control
![]() Urgent surgical decompression
Urgent surgical decompression
BASICS
![]() Condition that causes pressure on the spinal cord
Condition that causes pressure on the spinal cord
![]() Early recognition is key to improved outcomes
Early recognition is key to improved outcomes
ETIOLOGY
![]() Common complication of malignancy, usually from metastatic tumor
Common complication of malignancy, usually from metastatic tumor
![]() Also caused by arthritis, trauma, infection
Also caused by arthritis, trauma, infection
![]() Thoracic spine (60%), lumbar spine (30%), cervical spine (10%)
Thoracic spine (60%), lumbar spine (30%), cervical spine (10%)
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Back pain is first symptom
Back pain is first symptom
![]() Motor weakness, followed by gait disorders, then paralysis
Motor weakness, followed by gait disorders, then paralysis
![]() Sensory symptoms less common
Sensory symptoms less common
![]() Bowel and/or bladder dysfunction
Bowel and/or bladder dysfunction
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() MRI of entire spine imaging of choice
MRI of entire spine imaging of choice
![]() CT plus myelogram for those with contraindication to MRI
CT plus myelogram for those with contraindication to MRI
TREATMENT
![]() Pain control, steroids, surgical decompression, or radiation
Pain control, steroids, surgical decompression, or radiation
![]() Preserving or improving neurological function
Preserving or improving neurological function
BASICS
![]() Abscess anywhere along spinal cord which can compress
Abscess anywhere along spinal cord which can compress
ETIOLOGY
![]() Most common pathogen Staphylococcus aureus
Most common pathogen Staphylococcus aureus
![]() Risk factors include intravenous drug abuse (IVDA), vertebral osteomyelitis, bacteremia, recent spinal/epidural anesthesia or procedure/surgery, diabetes mellitus, HIV, trauma
Risk factors include intravenous drug abuse (IVDA), vertebral osteomyelitis, bacteremia, recent spinal/epidural anesthesia or procedure/surgery, diabetes mellitus, HIV, trauma
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Classic triad: fever, spinal pain, extremity weakness
Classic triad: fever, spinal pain, extremity weakness
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() MRI test of choice for diagnosis followed by CT with IV contrast
MRI test of choice for diagnosis followed by CT with IV contrast
![]() Blood cultures
Blood cultures
![]() CT-guided aspiration for culture
CT-guided aspiration for culture
TREATMENT
![]() Surgery and long-term antibiotics
Surgery and long-term antibiotics
BASICS
![]() Most commonly occurs at L4 to L5
Most commonly occurs at L4 to L5
![]() Most common cause of chronic low back pain
Most common cause of chronic low back pain
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Back pain, radiating down leg
Back pain, radiating down leg
![]() Limited spine flexion
Limited spine flexion
![]() Decreased reflexes
Decreased reflexes
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Straight leg raise
Straight leg raise
![]() Outpatient MRI
Outpatient MRI
TREATMENT
![]() Conservative
Conservative
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants, physical therapy
![]() Consider surgical referral
Consider surgical referral
BASICS
![]() Narrowing of spinal canal, nerve root canals, or intervertebral foramina
Narrowing of spinal canal, nerve root canals, or intervertebral foramina
![]() Causes nerve root entrapment
Causes nerve root entrapment
ETIOLOGY
![]() Congenital, herniated discs, tumors, injury
Congenital, herniated discs, tumors, injury
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Back pain, pain and tingling in legs, pain in calf/lower leg with ambulation and resolving with rest
Back pain, pain and tingling in legs, pain in calf/lower leg with ambulation and resolving with rest
![]() Pain relieved with sitting/spine flexion
Pain relieved with sitting/spine flexion
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Plain x-ray can show degeneration
Plain x-ray can show degeneration
![]() MRI to assess nerve root entrapment and to rule out malignancy
MRI to assess nerve root entrapment and to rule out malignancy
TREATMENT
![]() Conservative management with NSAIDs
Conservative management with NSAIDs
![]() Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections
Physical therapy, epidural steroid injections
![]() Surgery can improve symptoms and functionality after conservative measures fail
Surgery can improve symptoms and functionality after conservative measures fail
![]() Urgent treatment required where there are neuro deficits
Urgent treatment required where there are neuro deficits
![]() INFLAMMATORY AND INFECTIOUS DISORDERS OF JOINTS AND BONES
INFLAMMATORY AND INFECTIOUS DISORDERS OF JOINTS AND BONES
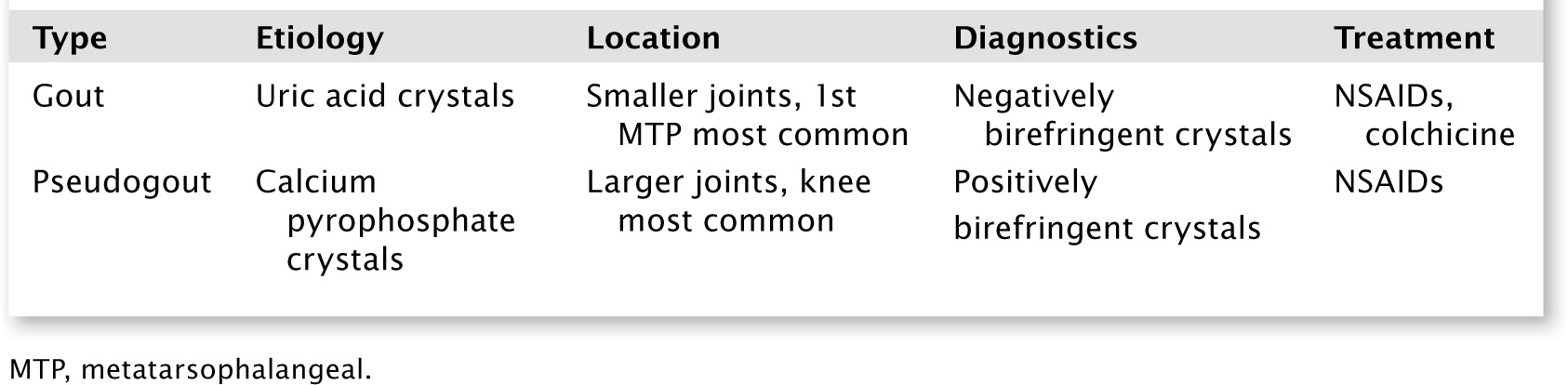
See Table 9.1
BASICS
![]() Painful inflammatory arthritis usually involving a single joint
Painful inflammatory arthritis usually involving a single joint
ETIOLOGY
![]() Uric acid forms crystals that build up in the joints
Uric acid forms crystals that build up in the joints
![]() Risk factors: trauma, diet, dehydration, alcohol ingestion, medications, chronic kidney disease
Risk factors: trauma, diet, dehydration, alcohol ingestion, medications, chronic kidney disease
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
![]() Severe pain, redness, swelling, warmth over 24 hours
Severe pain, redness, swelling, warmth over 24 hours
![]() Podagra: inflammation of first metatarsophalangeal, most common
Podagra: inflammation of first metatarsophalangeal, most common
DIAGNOSTICS
![]() Uric acid levels have no significant value
Uric acid levels have no significant value
![]() Joint aspiration reveals negatively birefringent crystals
Joint aspiration reveals negatively birefringent crystals
TREATMENT
![]() NSAIDs are first-line therapy (Indomethacin)
NSAIDs are first-line therapy (Indomethacin)
![]() Colchicine often aborts flairs if taken as soon as symptoms begin, dose often limited by gastrointestinal side effects
Colchicine often aborts flairs if taken as soon as symptoms begin, dose often limited by gastrointestinal side effects
![]() Allopurinol used for chronic prevention
Allopurinol used for chronic prevention
![]() Steroids may be given intra-articularly or orally
Steroids may be given intra-articularly or orally
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree