57. Marfan Syndrome
Definition
Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic defect of the connective tissue protein, fibrillin. It results in myriad clinical problems, predominately in the cardiac, musculoskeletal, and ocular systems.
Incidence
The incidence of Marfan syndrome is estimated to range from 1:5000 to 1:10,000.
Etiology
FBN 1 locus on chromosome 15 codes for the connective tissue protein, fibrillin. Mutations of the FBN 1 locus are believed to be responsible for Marfan syndrome.
Signs and Symptoms
Cardiovascular System
• Ascending aorta dilation
• Ascending aorta dissection
• Mitral valve annulus calcification
• Mitral valve prolapse
• Pulmonary artery dilation
• Thoracic or abdominal aorta dilation or dissection
Ocular System
• Abnormally flat cornea
• Ectopic lentis
• Hypoplastic ciliary muscle
• Hypoplastic iris
• Increased axial length of the globe
• Myopia
Pulmonary System
• Apical blebs
• Spontaneous pneumothorax
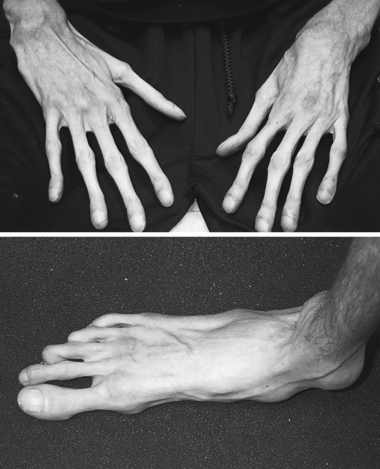 |
| Marfan Syndrome. This young man has prominent arachnodactyly of both fingers and toes. Note the clubbing due to associated cardiopulmonary problems and the flattening of the arch of his foot. |
Skeletal System
• Arachnodactyly
• Dolichocephaly
• Dolichostenomelia
• Downsloping palpebral fissures
• Enophthalmos
• High-arched palate with dental crowding
• Increased arm span–to-height ratio (>1.05)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





