![]() Rescue airway when unable to intubate or difficult ventilation via bag-valve mask (BVM)
Rescue airway when unable to intubate or difficult ventilation via bag-valve mask (BVM)
![]() Facilitate endotracheal intubation
Facilitate endotracheal intubation
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Absolute (When Used as an Airway Rescue Device): Ability to establish definitive airway with endotracheal intubation
Absolute (When Used as an Airway Rescue Device): Ability to establish definitive airway with endotracheal intubation
![]() Relative Contraindications
Relative Contraindications
![]() High risk of aspiration
High risk of aspiration
![]() Vomiting
Vomiting
![]() Massive hemoptysis or brisk upper gastrointestinal bleeding
Massive hemoptysis or brisk upper gastrointestinal bleeding
![]() Trismus
Trismus
![]() Laryngeal injuries or tracheal disruption
Laryngeal injuries or tracheal disruption
![]() Recent head and neck radiation
Recent head and neck radiation
![]() Significant upper airway infection such as epiglottitis
Significant upper airway infection such as epiglottitis
![]() Foreign body in upper airway
Foreign body in upper airway
![]() Conditions requiring high ventilation pressures (poor pulmonary compliance or increased airway resistance)
Conditions requiring high ventilation pressures (poor pulmonary compliance or increased airway resistance)
LANDMARKS
![]() Insert into oropharynx and advance until mask rests over glottic opening
Insert into oropharynx and advance until mask rests over glottic opening
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Choose appropriate laryngeal mask airway (LMA) size
Choose appropriate laryngeal mask airway (LMA) size
![]() Deflate and lubricate mask
Deflate and lubricate mask
![]() Insert along palate
Insert along palate
![]() Inflate cuff
Inflate cuff
![]() Confirm placement
Confirm placement
![]() Secure in place
Secure in place
TECHNIQUE—STANDARD LARYNGEAL MASK AIRWAY
![]() Preparation
Preparation
![]() Confirm all monitoring equipment is in place and functional, including oxygen saturation probe and cardiac telemetry
Confirm all monitoring equipment is in place and functional, including oxygen saturation probe and cardiac telemetry
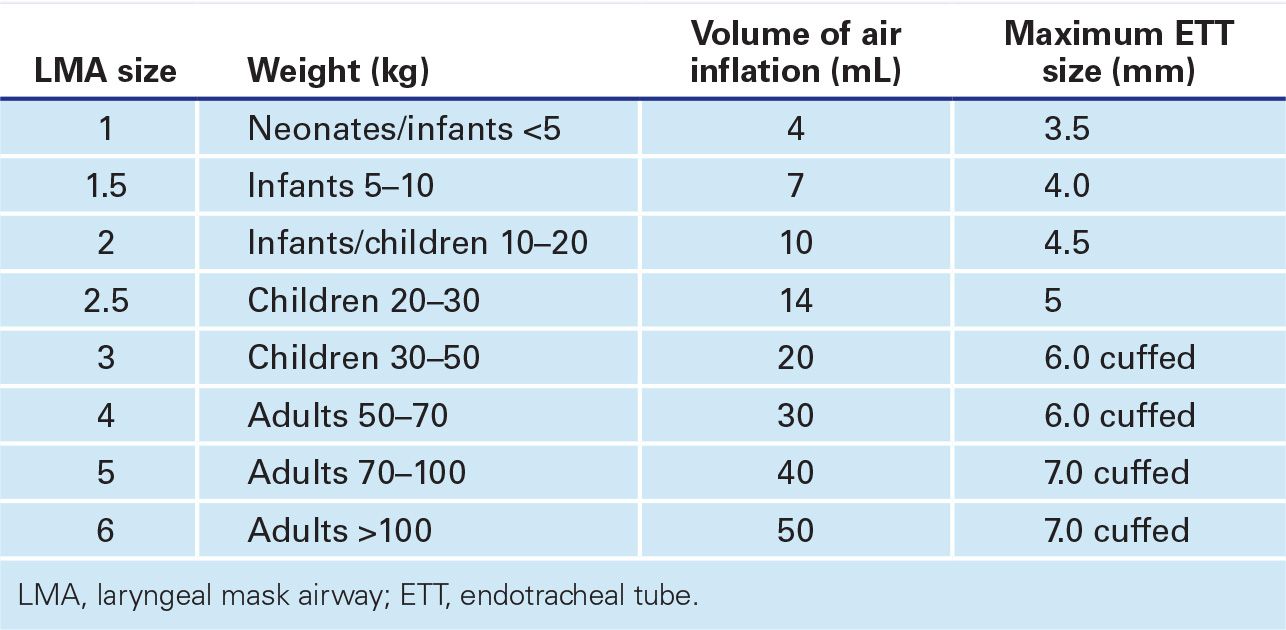
![]() Select appropriate LMA size based on estimated patient weight (TABLE 7.1)
Select appropriate LMA size based on estimated patient weight (TABLE 7.1)
![]() Assess cuff for air leaks
Assess cuff for air leaks
![]() Inject appropriate amount of air for the selected LMA (Table 7.1)
Inject appropriate amount of air for the selected LMA (Table 7.1)
![]() Deflate while pressing cuff against a flat surface to provide a smooth leading edge for insertion
Deflate while pressing cuff against a flat surface to provide a smooth leading edge for insertion
![]() Apply water-soluble lubricant to distal cuff surface
Apply water-soluble lubricant to distal cuff surface
![]() Preoxygenation
Preoxygenation
![]() Deliver 100% oxygen via nonrebreather mask or BVM ventilation
Deliver 100% oxygen via nonrebreather mask or BVM ventilation
![]() Administer medications, such as sedatives, if needed
Administer medications, such as sedatives, if needed
GUIDELINES FOR LARYNGEAL MASK AIRWAY SELECTION AND MASK INFLATION |

![]() Position
Position
![]() Use nondominant hand to adjust head position
Use nondominant hand to adjust head position
![]() Sniffing position is optimal for nonintubating LMAs
Sniffing position is optimal for nonintubating LMAs
![]() May maintain neutral head position if cervical spine immobilization is necessary
May maintain neutral head position if cervical spine immobilization is necessary
![]() Placement
Placement
![]() Hold LMA in dominant hand like a pencil with index finger placed on airway tube at the tube–mask junction (FIGURE 7.1)
Hold LMA in dominant hand like a pencil with index finger placed on airway tube at the tube–mask junction (FIGURE 7.1)
![]() Open airway with nondominant hand
Open airway with nondominant hand
![]() Insert into oropharynx with aperture facing the tongue (FIGURE 7.2A)
Insert into oropharynx with aperture facing the tongue (FIGURE 7.2A)
![]() Pressing against the hard palate, advance past the posterior border of the tongue
Pressing against the hard palate, advance past the posterior border of the tongue
![]() Resistance will be noted when the mask rests over the glottic opening (FIGURE 7.2B)
Resistance will be noted when the mask rests over the glottic opening (FIGURE 7.2B)
![]() Complete insertion by using fingers to push LMA further into the supraglottic region (FIGURE 7.2C)
Complete insertion by using fingers to push LMA further into the supraglottic region (FIGURE 7.2C)
![]() Inflate collar—the increased size will cause LMA to move slightly out of mouth
Inflate collar—the increased size will cause LMA to move slightly out of mouth
![]() Confirm successful ventilation with end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) detector and lung auscultation
Confirm successful ventilation with end-tidal carbon dioxide (ETCO2) detector and lung auscultation
![]() Protection
Protection
![]() Secure LMA with tape or tube-securing device
Secure LMA with tape or tube-securing device
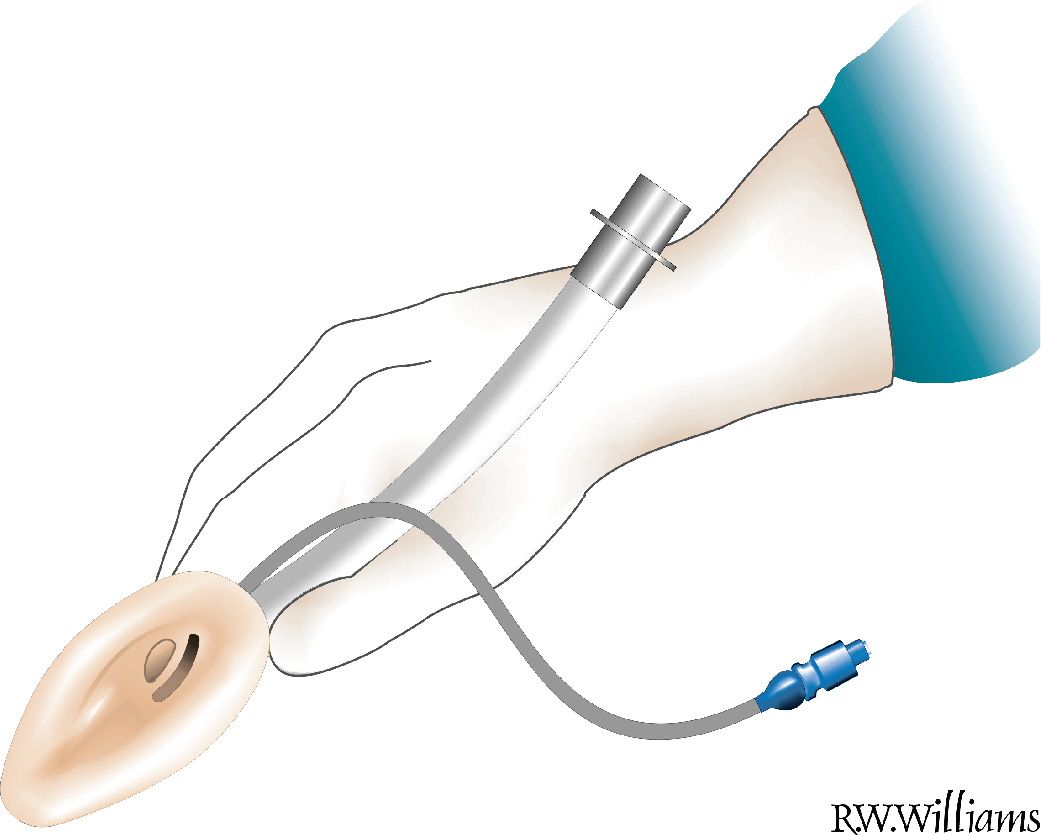
FIGURE 7.1 Correct position of the fingers for LMA insertion. From Murphy FM. Extraglottic devices. In: Walls RM, Murphy MF, eds. Manual of Emergency Airway Management. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2012:113–138.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


