INDICATIONS
![]() Used to evacuate abnormal fluid collections from the joint space for synovial fluid analysis
Used to evacuate abnormal fluid collections from the joint space for synovial fluid analysis
![]() Septic arthritis
Septic arthritis
![]() Crystal arthropathy
Crystal arthropathy
![]() Hemarthrosis
Hemarthrosis
![]() Inflammatory process
Inflammatory process
![]() Used to diagnose occult fracture or ligamentous injury
Used to diagnose occult fracture or ligamentous injury
![]() Used to decrease/relieve pressure in the joint to provide pain relief
Used to decrease/relieve pressure in the joint to provide pain relief
![]() Used to inject methylene blue and test for joint capsule integrity when concerned that overlying laceration communicates with joint space
Used to inject methylene blue and test for joint capsule integrity when concerned that overlying laceration communicates with joint space
![]() Used to inject medication for treatment and pain relief
Used to inject medication for treatment and pain relief
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Absolute Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
![]() Abscess/cellulitis in the tissue overlying the site to be punctured (often infectious arthritis can mimic an overlying soft-tissue infection)
Abscess/cellulitis in the tissue overlying the site to be punctured (often infectious arthritis can mimic an overlying soft-tissue infection)
![]() Relative Contraindications
Relative Contraindications
![]() Bleeding diatheses/anticoagulant therapy
Bleeding diatheses/anticoagulant therapy
![]() Prosthetic joint
Prosthetic joint
![]() Known bacteremia
Known bacteremia
RISKS/CONSENT ISSUES
![]() Potential for introducing infection (sterile technique must be utilized)
Potential for introducing infection (sterile technique must be utilized)
![]() Procedure can cause pain (local anesthesia will be given)
Procedure can cause pain (local anesthesia will be given)
![]() Needle puncture can cause localized bleeding
Needle puncture can cause localized bleeding
![]() Reaccumulation of fluid may occur
Reaccumulation of fluid may occur
![]() Risk of injuring articular cartilage with needle tip
Risk of injuring articular cartilage with needle tip
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Identify landmarks and prep area
Identify landmarks and prep area
![]() Sterilize
Sterilize
![]() Analgesia
Analgesia
![]() Aspirate
Aspirate
LANDMARKS
![]() Parapatellar Approach
Parapatellar Approach
![]() Can use medial or lateral approach
Can use medial or lateral approach
![]() Enter 1 cm from the edge of the patella along the superior one-third of the medial or lateral border
Enter 1 cm from the edge of the patella along the superior one-third of the medial or lateral border
![]() Direct the needle along the inferior surface of the patella and toward the intercondylar notch (FIGURE 55.1)
Direct the needle along the inferior surface of the patella and toward the intercondylar notch (FIGURE 55.1)
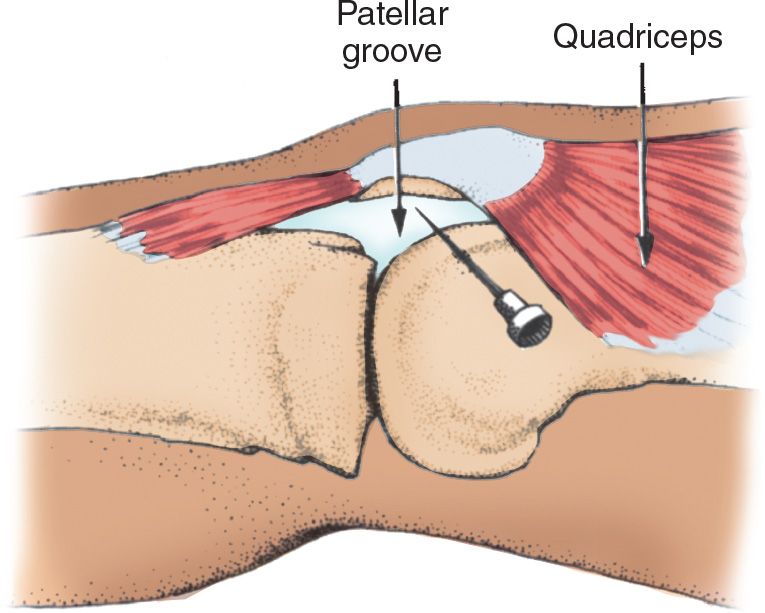
FIGURE 55.1 Medial parapatellar approach. (From Simon RR, Brenner BE. Emergency Procedures and Techniques. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002:245.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


