45. Hydatidiform Mole
Definition
Hydatidiform mole encompasses several conditions, including complete and partial moles, placental site trophoblastic tumors, choriocarcinomas, and invasive moles. Complete moles are devoid of any fetal tissue and the chorionic villi develop grapelike (hydatiform) swelling. In addition, trophoblastic hyperplasia is present. Hydatidiform mole is also called gestational trophoblastic disease.
Incidence
The incidence of hydatidiform mole in Western countries is 1:1000 to 1:1500 pregnancies; in Asia it is 1:120 pregnancies.
Etiology
Hydatidiform mole results from the transfer of only paternal chromosomes, either by single spermatic fertilization of an anucleate ovum, whereupon the paternal DNA replicates, or the fertilization of an ovum by two sperm. The chorionic villi subsequently develop grapelike, or hydatiform swelling.
Signs and Symptoms
• Absent fetal heart tones
• Hyperemesis
• Hyperthyroidism
• Preeclampsia
• Tachycardia
• Tremor
• Uterine enlargement greater than normal for estimated gestational age
• Uterine enlargement smaller than normal for estimated gestational age
• Warm skin
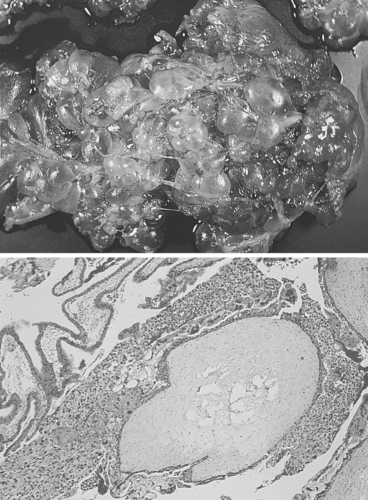 |
| Hydatidiform Mole. Complete hydatidiform mole. Nearly all villi are enlarged and are interconnected by thin nonedematous cordlike structures. |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





