![]() To anesthetize portions of the face and ears
To anesthetize portions of the face and ears
![]() Areas of distributions:
Areas of distributions:
![]() Supraorbital and supratrochlear: Forehead
Supraorbital and supratrochlear: Forehead
![]() Infraorbital: Upper lip, upper cheek, lateral portion of the nose, and anterior maxillary teeth
Infraorbital: Upper lip, upper cheek, lateral portion of the nose, and anterior maxillary teeth
![]() Inferior alveolar: Lower jaw, lower lip, lower teeth, and anterior two-thirds of the tongue
Inferior alveolar: Lower jaw, lower lip, lower teeth, and anterior two-thirds of the tongue
![]() Mental: Lower jaw, lower teeth, anterior tongue, and floor of the mouth
Mental: Lower jaw, lower teeth, anterior tongue, and floor of the mouth
![]() Auricular: External ear
Auricular: External ear
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Absolute Contraindications
Absolute Contraindications
![]() Anaphylaxis to local anesthetic agents
Anaphylaxis to local anesthetic agents
![]() Relative Contraindications
Relative Contraindications
![]() Coagulopathy
Coagulopathy
![]() Infection at the injection site
Infection at the injection site
![]() Uncooperative or obtunded patients
Uncooperative or obtunded patients
SUPPLIES
![]() 25-gauge to 30-gauge needle
25-gauge to 30-gauge needle
![]() Syringe
Syringe
![]() Topical anesthetic (optional)
Topical anesthetic (optional)
![]() Eutectic mixture of local anesthetics (EMLA), 20% benzocaine, or 5% to 10% lidocaine ointment can be used to decrease the pain of needle insertion
Eutectic mixture of local anesthetics (EMLA), 20% benzocaine, or 5% to 10% lidocaine ointment can be used to decrease the pain of needle insertion
![]() Bicarbonate (optional)
Bicarbonate (optional)
![]() 1:10 dilution with injectable anesthetic to decrease the pain of infiltration
1:10 dilution with injectable anesthetic to decrease the pain of infiltration
![]() Anesthetic agent
Anesthetic agent
![]() Lidocaine 1% to 2%
Lidocaine 1% to 2%
![]() Onset of action: 4 to 10 minutes
Onset of action: 4 to 10 minutes
![]() Duration of action: 1 to 2 hours
Duration of action: 1 to 2 hours
![]() Maximum one time dose: 4.5 mg/kg
Maximum one time dose: 4.5 mg/kg
![]() Bupivacaine 0.25%
Bupivacaine 0.25%
![]() Onset of action: 8 to 12 minutes
Onset of action: 8 to 12 minutes
![]() Duration of action: 4 to 8 hours
Duration of action: 4 to 8 hours
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Preparation
Preparation
![]() Identify landmarks
Identify landmarks
![]() Injection of anesthetic
Injection of anesthetic
PREPARATION
![]() Position patient and adjust lighting for optimal visualization
Position patient and adjust lighting for optimal visualization
![]() Apply topical local anesthetic
Apply topical local anesthetic
![]() Prepare nonmucosal injection sites with povidone–iodine solution or chlorhexidine
Prepare nonmucosal injection sites with povidone–iodine solution or chlorhexidine
![]() Use sterile gloves
Use sterile gloves
LANDMARKS AND TECHNIQUES
![]() Forehead Nerve Block (Supraorbital and Supratrochlear Nerve Blocks)
Forehead Nerve Block (Supraorbital and Supratrochlear Nerve Blocks)
![]() Locate the supraorbital notch which is at the intersection of the superior edge of the orbit and a vertical line through the middle of the pupil when the eyes are looking forward
Locate the supraorbital notch which is at the intersection of the superior edge of the orbit and a vertical line through the middle of the pupil when the eyes are looking forward
![]() Insert the needle slightly superior and medial to the supraorbital notch and inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
Insert the needle slightly superior and medial to the supraorbital notch and inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
![]() Move 0.5 to 1.0 cm medially and inject an additional 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic to block the supratrochlear nerve (FIGURE 80.1)
Move 0.5 to 1.0 cm medially and inject an additional 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic to block the supratrochlear nerve (FIGURE 80.1)
![]() Infraorbital Nerve Block
Infraorbital Nerve Block
![]() Locate the infraorbital foramen which is at the intersection of the inferior edge of the orbit and a vertical line through the middle of the pupil when the eyes are looking forward
Locate the infraorbital foramen which is at the intersection of the inferior edge of the orbit and a vertical line through the middle of the pupil when the eyes are looking forward
![]() Extraoral or intraoral approaches can be used
Extraoral or intraoral approaches can be used
![]() Extraoral
Extraoral
![]() Insert the needle 1 cm below the infraorbital foramen and inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
Insert the needle 1 cm below the infraorbital foramen and inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
![]() Intraoral
Intraoral
![]() Place one finger on the infraorbital foramen and retract the upper lip
Place one finger on the infraorbital foramen and retract the upper lip
![]() Identify the first maxillary premolar and insert the needle into the mucobuccal fold with the bevel facing the bone
Identify the first maxillary premolar and insert the needle into the mucobuccal fold with the bevel facing the bone
![]() Advance the needle toward the apex of the tooth or 1 cm below the infraorbital foramen
Advance the needle toward the apex of the tooth or 1 cm below the infraorbital foramen
![]() Take caution to avoid entering the orbit or the infraorbital foramen. If the patient feels paresthesias, retract the needle.
Take caution to avoid entering the orbit or the infraorbital foramen. If the patient feels paresthesias, retract the needle.
![]() Inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
Inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
![]() Mental Nerve Block
Mental Nerve Block
![]() Locate the mental foramen which lies in the plane of the supraorbital and infraorbital foramina (see above) at the apex of the lower second premolar
Locate the mental foramen which lies in the plane of the supraorbital and infraorbital foramina (see above) at the apex of the lower second premolar
![]() Extraoral or intraoral approaches can be used (FIGURE 80.2)
Extraoral or intraoral approaches can be used (FIGURE 80.2)
![]() Extraoral
Extraoral
![]() Insert the needle 1 cm inferolateral to the foramen
Insert the needle 1 cm inferolateral to the foramen
![]() Inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
Inject 2 to 4 mL of anesthetic
![]() Intraoral
Intraoral
![]() Retract the patient’s lower lip
Retract the patient’s lower lip
![]() Locate the space between the premolar and molar teeth
Locate the space between the premolar and molar teeth
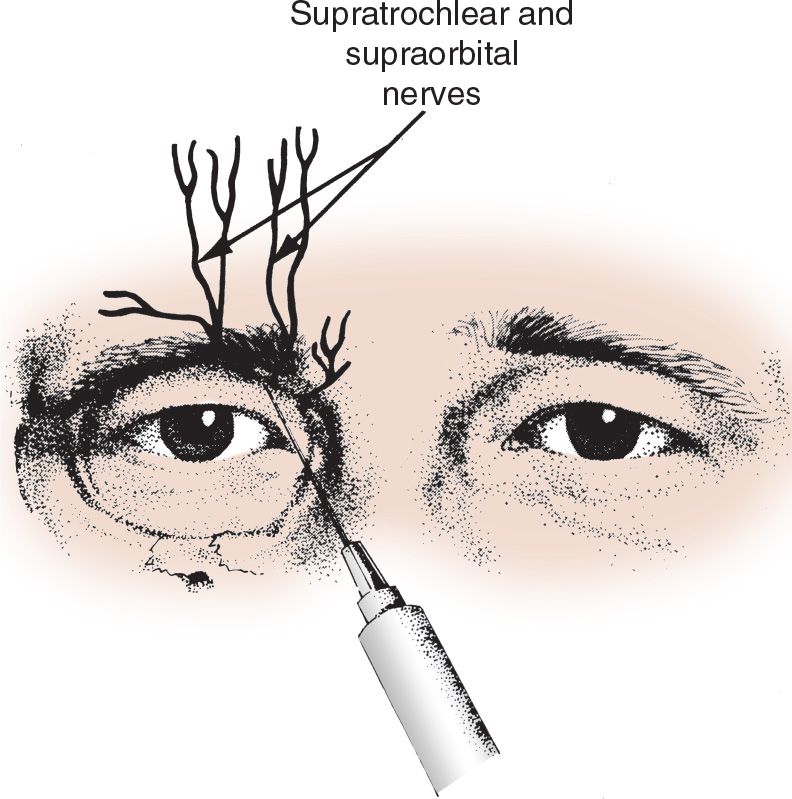
FIGURE 80.1 The supraorbital and supratrochlear nerves emerging through the notches at the upper border of the orbital ridge. (From Simon RR, Brenner BE. Emergency Procedures and Techniques. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2002:117, with permission.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


