Chapter 31 Environmental Emergencies
Cold-Induced Injuries
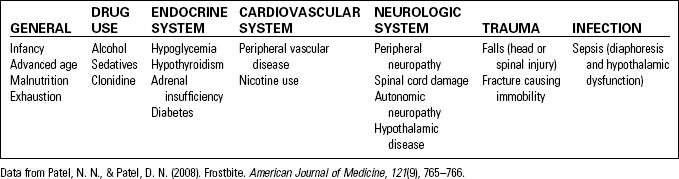
Cold-induced injuries include both tissue injuries (chilblains, immersion foot, and frostbite) and a decrease in core body temperature. Table 31-1 lists factors that increase susceptibility to cold.
Frostbite2–6
Deep Frostbite
Signs and Symptoms
• Slight burning pain followed by a feeling of warmth and then numbness as the area freezes
• Whitish or yellow-white discoloration of the skin followed by a waxy appearance
• Swelling and intense burning accompanying thawing
• Blisters (usually appear in 1 to 7 days)
• Edema of the entire extremity that may persist for months
Therapeutic Interventions
Escharotomy is indicated for treatment of severe vascular compromise in deep frostbite.
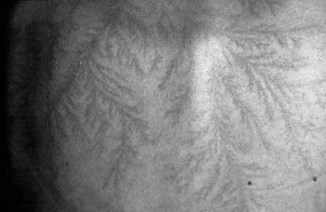
Fig. 31-1 Spiderlike cutaneous burns from path of lightning over surface of body.
(Courtesy Mary Ann Cooper, MD. From Marx, J. A., Hockberger, R. S., & Walls, R. M. [2009]. Rosen’s emergency medicine [7th ed.]. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby.)
General guidelines for the management of cold-related tissue injury are listed in Table 31-2.
TABLE 31-2 GENERAL MANAGEMENT PRINCIPLES FOR COLD-RELATED TISSUE INJURY
Hypothermia
• Neonates, because of limited body fat and an inability to shiver or seek warmth
• Elderly persons, because of medications, loss of body fat, and cardiovascular changes associated with aging
• Alcoholics and the homeless, because of poor nutrition and environmental exposure
Pathophysiology
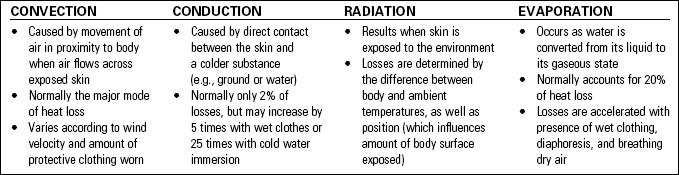
Body heat loss occurs by four different means, which alone or in combination can result in losses that overwhelm the body’s ability to compensate: convection, conduction, radiation, and evaporation (Table 31-3).
Normal body heat lost by conduction is only 2% but it may increase 5 times with wet clothes or 25 times with cold water immersion.7
Most of the metabolic and enzymatic processes of the body are temperature dependent and changes evolve with decreasing temperatures. At core body temperatures less than 32°C (90°F), defined as profound or severe hypothermia, pathologic changes are noted as the cold directly affects various body functions. Table 31-4 summarizes potential changes in various body systems.
TABLE 31-4 POTENTIAL PATHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN VARIOUS BODY SYSTEMS