Dolasetron (Anzemet): See 5HT3 Antagonists.
Droperidol (Inapsine)
Indication: (1) Prevention/treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Also used for (2) sedation, GA adjunct, treatment of delirium although alternate drugs are preferred
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 0.625–1.25 mg IV (2) 2.5 mg is max recommended, additional 1.25 mg doses if benefit > risk. Peds: 2–12 yrs: 0.03–0.07 mg/kg (0.1 mg/kg max)
Mechanism: Butyrophenone neuroleptic, primarily anti-dopaminergic with some antagonism at NE, 5HT, GABA, α-adrenergic receptors
Clearance: Extensive hepatic metabolism, renal excretion
Comments: Potentiates other CNS depressants; may also cause anxiety, restlessness, dysphoria. Mild α-adrenergic blockade may cause hypotension via peripheral vasodilation, reflex tachycardia (especially in hypovolemia). Avoid in Parkinson’s, pheochromocytoma (can precipitate catecholamine release). May cause extrapyramidal symptoms → rx with diphenhydramine. May prolong QT interval leading to serious arrhythmias including torsades de pointes, ventricular arrhythmias, cardiac arrest. Contraindicated in pre-existing prolonged interval (QTc >440 in males, >450 in females); use extreme caution if risk factors for QT prolongation including HR < 50, cardiac disease, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, co-administration of other QT prolonging drugs (includes calcium channel blockers, ondansetron, antidepressants, fluoroquinolones, antiarrhythmics)
Enoxaparin (Lovenox, LMWH)
Indication: (1) DVT prophylaxis, (2) treatment of acute DVT or PE, (3) acute coronary syndrome
Typical dose: (1) 40 mg SC daily or 30 mg SC q12h; (2) 1 mg/kg SC q12h (outpatient, with warfarin) or 1.5 mg/kg SC daily (inpatient, with warfarin); (3) 1 mg/kg SC bid with aspirin (30 mg IV bolus in STEMI). Peds: Safety/efficacy not established. (1) <2 mos: 0.75 mg/kg SC q12h; (2) 1.5 mg/kg SC q12h; >2 mos: (1) 0.5 mg/kg SC q12h; (2) 1 mg/kg SC q12h
Mechanism: LMWH, antithrombotic. Anti-factor Xa and antithrombin (anti-factor IIa) activity
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism, renal excretion
Comments: More predictable dose–response relationship and longer duration of action than unfractionated heparin. Preferred for DVT prophylaxis in arthroplasty, trauma. Unlike warfarin, may be used in pregnancy. Generally does not ↑ PT or PTT; monitor Factor Xa activity (4 hrs after dose) if needed (consider for dose adjustment in obesity, low body weight, pregnancy, renal impairment). Xa activity level not predictive of bleeding risk. Reduce dose for low body weight <45 kg, renal impairment with GFR < 30. Rarely causes thrombocytopenia, contraindicated in major active bleeding. Incomplete reversal with protamine. Risk of spinal or epidural hematomas and neurologic damage with spinal puncture, neuraxial anesthesia including indwelling catheters (wait 12 hrs after prophylactic dose or 24 hrs after therapeutic dose before performing neuraxial block; ↑ risk with twice-daily vs. once-daily dosing; delay enoxaparin dose for 2 hrs after neuraxial catheter removal)
Epinephrine, Racemic (Vaponefrin)
Indication: Croup (laryngotracheobronchitis), postextubation/traumatic airway edema; adjunct in bronchiolitis and bronchospasm
Typical dose: Inhaled via nebulizer. Adult: 0.5 mL of 2.25% solution in 3 mL NS q2–4h prn. Peds: <4 yrs: 0.05 mL/kg of 2.25% solution in 3 mL NS q2–4h prn; >4 yrs: 0.25–0.5 mL of 2.25% solution in 3 mL NS q2–4h prn
Mechanism: Mucosal vasoconstriction
Clearance: MAO/COMT metabolism
Comments: May cause tachycardia, arrhythmias. Rebound airway edema may occur up to 2 hrs after discontinuation
Epoprostenol (Flolan, Prostacyclin, Prostaglandin I2 [PGI2])
Indication: Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Typical dose: 2 ng/kg/min IV infusion, titrate by 1–2 ng/kg/min q15–30min. For short-term use in critical illness, may be inhaled via continuous nebulization (15–50 ng/kg/min doses studied, wean by 50%)
Mechanism: Pulmonary and systemic vasodilator; inhibits platelet aggregation
Clearance: Rapidly hydrolyzed in blood
Comments: Not for use in all types of pulmonary hypertension. Caution in pulmonary veno-occlusive disease or left ventricular systolic dysfunction; pulmonary edema may develop during initial IV dose titration. IV use cause brady- or tachycardia, hypotension, flu-like symptoms, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea. Avoid abrupt withdrawal or interruption of infusion (note half-life 2.7 min). Inhaled therapy offers potential benefit of minimal systemic hemodynamic effect, improvement of V/Q matching; use caution as “sticky” glycine preparation can clog ETT and cause ventilator malfunction. Potential uses for inhaled drug include acute pulmonary hypertensive crisis, post-cardiac surgery, ARDS, neonates with congenital heart defects
Eptifibatide (Integrilin)
Indication: Prevention of thrombus formation after PCI, treatment of acute coronary syndrome
Typical Dose: Bolus 180 mcg/kg, then 2 mcg/kg/min infusion up to 72 hrs. Reduce infusion to 1 mcg/min in renal impairment with CrCl <50
Mechanism: Prevents platelet adhesion and aggregation by reversible inhibition of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor
Clearance: Renal excretion, platelet function recovers within 4–8 hrs after discontinuation of infusion
Comments: Risk of bleeding complications including bleeding at sheath site (early removal encouraged, hold heparin first). May cause thrombocytopenia. Contraindicated with recent severe bleeding or bleeding disorder (specific contraindications similar to TPA)
Ethacrynic Acid (Edecrin): See Diuretics table on page 2H-56.
Factor VIIa (Novoseven)
Indication: Bleeding episodes and (1) surgical intervention in hemophilia A or B, (2) congenital factor VII deficiency or acquired hemophilia. Also used for intracranial hemorrhage, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage, (3) coagulopathy associated with massive blood loss in trauma, cardiac surgery
Typical dose: (1) 90 mcg/kg IV before intervention, then q2h for duration of surgery × 2–5 d, then q2–6h until healing has occurred, (2) 70–90 mcg/kg IV q2–3 hrs until hemostasis achieved (doses as low as 10 mcg/kg may be effective), (3) dosing is not standardized for these uses, ranges from 35–120 mcg/kg see hospital-based protocol
Mechanism: Promotes hemostasis through activation of extrinsic coagulation cascade; activates factors X, IX → converts prothrmobin to thrombin → converts fibrinogen to fibrin, helps form hemostatic plug
Comments: Off-label use (trauma, complex or cardiac surgery, postpartum hemorrhage) is controversial due to concerns about safety, efficacy, very high cost. Limited available data does not conclusively demonstrate benefit, and may be associated with higher rate of arterial and venous thrombotic complications. (Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Feb 16;(2):CD005011.) Consider risk/benefit for individual patients. Do not inject diluent directly onto powder, swirl gently (do not shake), administer within 3 hrs
Famotidine (Pepcid)
Indication: GERD, peptic ulcers
Typical dose: Adult: 10–20 mg IV q12h (dilute in 10 mL NS, administer <10 mg/min), 20–40 mg PO bid. Peds: 0.6–0.8 mg/kg/d IV, divide q8–12h (max 40 mg/d)
Mechanism: Competitive histamine (H2) receptor antagonist, effect on gastric parietal cells ↓ gastric acid secretion
Clearance: 30–35% hepatic metabolism; 65–70% renal elimination
Comments: Given preoperatively for pulmonary aspiration prophylaxis (maximum effect within 30 min of IV dose), and for ulcer prophylaxis in selected critically ill patients. May cause confusion, dizziness, headache, diarrhea, thrombocytopenia. Reduce dose in renal impairment
Flumazenil (Mazicon)
Indication: (1) Reversal of benzodiazepine sedation; (2) reversal of benzodiazepine overdose
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 0.2 mg IV over 15–30 sec, if no response may redose q1min with 0.3–0.5 mg (max 3 mg/hr), (2) as in (1); may ↑ to 5 mg, if still no response sedation unlikely to be benzodiazepine related. Peds: 0.01 mg/kg IV × 1 dose (max 0.2 mg/dose), subsequent doses 0.005–0.01 mg/kg IV q1min (max 1 mg)
Onset: 1–2 min, peak 6–10 min. Duration: 20–40 min, depends on doze of both benzodiazepine and flumazenil
Mechanism: Competitive antagonism of GABA receptor at benzodiazepine action site
Clearance: Extensive hepatic metabolism, renal excretion
Comments: May wear off before the effects of benzodiazepines; monitor for re-sedation and respiratory depression. Does not antagonize non-benzodiazepine CNS depression. May elicit withdrawal symptoms (including seizures) in chronic benzodiazepine users. Use lowest dose required. Avoid in unknown drug overdose, suspected tricyclic overdose; caution with ↑ ICP or seizure history (be prepared to manage seizures). Only partial reversal of respiratory depression
Furosemide (Lasix)
Indication: (1) Acute pulmonary edema/hypertensive crisis/elevated ICP, (2) symptomatic hyperkalemia, (3) chronic anti-hypertensive, (4) edema associated with CHF, cirrhosis, renal disease
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 0.5–1 mg/kg (or 40 mg) IV over 2 min, (2) 40–80 mg IV, (3) up to 40 mg PO bid, (4) 10–40 mg IV, may ↑ by 20 mg q2h, refractory CHF may require large doses. Infusion: 0.1 mg/kg/hr, titrate to effect (max 4 mg/min). Peds: 0.5–2 mg/kg/dose IV (max 6 mg/kg/d). Neonates: 0.5–1 mg/kg/dose IV (max 2 mg/kg/d)
Onset: <5 min (IV), peak <30 min. Duration: 2 hrs
Mechanism: Loop diuretic; inhibits reabsorption of sodium and chloride at proximal/distal tubules and loop of Henle
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism (10%), renal excretion
Comments: Oral dosing = ½ potency of IV. May cause hypovolemia and electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypochloremic alkalosis). Caution in lupus, sulfa allergy. Do not use in anuria or worsening azotemia. Can ↓ CSF production but less effective than mannitol at ↓ ICP
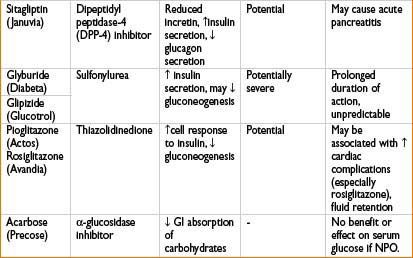
Glipizide (Glucotrol): See Oral Antidiabetics table on page 2H-64.
Glucagon (GlucaGen)
Indication: (1) Severe hypoglycemia, (2) GI diagnostics, also used for (3) refractory beta blocker/calcium channel blocker toxicity
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 1 mg IM/SC/IV, (2) 0.25–2 mg 1 min prior to procedure, repeat q20 min, (3) 50–150 mcg/kg IV bolus, then 1–5 mg/hr IV infusion. Peds: (1) 0.2–0.3 mg/kg (max 1 mg/dose). Repeat q20min prn. Neonates: 0.025–0.3 mg/kg/dose (max 1 mg/dose)
Mechanism: Stimulates adenylate cyclase → ↑ cAMP → promotes hepatic gluconeogenesis, glycogenolysis, catecholamine release. Insulin antagonist. Relaxes GI smooth muscle
Clearance: Hepatic and renal proteolysis
Comments: Positive inotrope and chronotrope (not blocked by b-blockade or catecholamine depletion), enhances AV nodal conduction in AV block. Use in cardiac (refractory low CO after bypass, low CO after MI, congestive heart failure, excessive b-blockade) limited by side effects (nausea and vomiting, hypokalemia, hypo- or hyperglycemia) and ↑ cost. Caution with insulinoma, pheochromocytoma. Give IV dextrose to replete glycogen stores
Glyburide (Diabeta): See Oral Antidiabetics table on page 2H-64.
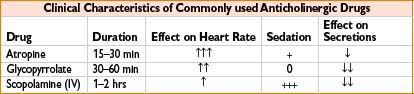
Glycopyrrolate (Robinul)
Indication: (1) Decreases gastrointestinal motility, antisialagogue; (2) bradycardia; (3) adjunct to reversal of neuromuscular blockade
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 0.1–0.2 mg IV/IM/SC; 2.5–10 mcg/kg/dose IV/IM q3–4h; 1–2 mg PO; (2) 0. 1–0.2 mg/dose IV; (3) 0.2 mg IV for each 1 mg neostigmine or 5 mg pyridostigmine or 0.01–0.02 mg/kg IV. Peds: (1) 4–10 mcg/kg/dose IV/IM q3–4h, max 0.2 mg/dose or 0.8 mg q24h; 40–100 mcg/kg/dose PO tid–qid. (2) 0.01–0.02 mg/kg IV. Neonates/infants: 4–10 mcg/kg/dose IV/IM q4–8 h; 40–100 mcg/kg/dose PO q8–12h
Mechanism: Blocks acetylcholine action at smooth muscle parasympathetic sites, secretory glands, and CNS
Clearance: Renal elimination
Comments: Longer duration, better antisialagogue with less CNS and chronotropic effect than atropine. Does not cross blood–brain barrier or placenta. Unreliable oral absorption. May cause bronchospasm, blurred vision, constipation. Caution with asthma, ulcerative colitis, glaucoma, ileus, or urinary retention
Granisetron (Granisol, Kytril): See 5HT3 Antagonists.
Haloperidol (Haldol)
Indication: Indicated for treatment of schizophrenia. Also used for agitation caused by delirium
Typical dose: Adult: (1) Mild agitation: 0.5–2 mg IV, moderate agitation: 5 mg IV, severe agitation: 10 mg IV. Peds: 3–12 yrs and 15–40 kg, 0.01–0.03 mg/kg/d div q8h (max 0.15 mg/kg/d). Antiemetic: 0.01 mg/kg/dose IV q8–12h
Mechanism: Butyrophenone neuroleptic; dopaminergic (D1 and D2) antagonist. Depresses reticular activating system
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism; renal/biliary elimination
Comments: Causes sedation, tranquility, immobility, antiemesis. IV use common in acute care but not FDA approved. Not for use with dementia-related psychosis. Avoid in Parkinson’s, glaucoma, leukopenia. Associated with extrapyramidal symptoms (rarely including laryngospasm, rx with diphenhydramine) and arrhythmias (torsades de pointes), cardiac arrest at ↑ doses. Monitor ECG for prolonged QT interval. Associated with neuroleptic malignant syndrome (presentation similar to malignant hyperthermia). Lowers seizure threshold
Heparin, Unfractionated (UFH)
Indication: (1) DVT prophylaxis; systemic anticoagulation for (2) thromboembolism, DIC; (3) cardiopulmonary bypass. Also used as (4) catheter lock to maintain patency
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 5,000 units SC q8h, (2) see hospital-specific protocols for infusion dosing and PTT goals, generally load 5,000 units IV, then 15–25 units/kg/hr IV infusion, (3) 300 units/kg IV bolus, monitor and maintain ACT > 400, (4) 100 units/mL, volume depends on catheter. Peds: (1) See hospital-specific protocols for infusion dosing and PTT goals, generally load 50 units/kg IV, then 20 units/kg/h IV infusion, titrate to goal PTT, (2) neonates: 400 units/kg, children: 300 units/kg, monitor and maintain ACT >400, (4) >10 kg: 100 units/mL; <10 kg: 10 units/mL; premature infants: 1 unit/mL, volume depends on catheter
Mechanism: Binds/activates antithrombin III → inactivates thrombin and other proteases (including IX, Xa, XI, XII, thrombin). Net effect prevents cleavage of prothrombin to active thrombin, inhibits conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin, inhibits activation of factor VIII
Clearance: Partial hepatic metabolism, renal excretion
Comments: Infusion requires PTT monitoring and dose titration. Prevents thrombus formation/extension but will not lyse existing clots. Requires ATIII, suspect deficiency and rx with FFP if unable to achieve therapeutic PTT. Enoxaparin is the preferred agent for DVT prophylaxis in arthroplasty, trauma. Contraindicated in severe thrombocytopenia, uncontrollable active bleeding (unless due to DIC). May cause hemorrhage; non-immune (Type 1, within 2 d) and immune-mediated (Type 2, 4–10 d after initial exposure) thrombocytopenia (and thrombosis in Type 2) which can be life-threatening. Adjust dose in hepatic impairment. Reversed by protamine. Caution with lumbar puncture, neuraxial anesthesia including indwelling catheters due to risk of hematoma and neurologic impairment
Highly Active Anti-retroviral Therapy (HAART)
Indication: Treatment of infection by retroviruses, primarily HIV
Comments: Continue whenever possible in perioperative period to minimize increase in viral load and drug resistance. Evidence is sparse, though numerous potential interactions with anesthetic drugs including ↓ fentanyl clearance (ritonavir), ↑ level of meperidine active metabolite (ritonavir), ↑ duration of action of midazolam (saquinavir), prolonged neuromuscular blockade, altered pharmacokinetics of CYP/P450 metabolized drugs, and ↑ mitochondrial toxicity/lactic acidosis when nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) used with propofol. See www.hiv-druginteractions.org or hivinsite.ucsf.edu for more information
Hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ, Microzide): See Diuretics table on page 2H-56.
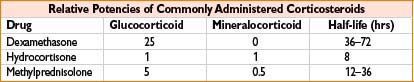
Hydrocortisone (Solu-Cortef)
Indication: (1) Severe acute adrenal insufficiency, (2) perioperative supplementation in patients taking chronic steroids, (3) status asthmaticus, (4) physiologic replacement in chronic adrenal insufficiency
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 100 mg IV, then 200–400 mg IV daily, divided q6h, (2) 25 mg IV at start of procedure, then 100 mg IV over 24 hrs, (3) 1–2 mg/kg q6h, decrease to 0.5–1 mg/kg when stable, (4) 20–30 mg PO daily. Peds: (1) 1–12 mos: 1–2 mg/kg bolus then 50 mg/m2/d infusion or 150–250 mg/d divided q6–8h, (3) 4–8 mg/kg IV × 1 (max 250 mg), then 2 mg/kg/d divided q6h, (4) 0.5–0.75 mg/kg/d PO divided q8h
Mechanism: Corticosteroid with glucocorticoid (prevents/controls inflammation by controlling rate of inflammatory modulator protein synthesis, suppressing migration of inflammatory cells, reversing capillary permeability) and mineralocorticoid (promotes Na+ and H2O retention, K+ excretion) effects
Clearance: In tissues and liver to inactive metabolites, renal excretion
Comments: High doses are generally not recommended as they may cause hypernatremia, hypokalemia, hypertension (mineralocorticoid effect). Dose-dependent association with GI bleeding, secondary infection, psychosis, hyperglycemia, and delayed wound healing. Use lowest effective dose. Use with caution in severe infection, latent TB. With chronic (even topical) use, normal adrenal response can be suppressed as long as 9–12 mos. Consider “stress-dose” supplementation in adrenally suppressed patients undergoing major surgery (adequate dose is unclear, may vary, and may be lower than previously thought)
Hydroxyzine (Vistaril, Atarax)
Indication: Anxiety, itching, nausea/vomiting
Typical dose: Adults: 25–100 mg IM or 50–100 mg PO q6. Peds: >6 yrs 50–100 mg PO daily (divided); <6 yrs 50–100 mg PO daily (divided). Preoperative sedation: 0.5–1 mg/kg IM
Mechanism: H1 receptor antagonist; has muscle relaxant, analgesic, anti-histaminic, antiemetic effects
Clearance: Hepatic (P450) metabolism; renal elimination
Comments: Not for IV use. Chemically unrelated to phenothiazines or benzodiazepines. May cause oversedation; potentiates CNS depressants including meperidine and barbiturates
Indigo Carmine
Indication: Evaluation of urine output and localization of ureteral orifices during urologic procedures
Typical dose: 40 mg IV slowly (5 mL of 0.8% solution), ↓ dose in infants/children to prevent skin discoloration
Mechanism: Rapid glomerular filtration produces blue urine; appears in urine in 10 min (average)
Clearance: Renal
Comments: May cause HTN from α-adrenergic stimulation, lasts 15–30 min after IV dose. Also causes transient false low pulse oximetry readings.
Indocyanine Green (Cardio-green)
Indication: Determining cardiac output, hepatic function, liver blood flow
Typical dose: Adult: 5 mg IV. Children: 2.5 mg IV. Infants: 1.25 mg IV. Max 2 mg/kg. Dilute with provided aqueous solvent to various concentrations (depends on application)
Mechanism: Binds to plasma proteins (albumin), distributes within plasma volume
Clearance: No metabolism, biliary excretion
Comments: Inject rapidly into central circulation for indicator-dilution curves. May cause anaphylaxis; use caution in patients with history of allergy to iodides. Absorption spectra (and therefore results) changed by heparin. Use within 6 hrs of reconstitution. May cause transient false low pulse oximetry readings
Insulin, Regular
Indication: (1) Hyperglycemia; (2) diabetic ketoacidosis; (3) hyperkalemia
Typical dose: (1) Individualized; hospital-specific perioperative bolus and/or infusion protocols are generally available. 0.5–1 units/hr (Type 1 diabetes) or 2–3 units/hr (Type 2 diabetes) is typical starting infusion rate. (2) 0.05–0.2 units/kg/hr for severe hyperglycemia, ↓ when glucose is <300 mg/dL. Consider loading bolus 0.1 unit/kg. (3) 10 units IV (with 50 mL D5W if blood glucose is <250 mg/dL) over 5 min; consider dextrose infusion if dose is repeated
Mechanism: Protein hormone, stimulates glucose uptake by cells; shifts potassium into cells
Clearance: Liver >50%, kidney 30%, tissue/muscle 20%
Comments: Hypoglycemia is dangerous; symptoms of intraoperative hypoglycemia may be misinterpreted as “light” anesthesia or masked by beta blockers. Monitor blood glucose carefully. Mix 1 unit/mL normal saline for infusion. Glycemic goal for critically ill patients is 140–180 mg/dL, although lower range (110–140) may be beneficial if it can be achieved without hypoglycemia; IV infusion of insulin and dextrose is the preferred route in ICU. (Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2011. American Diabetes Association). Infusion tubing absorbs insulin, priming may enhance delivery
Ipratropium Bromide (Atrovent)
Indication: Bronchodilation, especially in chronic treatment of obstructive pulmonary disease
Typical dose: Adult: 500 mcg; Peds <12 yrs: 150–500 mcg nebulized, q20min up to 3 doses
Mechanism: Inhaled anticholinergic
Clearance: Hepatic, renal excretion
Comments: Combine with β2 agonist in acute bronchospasm (solution may be mixed with albuterol). Caution in glaucoma, BPH
Levetiracetam (Keppra)
Indication: (1) Seizures, also used for (2) seizure prophylaxis in traumatic brain injury
Typical dose: (1) 500–1,000 mg IV/PO bid (max 3 g/d), (2) 20 mg/kg over 60 min then 1,000 mg q12 × 7 d
Mechanism: Unknown, may inhibit calcium channels or modulate neurotransmitter release
Clearance: Hepatic enzymatic hydrolysis, renal excretion
Comments: Adjust dose in renal disease. May cause somnolence. Avoid abrupt discontinuation
Levothyroxine (Synthroid, T4)
Indication: (1) Hypothyroidism, (2) myxedema coma, also used for (3) preservation of organ function in brain-dead donors
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 0.1–0.2 mg/d PO titrated to thyroid function tests; for IV use give 50–75% of daily oral dose, (2) 200–500 mcg IV x1, then 100–300 mcg in 24 if needed, (3) 20 mcg IV x1, then 10 mcg/hr infusion. Peds: PO: 0–6 mos: 8–10 mcg/kg/d; 6–12 mos: 6–8 mcg/kg/d; 1–5 yrs: 5–6 mcg/kg/d; 6–12 yrs: 4–5 mcg/kg/d; >12 yrs: 150 mcg/d
Mechanism: Synthetic thyroxine hormone; increases basal metabolic rate, utilization of glycogen store, promotes gluconeogenesis
Clearance: Metabolized in the liver to triiodothyronine (T3, active); eliminated in feces and urine
Comments: Multiple drug interactions including phenytoin (may ↓ levothyroxine levels), warfarin (↑ effect), tricyclic antidepressants (may ↑ toxic potential of both drugs). May cause HTN, arrhythmias, diarrhea, weight loss. Contraindicated with recent myocardial infarction, thyrotoxicosis, or uncorrected adrenal insufficiency. Reduces vasopressor requirement in organ donors
Magnesium Sulfate (MgSO4)
Indication: (1) Prevention and treatment of eclamptic seizures, (2) hypomagnesemia, (3) torsades de pointes. Also used for ventricular ectopy, preterm labor management, (4) pediatric asthma
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 4–5 g IV load (may give 8–10 mg IM simultaneously), then 1–3 g/hr infusion titrated to serum level and avoidance of toxicity, (2) 1–2 g over 15 min, then 1 g/hr until serum level normal (generally 2–6 g), (3) 1–2 g over 5–10 min. Peds: (1) 25–50 mg IV. (2) 25–50 mg IV over 10–15 min
Mechanism: Enzymatic cofactor, important role in neurotransmission and muscular excitability; bronchial smooth muscle relaxation
Clearance: Renal excretion
Comments: Causes CNS depression, anticonvulsant effect, blocks peripheral neuromuscular transmission (monitor deep tendon reflexes, respiratory rate, mental status in high-dose therapy). Rx overdose with calcium chloride or gluconate. Dose cautiously in renal impairment. May cause hypotension, particularly if infused rapidly. Potentiates neuromuscular blockade and predisposes to uterine atony
Mannitol (Osmitrol)
Indication: Increased intracranial pressure, oliguric acute renal injury, promotion of urinary excretion of toxic materials
Typical dose: 0.25–2 g/kg over 30–60 min (in acutely elevated ICP can bolus 12.5–25g over 5–10 min). Max 1–2 g/kg over 6 hrs
Mechanism: Increases serum osmolarity, ↓ cerebral edema. Freely filtered by glomerulus, induces osmotic diuresis
Clearance: Rapid renal excretion
Comments: Avoid in anuria/severe renal disease, pulmonary edema, active intracranial bleeding, dehydration/hypovolemia. Causes transient expansion of intravascular volume; caution in hypertension or heart failure. Rapid administration may cause vasodilation, hypotension. Use filter on IV tubing, do not use solution if crystals are present
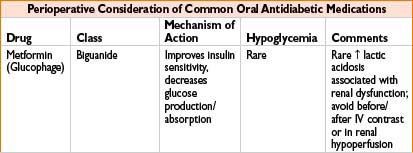
Metformin (Glucophage): See Oral Antidiabetics table on page 2H-64.
Methylergonovine (Methergine)
Indication: Uterine atony and postpartum hemorrhage
Typical dose: Not for IV use. 0.2 mg IM q15–20 min (max 4 doses)
Mechanism: Synthetic ergot alkaloid, causes dose-dependent ↑ in uterine contraction/tone, likely through α-adrenergic receptors
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism
Comments: Must be refrigerated; administer only if clear/colorless. α-adrenergic effect may cause peripheral vasoconstriction and potentially severe hypertension, especially when used with other vasopressor agents. Avoid in hypertension/preeclampsia, ischemic heart disease, pulmonary hypertension. May cause nausea
Methylene Blue (Methylthionine Chloride, Urolene Blue)
Indication: (1) Methemoglobinemia, also used for (2) vasoplegic syndrome post-cardiopulmonary bypass, refractory septic shock
Typical dose: (1) 1–2 mg/kg (0.1–0.2 mL) IV over 5 min, may repeat in 1 hr. Give slowly to avoid local ↑ concentration and promotion of additional methemoglobin, (2) 1.5 mg/kg
Mechanism: Increases erythrocyte reduction of methemoglobin to hemoglobin at low doses, may cause formation of methemoglobin at high doses. Potent reversible MAO-A inhibitor, inhibits MAO-B at high doses. Inhibits nitric oxide/cGMP pathway
Clearance: Tissue reduction; urinary and biliary elimination
Comments: Causes transient false low pulse oximeter readings and blue coloration of blood (alert surgeon/perfusionist of use in cardiac surgery), urine, skin. Contraindicated in G6PD deficiency; extreme caution in pulmonary hypertension and acute lung injury/ARDS. Avoid with concurrent use of pulmonary vasodilators, or nitrates for coronary vasodilation due to competing mechanism of action. Extravasation may cause necrosis. Risk of serotonin syndrome, avoid co-administration of serotonergic psychiatric drugs if possible. May cause nausea, diaphoresis, confusion. Facilitates pressor weaning and ↑ arterial pressure in septic shock, unknown effect on outcomes (2–3 hrs after bolus dose, some studies use continuous infusion). Sparsely studied but appears to improve vasoplegia and mortality after cardiac surgery, may have role in vasoplegic syndrome in anaphylaxis, liver transplant, other settings
Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol)
Indication: (1) Allergic reactions, conditions treated with immunosuppression. Also used in (2) acute spinal cord injury, (3) induction of immunosuppression in solid organ transplant, (4) status asthmaticus
Typical dose: Adult: (1) 10–40 mg/d PO, may divide q6–12 or 10–250 mg IV/IM up to 6 doses/d, depending on condition treated, (2) 30 mg/kg over 15 min, then 5.4 mg/kg/hr for 24–48 hrs. Must start within 8 hrs of injury, (3) 500–100 mg as directed by surgeon. Peds: Varies by indication: (1) 0.5–2 mg/kg/d, divide q12h IV/PO/IM, (2) 2 mg/kg/d load, then 2 mg/kg/d divided q6h IV/IM
Mechanism: See hydrocortisone
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism; renal excretion
Comments: Potent glucocorticoid, relatively ↓ mineralocorticoid activity (see table accompanying hydrocortisone). As with other corticosteroids, dose-dependent association with GI bleeding, secondary infection, psychosis, hyperglycemia, and delayed wound healing. Use with caution with ↑ doses in severe infection, latent TB Use lowest effective dose
Metoclopramide (Reglan)
Indication: Treatment of gastroparesis, antiemetic
Typical dose: Adult: 10–20 mg IV (near end of procedure for PONV prophylaxis) q6h. Peds: 6–14 yrs: 2.5–5 mg IV. <6 yrs: 0.1 mg/kg IV
Mechanism: Peripheral cholinomimetic, ↑ lower esophageal sphincter tone and upper GI motility/peristalsis without ↓ gastric pH. Dopamine antagonist in chemoreceptor trigger zone
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism, renal excretion
Comments: May cause extrapyramidal symptoms (i.e., acute dystonic reactions with involuntary muscle movement, potential laryngospasm) → rx with diphenhydramine. Rarely associated with neuroleptic malignant syndrome (presentation similar to malignant hyperthermia) and irreversible tardive dyskinesia. Rapid injection may cause anxiety. Avoid in intestinal obstruction, Parkinson’s, pheochromocytoma; caution in hypertension, recent GI anastomoses, and with other drugs that can cause EPS. Transient ↑ in serum aldosterone → fluid retention (caution in CHF, cirrhotic patients)
Nitric Oxide, Inhaled (NO, iNO, INOmax)
Indication: Neonatal hypoxic respiratory failure (congenital cardiac defects and pulmonary hypertension); also used for hypoxic respiratory failure, acute pulmonary hypertension and right heart failure in adults
Typical dose: Adult: 20–40 ppm (80 ppm also studied). Peds: 20 ppm. Wean slowly
Mechanism: Selective relaxation of pulmonary vasculature, improved arterial oxygenation
Clearance: Combines with oxyhemoglobin to produce methemoglobin and nitrate (nitrate quickly renally excreted)
Comments: Requires special equipment to administer. Do not discontinue abruptly. Little systemic hemodynamic effect. May cause ↑ bleeding by inhibition of platelet aggregation; dose-dependent methemoglobinemia especially with other nitrates (sodium nitroprusside, nitroglycerin). Caution in left ventricular dysfunction, may cause pulmonary edema. Expensive, adult clinical outcomes do not show clear benefit
Octreotide (Sandostatin)
Indication: (1) Secretory neuroendocrine tumors (e.g., carcinoid), also used for (2) esophageal variceal and upper GI bleeding
Typical dose: (1) 100–600 mcg/d SC q6–12h, (2) 50 mcg IV bolus, then 25–50 mcg/hr × 1–5 d
Mechanism: Somatostatin analogue (suppresses release of serotonin, gastrin, vasoactive intestinal peptide, insulin, glucagon, thyroid stimulating hormone, and secretin)
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism, renal excretion
Comments: May cause nausea, decreased GI motility, hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, cholelithiasis, cholestatic hepatitis, hypothyroidism, arrhythmia including bradycardia, conduction abnormalities
Omeprazole (Prilosec)
Indication: GERD, GI ulcer, esophagitis, GI bleed prophylaxis
Typical dose: Adults: 20–40 mg PO daily. Peds: 0.6–0.7 mg/kg/d, max 3.3 mg/kg/d
Mechanism: Proton pump inhibitor, binds to H+/K+ ATPase (proton pump) in gastric parietal cells, blocking acid secretion
Clearance: Hepatic via P450 enzymes, renal elimination
Comments: Onset of action within 1 hr, peak effect within 2 hrs. Inhibits some cytochrome P450 enzymes. For intravenous use, single enantiomer esomeprazole (Nexium) available in US
Ondanestron (Zofran): See 5HT3 Antagonists.
ORAL ANTIDIABETICS
Oxytocin (Pitocin)
Indication: (1) Treatment and (2) prophylaxis of postpartum hemorrhage, also used for labor induction
Typical dose: (1) 10–40 units IV in 1 L electrolyte solution, run at rate necessary to control atony, (2) 1–3 units IV bolus if low risk of uterine atony (e.g., elective caesarean delivery). Higher (5–10 units) or repeat doses may be required in prolonged or oxytocin augmented labor due to down-regulation of receptors
Mechanism: Uterine stimulant, improves postpartum uterine atony
Clearance: Rapidly degraded in liver and kidneys
Comments: Structural similarity to antidiuretic hormone. May cause hypotension (caution in hypovolemia), tachycardia, nausea/vomiting, flushing, headache. Rarely, large doses may cause water retention, hyponatremia. In refractory atony with hemorrhage, consider other uterotonics: Methylergonovine, prostaglandins F2a (carboprost) and E1 (misoprostol)
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Indication: (1) Status epilepticus; seizure prophylaxis, (2) arrhythmias (digoxin induced)
Typical dose: Adult: (1) Load 10–20 mg/kg IV at <50 mg/min (up to 1,000 mg cautiously, with ECG monitoring); maintenance: 300 mg/d or 5–6 mg/kg/d div q8h; for neurosurgical prophylaxis, 100–200 mg IV q4h (at <50 mg/min). Use of prodrug fosphenytoin facilitates rapid loading in emergent situations (15–20 mg/kg IV at 100–150 mg/min). (2) 1.5 mg/kg or 50–100 mg IV at <50 mg/min q5–15min until dysrhythmia is abolished, side effects occur, or a maximal dose of 10–15 mg/kg is given. Peds: Load 15–20 mg/kg mg IV; maintenance: Age specific
Mechanism: Anticonvulsant effect via membrane stabilization, inhibiting depolarization. Antidysrhythmic effect, blocking calcium uptake during repolarization prolonging refractory period
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism; renal elimination (enhanced by alkaline urine)
Comments: Contraindicated in heart block, sinus bradycardia. May cause nystagmus, diplopia, ataxia, drowsiness, gingival hyperplasia, GI upset, hyperglycemia, or hepatic P450 enzyme induction. Asian patients with HLA-B*1502 have ↑ incidence severe dermatologic reaction (e.g., TEN, Stevens–Johnson syndrome). IV bolus may cause bradycardia, hypotension, cardiorespiratory arrest, or CNS depression. Venous irritant. Crosses the placenta. Significant variation in dose needed to achieve therapeutic concentration of 7.5–20.0 mcg/mL; measuring unbound levels may be helpful in patients with renal failure or hypoalbuminemia. Caution in renal and hepatic disease
Phosphorus (Phospho-soda, neutra-phos)
Indication: Hypophosphatemia
Typical Dose: 250–500 mg PO tid or 0.08–0.15 mmol/kg IV over 6–12 hrs
Mechanism: Electrolyte replacement
Clearance: Renal excretion (and reabsorption)
Comments: Risks of rapid IV infusion include hypocalcemia, hypotension, muscular irritability, calcium deposition, deteriorating renal function, hyperkalemia. Orders for IV phosphate preparations should be written in mmol (1 mmol = 31 mg). Use with caution in patients with cardiac disease and renal insufficiency. Do not give with magnesium- and aluminum-containing antacids or sucralfate, which can bind with phosphate. Causes osmotic diarrhea, may be used as bowel prep
Physostigmine (Antilirium)
Indication: Anticholinergic toxicity
Typical dose: Adult: 0.5–1 mg IV/IM (max rate 1 mg/min, max dose 2 mg). Peds: 0.02 mg/kg (max rate 0.5 mg/min, max dose 2 mg), repeat q5–10min if needed
Mechanism: Prolongs central and peripheral cholinergic effects; inhibits cholinesterase
Clearance: Plasma esterases
Comments: Crosses blood–brain barrier, therefore useful for CNS anticholinergic toxicity (symptoms include delirium, somnolence, flushing, dry mouth, mydriasis, fever; occurs with administration of drugs including atropine and scopolamine, other tranquilizers and antihistamines). May cause bradycardia, tremor, convulsions, hallucinations, CNS depression, mild ganglionic blockade, or cholinergic crisis. Antagonized by atropine. Contains sulfite. Avoid in asthma, cardiovascular disease, intestinal/urologic obstruction
Pioglitazone (Actos): See Oral Antidiabetics table on page 2H-64.
Potassium Chloride (KCl, KDur)
Indication: Hypokalemia
Typical dose: Adult: 20–40 mEq IV or PO q6–12, adjust dose to serum potassium levels. Peds: 0.5–2 mEq/kg PO q12h, 0.5 mEq/kg/hr for 1–2 hrs (monitor closely)
Mechanism: Crucial for multiple physiologic processes including nerve conduction, myocardial contraction
Clearance: Renal
Comments: Indicated for hypokalemia, digoxin toxicity. IV bolus administration may cause cardiac arrest. Generally infuse at rate ≤10 mEq/hr; may infuse 20 mEq/hr with continuous ECG monitoring; can ↑ to max 40 mEq/hr in urgent situations (serum level <2 mEq/L and/or ECG changes). Central line preferred route for concentrated solutions. May cause pain/phlebitis at injection site. Use potassium acetate instead in metabolic/hyperchloremic acidosis. PO administration may cause nausea, vomiting, delayed gastric emptying. Use caution in renal failure due to ↓ excretion capacity
Prasugrel (Effient)
Indication: Acute coronary syndrome, ↓ thrombotic cardiovascular events (including stent thrombosis)
Typical dose: 60 mg PO load, then 10 mg PO daily with aspirin
Mechanism: Thienopyridine, irreversible inhibition of platelet activation/aggregation through binding to ADP receptors
Clearance: Prodrug metabolized in intestine to active metabolite
Comments: Less inter-individual variability in effect than clopidogrel. Discontinuation is associated with ↑ cardiovascular events, especially with recent acute coronary syndrome. If possible, discontinue 7 d before surgery. Avoid neuraxial anesthesia for 7–10 d after discontinuation
Prochlorperazine (Compazine)
Indication: (1) Severe nausea and vomiting, also used for psychosis
Typical dose: Adults: (1) 2.5–10 mg IV q3–4h or 5–10 mg PO q6–8h (max 40 mg/d). Peds: (1) 2.5 mg PO (max 7.5 mg/d if >2 yrs and 9–14 kg; max 10 mg/d if >2 yrs and 14–18 kg; max 15 mg/d if 18–39 kg, max 20 mg/d if >39 kg)
Mechanism: Phenothiazine with more anti-dopaminergic potency than promethazine
Clearance: Hepatic
Comments: May cause hypotension, excess sedation, extrapyramidal symptoms (acute dystonic reaction, rx with diphenhydramine); rarely associated with irreversible tardive dyskinesia or neuroleptic malignant syndrome (presentation similar to malignant hyperthermia). Not for use in children <2 yrs, Parkinson’s disease, or dementia-related psychosis
Promethazine (Phenergan)
Indication: (1) Rescue treatment in postoperative nausea and vomiting, (2) sedation, adjunct in anaphylaxis
Typical dose: Adults: (1) 6.25–12.5 mg IV/IM/PO, (2) 25–50 mg IV/IM/PO. Peds: 0.25–1 mg/kg PO/IV/IM q4–6h
Mechanism: Phenothiazine; potent antagonist of histamine (H1), also antagonizes dopaminergic, α-adrenergic, muscarinic receptors
Clearance: Hepatic
Comments: May cause sedation and respiratory depression, especially with use of narcotics or barbiturates (use lowest effective dose for PONV). Contraindicated in children <2 yrs due to risk of fatal respiratory depression. Avoid in Parkinson’s, glaucoma, BPH. Caution in pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, seizures, bone-marrow depression, sulfite allergy, elderly. Severe tissue damage/necrosis with extravasation or intra-arterial injection. May cause extrapyramidal symptoms (rx with diphenhydramine); rarely associated with neuroleptic malignant syndrome (presentation similar to malignant hyperthermia). Administer slowly to minimize risk of hypotension
Prostaglandin E1 (Alprostadil, Prostin VR)
Indication: Ductal-dependent and flow-restricting congenital cardiac defects (temporarily maintains patent ductus arteriosus until surgical correction)
Typical dose: Neonates: Starting dose 0.05–0.1 mcg/kg/min. Titrate to effect (typical 0.1–0.4 mcg/kg/min, max 0.6 mcg/kg/min). Usual dilution: 500 mcg/99 mL of NS or D5W = 5 mcg/mL
Mechanism: Vasodilation, inhibits platelet aggregation, vascular smooth muscle relaxation, and uterine and intestinal smooth muscle relaxation
Clearance: Rapid pulmonary metabolism; renal excretion
Comments: Used in pulmonary atresia/stenosis, tricuspid atresia, tetralogy of Fallot, coarct/interruption of aorta, transposition of great vessels. May cause hypotension, apnea (10–12%), flushing, and bradycardia. Decrease to lowest effective dose after observing ↑ in PaO2 (in restricted pulmonary blood flow) or ↑ in pH, systemic blood pressure (in restricted systemic flow)
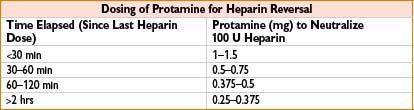
Protamine Sulfate
Indication: (1) Heparin neutralization, (2) enoxaparin overdose
Typical dose: (1) Time elapsed since last heparin dose (see the table below); based on ACT: 1.3 mg/100 U heparin calculated from ACT. Give via slow IV, ≤5 mg/min. (2) ∼1 mg protamine/1 mg enoxaparin
Mechanism: Heparin antagonist. Polybasic compound combines with polyacidic heparin to form stable, inactive salt
Clearance: Fate of the heparin–protamine complex is unknown
Comments: May cause anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid reaction, severe pulmonary hypertension (particularly with rapid infusion after cardiopulmonary bypass), myocardial depression and peripheral vasodilation with sudden hypotension (secondary to histamine release) or bradycardia. Protamine–heparin complex antigenically active (particularly in pts receiving procaine and with fish allergy). Transient reversal of heparin may be followed by rebound heparinization. Can cause anticoagulation if given in excess relative to amount of circulating heparin (significance controversial). Monitor response with activated partial thromboplastin time or activated clotting time 5–15 min after dose. Only partially reverses enoxaparin
Recombinant Factor VIIa (Novoseven): See Factor VIIa
Rosiglitazone (Avandia): See Oral Antidiabetics table on page 2H-64.
Scopolamine Patch (Transderm Scóp)
Indication: Prevention of postoperative nausea/vomiting
Typical dose: Adult: 1.5 mg/72 hrs. Peds: Not available. Patch cannot be cut. Apply to dry skin behind ear
Mechanism: Anticholinergic with peripheral and central muscarinic antagonism. May block transmission from vestibular nuclei to higher CNS centers and/or from reticular formation to vomiting center
Comments: Most effective for prophylactic use (instruct patients to apply night before and remove 24 hrs after surgery). Use care when handling patch: Contact with eyes may cause long-lasting mydriasis and cycloplegia. Common side effects include blurred vision, dizziness, dry mouth; may cause sedation, urinary retention, confusion. Avoid in glaucoma, seizures, intestinal obstruction; use with caution in elderly patients
Scopolamine Injection (Hyoscine)
Indication: Pre-anesthetic sedation, antisialagogue, anesthetic adjunct
Typical dose: Adult: 0.3–0.6 mg IV/IM q6–8h. Peds: 6 mcg/kg/dose IM/IV/SC < q6–8h, max 0.3 mg/dose
Mechanism: Anticholinergic, antimuscarinic; crosses blood–brain barrier
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism; renal elimination
Comments: May be used to provide amnesia during surgery in severe hypotension (i.e., exploratory trauma surgery with hemorrhagic shock). Amnesia unpredictable, combine with benzodiazepines and other anesthetic agents when feasible. Causes bradycardia at low doses, tachycardia, mydriasis (use caution interpreting pupillary examination). May cause central anticholinergic syndrome with delirium, restlessness, confusion, sedation; physostigmine 1–3 mg antagonizes CNS effects
Sildenafil (Viagra, Revatio)
Indication: (1) Pulmonary arterial hypertension. Also indicated in erectile dysfunction
Typical dose: 20 mg PO tid, 10 mg IV bolus tid
Mechanism: Inhibits phosphodiesterase Type 5, increasing cGMP to allow smooth muscle relaxation (pulmonary vasodilation)
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism (CYP3A4), biliary (83%) and renal (13%) excretion
Comments: Used in management of severe perioperative pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular dysfunction. Has both pulmonary and systemic vasodilatory effect. Avoid in hypotension, hypovolemia, autonomic dysfunction, pulmonary veno-occlusive disease. Potential for severe, refractory hypotension with organic nitrates (nitroglycerin, nitroprusside, isosorbide)
Sitagliptin (Januvia): See Oral Antidiabetics table on page 2H-64.
Spironolactone (Aldactone): See Diuretics table on page 2H-56.
THAM: See Tromethamine.
Tissue Plasminogen Activator (Alteplase, Activase, Tpa)
Indication: (1) Lysis of coronary arterial thrombi in hemodynamically unstable patients with acute MI, (2) management of acute massive PE in adults, (3) acute embolic stroke. Also used in (4) central venous catheter occlusion.Typical dose: (1) Load: 15 mg (30 mL of the infusion) IV over 1 min followed by 0.75 mg/kg (not to exceed 50 mg) given over 30 min. Maintenance: 0.5 mg/kg IV up to 35 mg/hr for 1 hr immediately following the loading dose. Total dose not to exceed 100 mg, (2) 100 mg IV continuous infusion over 2 hrs, (3) total dose of 0.9 mg/kg IV (maximum 90 mg); administer 10% as a bolus and the remainder over 60 min, (4) 2 mg in 2 mL instilled into occluded catheter, allow 30–120 min dwell time and may redose at 120 min. Remove via aspiration
Mechanism: Tissue plasminogen activator, generates plasmin and produces fibrinolysis
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism, renal excretion
Comments: Doses >150 mg have been associated with ↑ intracranial hemorrhage. Contraindicated with active internal bleeding, history of hemorrhagic stroke, intracranial neoplasm, aneurysm, or recent (within 2 mos) intracranial or intraspinal surgery, or trauma. Should be used with caution in pts who have received chest compressions or other anticoagulants and in hypertension, cerebrovascular disease, severe neurologic deficit, severe renal/hepatic dysfunction. Avoid IM injections, procedures involving arterial puncture (if possible) and central venous line placement at internal jugular/subclavian sites in patients who have recently received TPA
Tranexamic Acid (Cyklokapron)
Indication: (1) Hemophilia. Also used in cardiopulmonary bypass, spine surgery, liver transplant, (2) trauma
Typical dose: (1) 10 mg/kg q6–8h (up to 8 d post-procedure), (2)1 g over 10 min, then 1 g over 8 hrs
Mechanism: Lysine analog. Inhibits fibrinolysis; competitive inhibitor of plasminogen inactivation, antiplasmin activity at high doses
Clearance: Renal excretion (>90% unchanged)
Comments: Mechanism similar to aminocaproic acid. May cause headache, visual changes, hypotension with rapid injection. Reduce dose in renal failure. Associated with ↓ mortality in bleeding trauma patients when given within 3 hrs of injury (CRASH-2 trial, Lancet. 2010; Jul 3;376(9734):23–32)
Tromethamine (THAM Acetate)
Indication: Metabolic acidosis associated with cardiac bypass surgery and cardiac arrest
Typical dose: mL of (0.3 M) solution = Body Weight (kg) x Base Deficit (mEq/L) × 1.1, given by IV infusion
Mechanism: Alkalinizing agent/organic buffer (pH 8.6). Actively binds H+ ions. Binds not only cations of fixed or metabolic acids, but also hydrogen ions of carbonic acid, thus ↑ bicarbonate anion (HCO3−)
Clearance: Renal
Comments: Unlike bicarbonate, does not raise pCO2. May be used in mixed respiratory/metabolic acidosis along with assisted ventilation. Also acts as an osmotic diuretic, increasing urine flow, urinary pH, and excretion of fixed acids, carbon dioxide and electrolytes. Avoid use in uremia, anuria (↓ excretion, potential hyperkalemia). Large doses may depress ventilation (↑ pH, ↓ CO2). May cause severe tissue damage if extravasation occurs, hypoglycemia
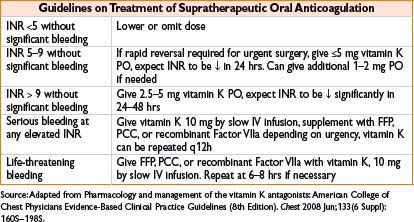
Vitamin K (Phytonadione, AquaMEPHYTON)
Indication: Indicated for deficiency of vitamin K–dependent clotting factors, reversal of warfarin anticoagulation
Typical dose: See table, do not exceed 1 mg/min when giving IV infusion
Mechanism: Vitamin K is required for synthesis of clotting factors II, VII, IX, X
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism
Comments: INR may decrease within 4 hrs, effects peak at 24–48 hrs; high doses provide rapid reversal though make pt refractory to further oral anticoagulation (up to 7 d after 10 mg dose). May fail with hepatocellular disease. Rapid IV bolus can cause profound hypotension, fever, diaphoresis, bronchospasm, fatal anaphylaxis, and pain at injection site. Reserve IV administration for emergency use (serious or life-threatening bleeding, INR >20)
Warfarin (Coumadin)
Indication: Chronic anticoagulation in deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, atrial fibrillation, valve replacement
Typical dose: 2–15 mg/d (typically start 5 mg PO qd unless genotype available), individualize by monitoring INR (goal varies with indication)
Mechanism: Interferes with utilization of vitamin K by the liver and inhibits synthesis of factors II, VII, IX, X, proteins C & S, prothrombin
Clearance: Hepatic metabolism (influenced by P450 genetics, testing available); renal elimination
Comments: Narrow therapeutic range but varies required dose widely across patients, affected by many factors (diet, multiple drug interactions) within individuals. May cause fatal bleeding, skin necrosis. Contraindicated in severe renal or hepatic disease, GI ulcers, neurosurgical procedures, malignant HTN, pregnancy (teratogenic). Thrombostatic only, no lysis of existing thrombus
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree








