24. DiGeorge Syndrome
Definition
DiGeorge syndrome is a congenital disorder involving hypoplasia or aplasia of the thymus and parathyroid glands secondary to defective development of the third and fourth pharyngeal pouches.
Incidence
DiGeorge syndrome occurs very sporadically. The prevalence is the subject of much debate; however, current estimates of the incidence range from 1:4000 to 1:6395. Male to female ratio is 1:1.
Etiology
The anomaly results from deletion of the DiGeorge syndrome chromosome region (DGCR), represented as deletion on chromosome 22q11.2.
Conditions Associated with DiGeorge Syndrome
CHARGE Association
Coloboma of the iris, choroid, and/or microphthalmia
Heart defect
Atresia of the choanae
Retarded growth and development
Genitourinary abnormalities (cryptorchidism, microphallus, hydronephrosis)
Ear defects associated with deafness
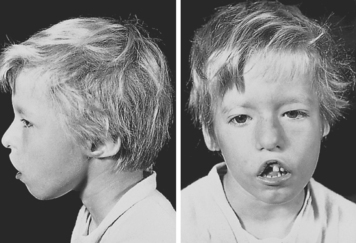 |
| DiGeorge Syndrome. Facial anomalies associated with DiGeorge syndrome. Note the wide-set eyes, low-set ears, and shortened structure of the upper lip. |
Signs and Symptoms
Cardiac
• Aberrant right subclavian artery
• Right aortic arch
• Tetralogy of Fallot
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





