29 Chest injury is a contributing factor in over half of all deaths from trauma. Mortality from an isolated chest injury is in the range of 4–8%. In the context of multiple organ involvement this rises to over 35%. It is therefore essential that pre-hospital care teams are able to assess rapidly and manage life-threatening chest injuries. In the pre-hospital care setting, it may be difficult to elicit and witness ‘textbook signs’ as injuries are often evolving and may not be fully established. Thoracostomy involves making an incision in the pleural cavity. It may be used as the first step in the placement of a formal intercostal drain (tube thoracocentesis) or on its own to drain the pleura (simple thoracostomy). The advantages and disadvantages of each of the procedures is summarised in Table 29.1. Simple thoracostomy is performed more frequently in the pre-hospital setting. Table 29.1 Advantages and disadvantages of tube thoracocentesis and simple thoracostomy
Chest techniques
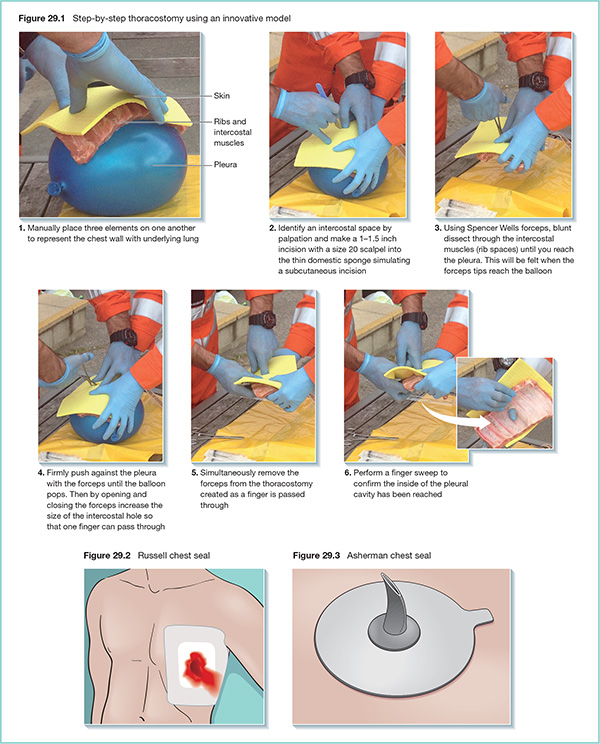
Thoracostomy
Tube thoracocentesis
Simple thoracostomy
Advantages
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree

 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access






