![]() Confirmation of the diagnosis of obstructive uropathy in patients suspected of ureteral colic
Confirmation of the diagnosis of obstructive uropathy in patients suspected of ureteral colic
![]() Abdominal or flank pain
Abdominal or flank pain
![]() Hematuria
Hematuria
![]() Groin pain
Groin pain
![]() Acute urinary retention
Acute urinary retention
![]() Known or suspected acute renal failure
Known or suspected acute renal failure
![]() Laboratory evidence of renal failure
Laboratory evidence of renal failure
![]() Oliguria or anuria
Oliguria or anuria
![]() Painless hematuria or proteinuria
Painless hematuria or proteinuria
![]() Suspected renal abscess
Suspected renal abscess
![]() Infected urine with fever and abdominal or flank pain
Infected urine with fever and abdominal or flank pain
![]() Suspected or known abdominal trauma
Suspected or known abdominal trauma
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() None
None
RISKS/CONSENT ISSUES
![]() Allergy to the ultrasonography gel
Allergy to the ultrasonography gel
LANDMARKS
![]() The right kidney is usually located inferior and posterior to the liver
The right kidney is usually located inferior and posterior to the liver
![]() The left kidney is located inferior to the spleen
The left kidney is located inferior to the spleen
![]() The bladder should be imaged in the suprapubic region
The bladder should be imaged in the suprapubic region
TECHNIQUE
![]() A 3.5-MHz probe is commonly suitable for most adults, although a 5.0-MHz probe can be used in patients with a thinner body habitus and in children
A 3.5-MHz probe is commonly suitable for most adults, although a 5.0-MHz probe can be used in patients with a thinner body habitus and in children
![]() The Right Kidney
The Right Kidney
![]() With the patient supine, start at the midaxillary line at the level of the lower ribs holding the probe in the longitudinal axis or slightly oblique and scan laterally until the sagittal view of the hepatorenal space (Morison pouch) and the right kidney are visible
With the patient supine, start at the midaxillary line at the level of the lower ribs holding the probe in the longitudinal axis or slightly oblique and scan laterally until the sagittal view of the hepatorenal space (Morison pouch) and the right kidney are visible
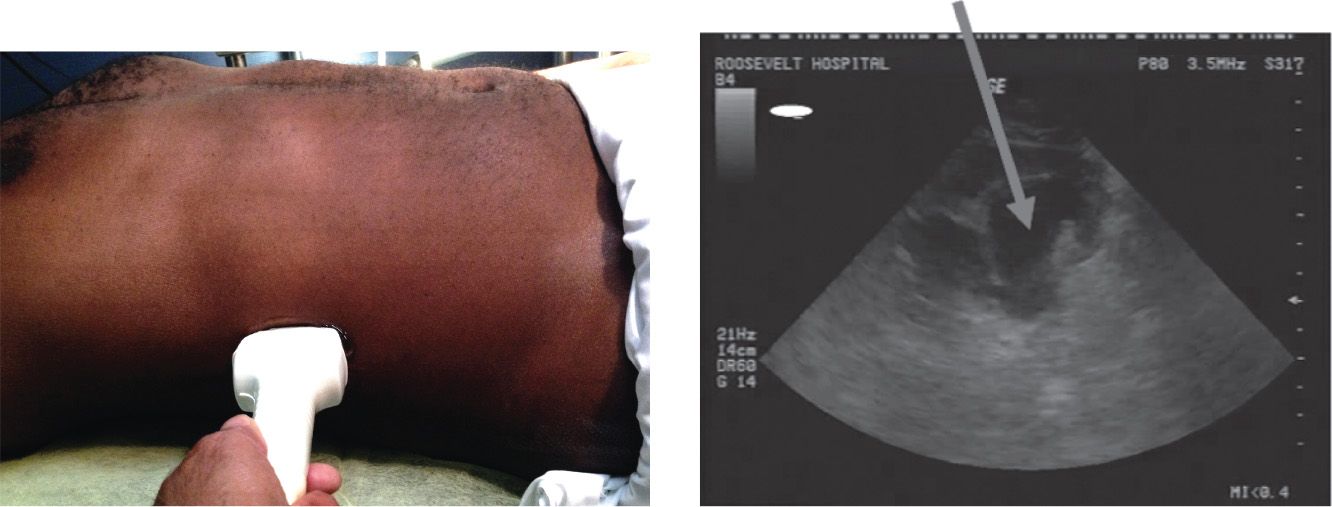
![]() Rotate the probe 90 degrees to obtain a transverse image of the kidney. Move the probe superiorly and inferiorly to locate the renal hilum and visualize the full extent of the parenchyma (FIGURE 40.1).
Rotate the probe 90 degrees to obtain a transverse image of the kidney. Move the probe superiorly and inferiorly to locate the renal hilum and visualize the full extent of the parenchyma (FIGURE 40.1).
![]() The Left Kidney
The Left Kidney
![]() The left kidney is most easily located by placing the probe hand against the bed while scanning the left flank at the posterior axillary line at the level of the lower ribs
The left kidney is most easily located by placing the probe hand against the bed while scanning the left flank at the posterior axillary line at the level of the lower ribs
![]() Rotate the probe 90 degrees to obtain a transverse view of the left kidney
Rotate the probe 90 degrees to obtain a transverse view of the left kidney
![]() The Bladder
The Bladder
![]() The bladder is best imaged when it is moderately filled at the time of examination
The bladder is best imaged when it is moderately filled at the time of examination
![]() Place the probe suprapubically in the transverse plane. Angle the probe toward the patient’s feet. Color Doppler techniques can be used over the trigone area to verify the presence of ureteral flow jets indicating urine flow into the bladder.
Place the probe suprapubically in the transverse plane. Angle the probe toward the patient’s feet. Color Doppler techniques can be used over the trigone area to verify the presence of ureteral flow jets indicating urine flow into the bladder.
![]() Rotate the probe 90 degrees to obtain a sagittal view
Rotate the probe 90 degrees to obtain a sagittal view
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree