![]() To assess for the absence of lung sliding, suggestive of a pneumothorax, in the following conditions:
To assess for the absence of lung sliding, suggestive of a pneumothorax, in the following conditions:
![]() Blunt thoracoabdominal trauma
Blunt thoracoabdominal trauma
![]() Penetrating thoracoabdominal trauma
Penetrating thoracoabdominal trauma
![]() Unexplained hypotension
Unexplained hypotension
![]() To assess for the presence of pleural fluid, suggestive of a hemothorax, in the following conditions:
To assess for the presence of pleural fluid, suggestive of a hemothorax, in the following conditions:
![]() Blunt thoracoabdominal trauma
Blunt thoracoabdominal trauma
![]() Penetrating thoracoabdominal trauma
Penetrating thoracoabdominal trauma
![]() Unexplained hypotension
Unexplained hypotension
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() If the EFAST examination delays a patient’s transport to the operating room
If the EFAST examination delays a patient’s transport to the operating room
![]() Theoretical allergy to the ultrasound gel
Theoretical allergy to the ultrasound gel
ADVANTAGES
![]() Noninvasive
Noninvasive
![]() No sedation required
No sedation required
![]() Performed at the bedside amidst simultaneous resuscitative efforts
Performed at the bedside amidst simultaneous resuscitative efforts
![]() Does not require transportation to the radiology suite
Does not require transportation to the radiology suite
![]() Serial examinations may be performed with changes in symptoms or hemodynamics
Serial examinations may be performed with changes in symptoms or hemodynamics
LANDMARKS
![]() Anterior Thorax
Anterior Thorax
![]() The apical midclavicular line in the sagittal plane; transducer marker positioned cephalad
The apical midclavicular line in the sagittal plane; transducer marker positioned cephalad
![]() Lateral Thorax
Lateral Thorax
![]() The lateral thorax in the axillary region; transducer marker positioned obliquely and cephalad
The lateral thorax in the axillary region; transducer marker positioned obliquely and cephalad
![]() Pleural (Right: Hepatorenal and Left: Splenorenal)
Pleural (Right: Hepatorenal and Left: Splenorenal)
![]() Transducer placed in the axillary line in the coronal plane at the level of 8th and 11th ribs; anterior axillary line on the right and posterior axillary line on the left, with the diaphragm as a landmark; transducer marker positioned toward the axilla.
Transducer placed in the axillary line in the coronal plane at the level of 8th and 11th ribs; anterior axillary line on the right and posterior axillary line on the left, with the diaphragm as a landmark; transducer marker positioned toward the axilla.
TECHNIQUE
![]() The EFAST standard views in addition to the basic FAST examination:
The EFAST standard views in addition to the basic FAST examination:
![]() Bilateral anterior thorax
Bilateral anterior thorax
![]() Bilateral lateral thorax
Bilateral lateral thorax
![]() Bilateral pleural spaces
Bilateral pleural spaces
![]() Anterior Thorax
Anterior Thorax
![]() Place the transducer in the second or third intercostal space in the midclavicular line
Place the transducer in the second or third intercostal space in the midclavicular line
![]() The indicator should be cephalad
The indicator should be cephalad
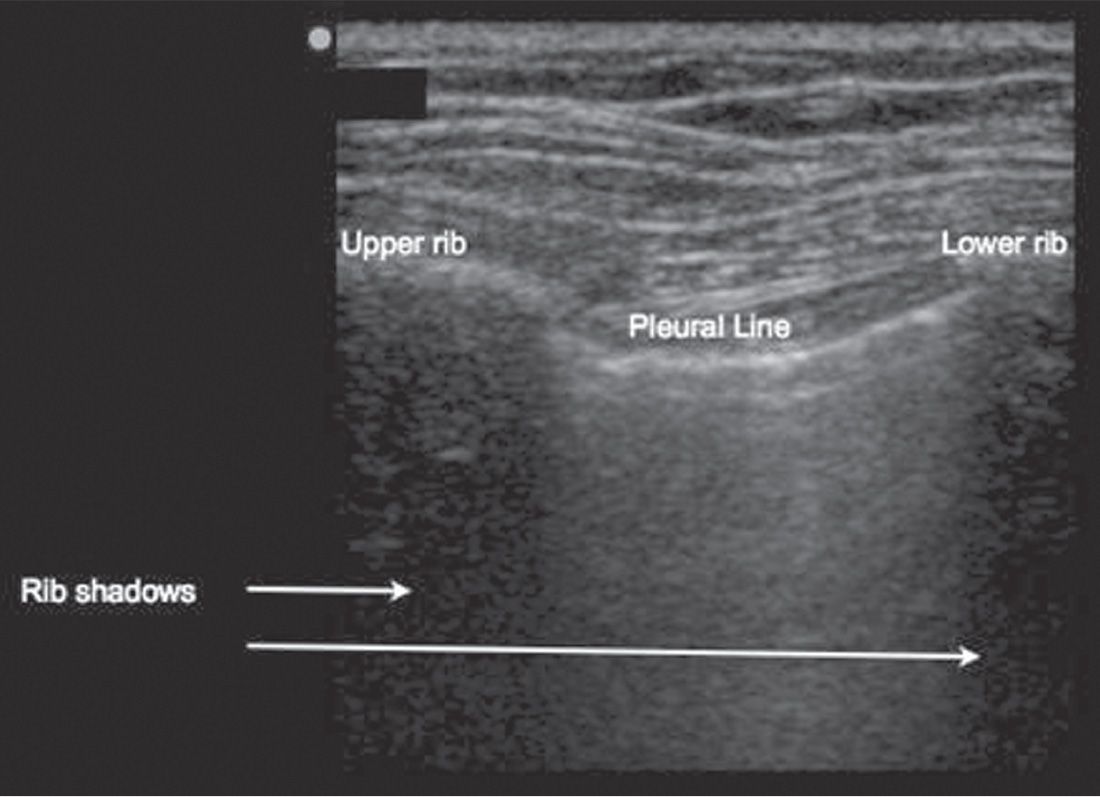
![]() Identify the bat sign: The upper rib–pleural line–lower rib profile (FIGURE 19.1)
Identify the bat sign: The upper rib–pleural line–lower rib profile (FIGURE 19.1)
![]() Normal lung findings
Normal lung findings
![]() B-mode: Visible sliding (shimmering or twinkling) at the level of the pleura
B-mode: Visible sliding (shimmering or twinkling) at the level of the pleura
![]() B-mode: Comet tails—vertical reverberation artifacts arising from the pleural line (FIGURE 19.2)
B-mode: Comet tails—vertical reverberation artifacts arising from the pleural line (FIGURE 19.2)
![]() M-mode: Seashore sign (FIGURE 19.3)
M-mode: Seashore sign (FIGURE 19.3)
![]() Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax
![]() B-mode: Loss of pleural sliding, as there is loss of contact between the visceral and the parietal pleura
B-mode: Loss of pleural sliding, as there is loss of contact between the visceral and the parietal pleura
![]() B-mode: Absence of comet tails
B-mode: Absence of comet tails
![]() M-mode: Stratosphere sign or bar-code sign (FIGURE 19.4)
M-mode: Stratosphere sign or bar-code sign (FIGURE 19.4)
![]() Lung point: Transition between collapsed and normally expanded lung; 100% specific for pneumothorax when identifiable
Lung point: Transition between collapsed and normally expanded lung; 100% specific for pneumothorax when identifiable
![]() TABLE 19.1 compares the signs suggestive of normal lung with those of pneumothorax
TABLE 19.1 compares the signs suggestive of normal lung with those of pneumothorax
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree