![]() A subperichondrial hematoma that separates the perichondrium from the underlying auricular cartilage
A subperichondrial hematoma that separates the perichondrium from the underlying auricular cartilage
![]() Result of a shearing force to the ear, but can also develop after blunt trauma
Result of a shearing force to the ear, but can also develop after blunt trauma
![]() The hematoma disrupts normal blood supply provided by the overlying perichondrium causing necrosis, fibrosis, and disfigurement of the auricle
The hematoma disrupts normal blood supply provided by the overlying perichondrium causing necrosis, fibrosis, and disfigurement of the auricle
![]() Commonly seen in wrestlers
Commonly seen in wrestlers
![]() Early diagnosis and treatment is the key—necrosis begins within 24 hours
Early diagnosis and treatment is the key—necrosis begins within 24 hours
![]() In general, needle aspiration is sufficient. However, if a hematoma reaccumulates, incision and drainage (I&D) may be indicated.
In general, needle aspiration is sufficient. However, if a hematoma reaccumulates, incision and drainage (I&D) may be indicated.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() There are no absolute contraindications
There are no absolute contraindications
![]() Anticoagulation is a relative contraindication. Consult with ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist if there are any concerns.
Anticoagulation is a relative contraindication. Consult with ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist if there are any concerns.
RISKS/CONSENT ISSUES
![]() Risk of infection is low. If clinical suspicion is high, an antistaphylococcal antibiotic may be prescribed.
Risk of infection is low. If clinical suspicion is high, an antistaphylococcal antibiotic may be prescribed.
![]() Recurrent and untreated injuries allow new cartilage to develop, which leads to deformity of the auricle (cauliflower ear) (FIGURES 77.1 and 77.2)
Recurrent and untreated injuries allow new cartilage to develop, which leads to deformity of the auricle (cauliflower ear) (FIGURES 77.1 and 77.2)
LANDMARKS
![]() The pinna is most commonly involved
The pinna is most commonly involved
![]() The needle/scalpel is used in the area of greatest fluctuance
The needle/scalpel is used in the area of greatest fluctuance
![]() General Basic Steps—Aspiration
General Basic Steps—Aspiration
![]() Cleanse
Cleanse
![]() Aspirate
Aspirate
![]() “Milk” hematoma
“Milk” hematoma
![]() Pressure dressing
Pressure dressing
TECHNIQUE
![]() For needle aspiration, a 10-mL syringe and a 20-gauge needle are required
For needle aspiration, a 10-mL syringe and a 20-gauge needle are required
![]() Cleanse the outer ear with a topical antiseptic (Betadine or chlorhexidine)
Cleanse the outer ear with a topical antiseptic (Betadine or chlorhexidine)
![]() Local anesthesia is seldom required. If used, avoid epinephrine (causes tissue necrosis).
Local anesthesia is seldom required. If used, avoid epinephrine (causes tissue necrosis).
![]() Stabilize pinna with thumb and fingers
Stabilize pinna with thumb and fingers
![]() Puncture area of greatest fluctuance with needle
Puncture area of greatest fluctuance with needle
![]() “Milk” hematoma with thumb and index finger until completely evacuated
“Milk” hematoma with thumb and index finger until completely evacuated
![]() Maintain pressure on ear for 3 minutes after needle has been withdrawn
Maintain pressure on ear for 3 minutes after needle has been withdrawn
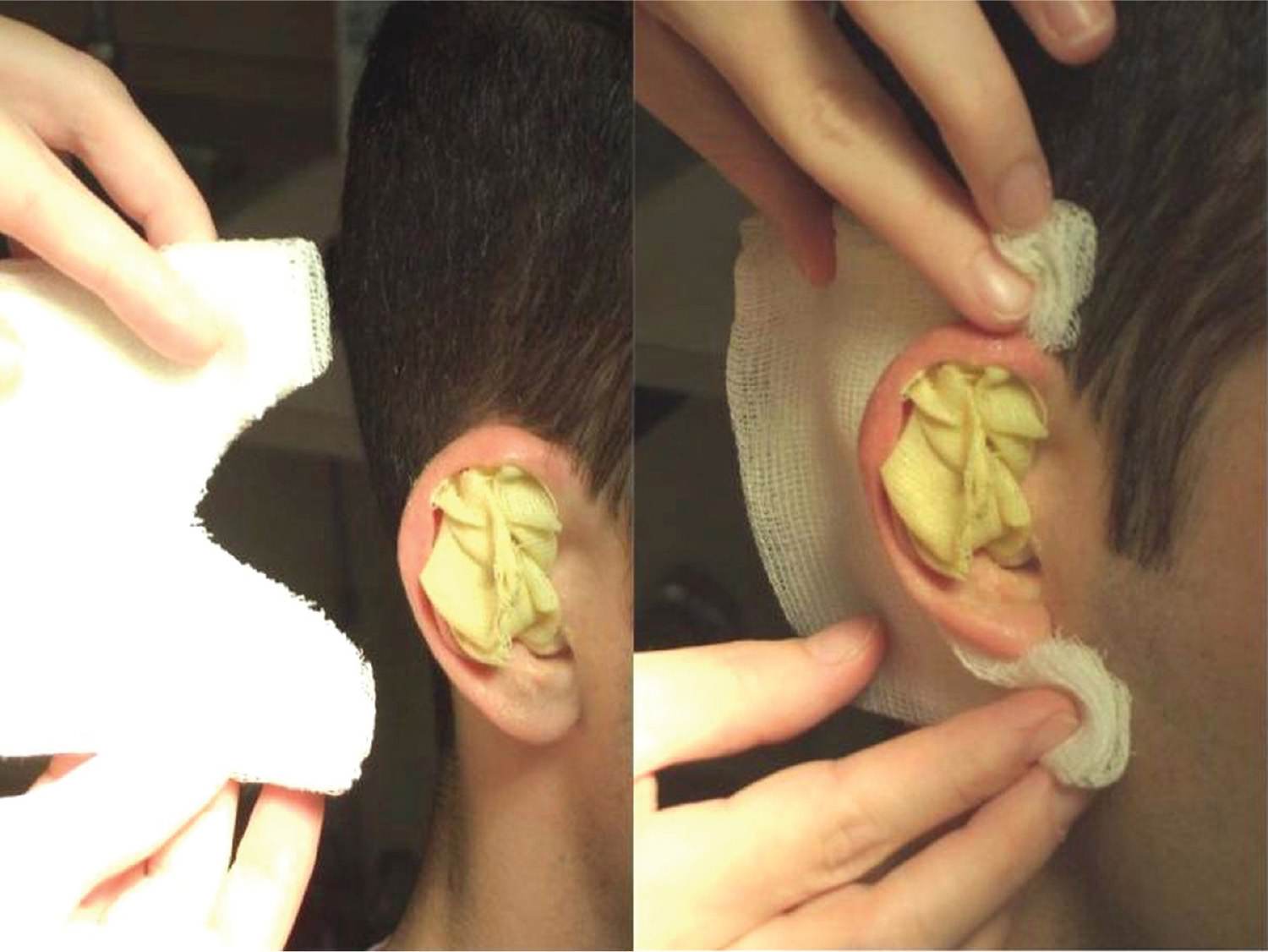
![]() Apply antibiotic ointment and a pressure dressing
Apply antibiotic ointment and a pressure dressing
![]() Patient should be advised to avoid strenuous activity
Patient should be advised to avoid strenuous activity
![]() Check ear again in 24 hours for reaccumulation of hematoma
Check ear again in 24 hours for reaccumulation of hematoma
![]() Reaspiration may be required, whereas persistent reaccumulation warrants I&D
Reaspiration may be required, whereas persistent reaccumulation warrants I&D
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree