![]() Used to provide regional anesthesia to the foot in order to facilitate the following:
Used to provide regional anesthesia to the foot in order to facilitate the following:
![]() Primary closure/exploration of foot wounds
Primary closure/exploration of foot wounds
![]() Incision and drainage
Incision and drainage
![]() Removal of foreign bodies
Removal of foreign bodies
![]() Operative intervention
Operative intervention
![]() Preferred technique because glabrous skin of the epidermis and fibrous septae in the dermis of the foot limit local diffusion of anesthetic
Preferred technique because glabrous skin of the epidermis and fibrous septae in the dermis of the foot limit local diffusion of anesthetic
CONTRAINDICATIONS
![]() Patient refusal
Patient refusal
![]() Infection overlying injection sites
Infection overlying injection sites
![]() Relative contraindications: Coagulopathy, systemic infection
Relative contraindications: Coagulopathy, systemic infection
LANDMARKS
![]() There are five nerves which supply the entire surface of the foot (FIGURE 81.1); anatomic landmarks to locate individual nerves are found in the text
There are five nerves which supply the entire surface of the foot (FIGURE 81.1); anatomic landmarks to locate individual nerves are found in the text
TECHNIQUE
![]() Preparation
Preparation
![]() Obtain informed consent
Obtain informed consent
![]() Position patient supine with knee in flexion and foot placed flat on the gurney
Position patient supine with knee in flexion and foot placed flat on the gurney
![]() Sterilize the area of injection with povidone–iodine or chlorhexidine solution
Sterilize the area of injection with povidone–iodine or chlorhexidine solution
![]() Drape the area with sterile towels
Drape the area with sterile towels
![]() Prepare one to three 10-mL syringes filled with anesthetic of choice
Prepare one to three 10-mL syringes filled with anesthetic of choice
![]() Use 25-gauge to 30-gauge needle
Use 25-gauge to 30-gauge needle
![]() General Basic Steps
General Basic Steps
![]() Identify landmarks
Identify landmarks
![]() Prepare for sterile procedure
Prepare for sterile procedure
![]() Inject anesthetic
Inject anesthetic
POSTERIOR TIBIAL NERVE BLOCK
![]() Innervation: Divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves to supply most of the plantar aspect of the foot
Innervation: Divides into medial and lateral plantar nerves to supply most of the plantar aspect of the foot
![]() Location: Medial aspect of the ankle between medial malleolus and Achilles tendon
Location: Medial aspect of the ankle between medial malleolus and Achilles tendon
![]() Technique (FIGURE 81.2)
Technique (FIGURE 81.2)
![]() Palpate posterior tibial artery posterior to medial malleolus
Palpate posterior tibial artery posterior to medial malleolus
![]() Direct needle at 45-degree angle to mediolateral plane, posterior to artery
Direct needle at 45-degree angle to mediolateral plane, posterior to artery
![]() At depth of artery (0.5–1 cm deep), move needle slightly to induce paresthesia
At depth of artery (0.5–1 cm deep), move needle slightly to induce paresthesia
![]() If elicited, 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected after aspiration
If elicited, 3 to 5 mL of anesthetic is injected after aspiration
![]() Withdraw 1 mm, then infiltrate 5 to 7 mL of anesthetic while withdrawing 1 cm
Withdraw 1 mm, then infiltrate 5 to 7 mL of anesthetic while withdrawing 1 cm
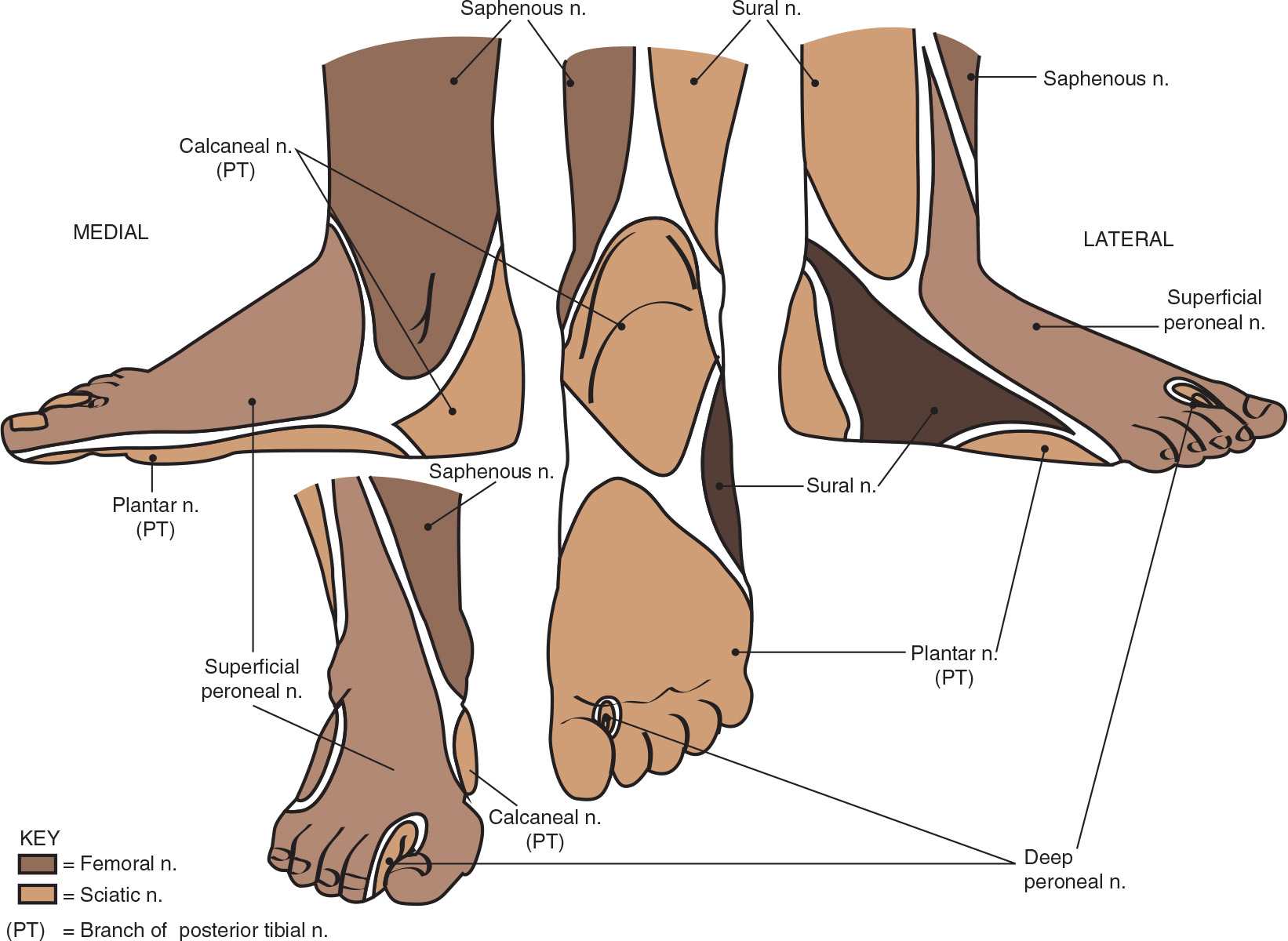
FIGURE 81.1 The sensory nerve supply to the foot. (From Brown DL, ed. Atlas of Regional Anesthesia. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2010:135–138.)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


