• Reduction of risk (Anesth Analg 2007;105:1615–1628)
• Regional techniques (general anesthesia has 11-fold ↑ risk of PONV)
• Propofol (19% ↓ PONV risk compared to inhalational agents)
• Avoid nitrous oxide (12% ↓ PONV risk), inhaled anesthetics, neostigmine
• Minimize opioids
• Ensure adequate hydration
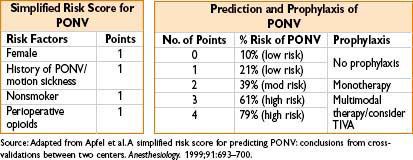
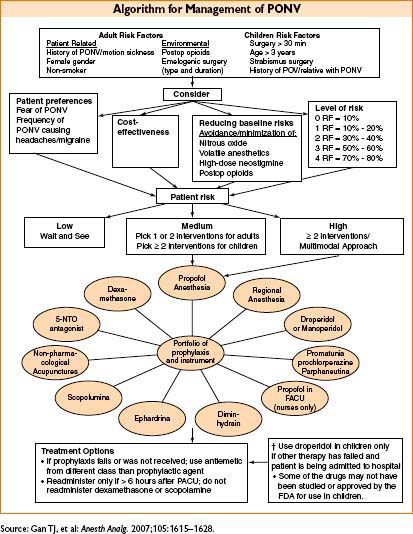
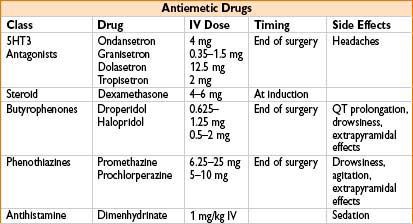
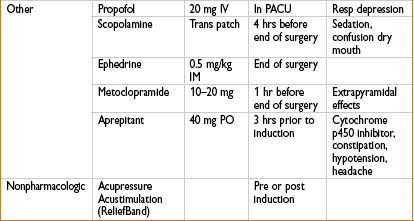
• PONV rescue strategy
• If initial agent is ineffective → give drug from a different class
• Repeat droperidol and 5-HT3 antagonists q6h
• Repeat administration of dexamethasone not recommended
• Discharge criteria
• Often based on formal scoring systems (see Chapter 13-6, PACU Management) or RN/MD assessment
• Oral intake: Not required prior to discharge
• Voiding: Only required if pt received neuraxial anesthesia or had gynecologic, hernial, anorectal, or genital surgery
• Spinal/epidural anesthesia: pt must have return of sensation & no motor block
• Nerve blocks: discharge can occur before full return of motor/sensory function, instruct pt to protect numb limb from injury
PAIN ISSUES FOR THE OUTPATIENT SETTING
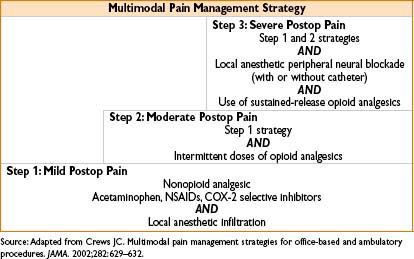
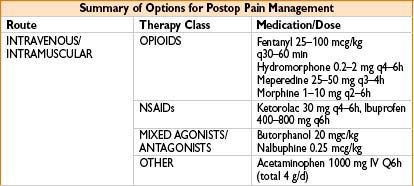
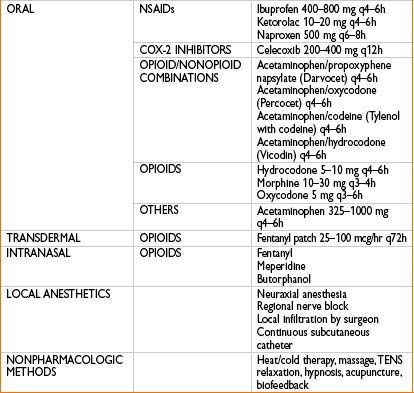
< div class='tao-gold-member'>









