Migraine
Cancer pain
Neuropathic pain
Chemo-induced neuropathic pain
Chronic neuropathic pain
Fibromyalgia
CRPS
Ischemic limb pain
Traumatic nerve injury pain
Phantom limb pain
Postherpetic neuralgia
Spinal cord injury pain
TMJ pain
Trigeminal neuralgia
Whiplash injury pain
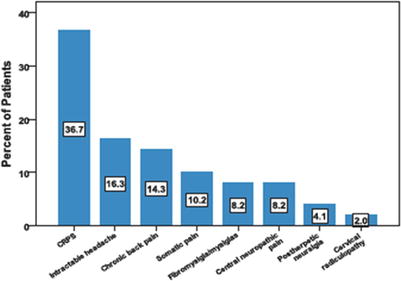
Fig. 6.1
Patients suffering from a variety of chronic refractory conditions reported effective pain relief in a retrospective cohort followed retrospectively for 5 years. The graph below shows percentage of patients suffering from those conditions in this series of 49 individuals [10]
The most important CNS effects are psychotropic. Psychedelic effects are dose dependent but are not uncommon even at the low doses used in the treatment of chronic pain (20–30 mg/h). In a study in healthy volunteers, ketamine caused distortion of reality, auditory hallucinations, paranoid ideas, anxious feelings (panic attacks) an inability to control thoughts, derealization in time and space, visual hallucinations, and increased awareness of sound and color. An intense feeling of a high was felt, which some described as extremely unpleasant; others expressed an intense feeling of euphoria. Other CNS adverse effects are dizziness, blurred vision, vertigo, nausea/vomiting, dysphasia, nystagmus, nightmares or vivid dreams, impaired motor function, and memory deficits [11, 12]. These effects decrease rapidly after termination of ketamine administration, although unpleasant dreams may persist up to three nights afterward. In clinical studies the incidence of psychological or psychedelic effects, although common, is still low. Sedation is most common during the infusion; the incidence of other effects is approximately less than 5% [10, 13].
Adverse effects were overall considered mild by patients in a retrospective study where subanesthetic doses of ketamine was administered over 30–60 min (Table 6.2) [10].
Table 6.2
Common side effects reported by patients undergoing ketamine infusions for refractory chronic pain states
Patient group: N (%) of patients | |||
|---|---|---|---|
CRPS (N = 18) | Non-CRPS (N = 31) | Total (N = 49) | |
Any event | 9 (50.0%) | 14 (45.2%) | 23 (46.9) |
Agitation | 1 (5.7%) | 1 (3.2%) | 2 (4.1%) |
Confused state | 1 (5.7%) | 2 (6.5%) | 3 (6.1%) |
Disorientation | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.2%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Dissociation | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.2%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Feeling cold | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.2%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Hallucination | 1 (5.7%) | 4 (13.2%) | 5 (10.2%) |
Hypertension | 4 (22.2%) | 2 (6.5%) | 6 (12.2%) |
Nausea | 1 (5.7%) | 1 (3.2%) | 2 (4.1%) |
Nystagmus | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.2%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Paresthesia | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.2%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Pharyngolaryngeal pain | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.2%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Restlessness | 1 (5.7%) | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (2.0%) |
Sedation | 2 (11.1%) | 2 (6.5%) | 4 (8.0%) |
Somnolence
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

| |||



