Yin
Yang
Ventral
Dorsal
Internal
External
Lower
Upper
Flaccid
Spastic
Hypofunction
Hyperfunction
Deficiency
Excess
Cold
Warm
Relaxed
Agitated
These ideas are very closely related to the concept of Qi . In Chinese medicine , Qi is the life force; every life process or organ function is an expression of the action and movement of the Qi. In Chinese medicine, there are three important sources of Qi. Each person inherits the Yuan Qi or source Qi . The Zong Qi is received from respiration, while the Yin Qi is obtained through food.
The Qi flows through the body in pathways, which are called meridians or channels . The meridians correspond to the organs of the body. In Chinese medicine, the organs are lung, large intestine, stomach, spleen, heart, small intestine, urinary bladder, kidney, pericardium, san jiao (triple warmer), gall bladder, and liver. The organs in Chinese medicine are not only the physical organs, but the larger functions that they are thought to govern. For example, the kidney functions in filtering impurities and in the creation of urine, but is also involved in sexual function. In addition, it influences a person’s will. The lung governs respiration as well as proper functioning of the skin. It is also related in some way to mood, especially depression. See Table 45.2.
Table 45.2
Categorization of organs in Chinese Medicine
Yin Organ | Yang Organ |
|---|---|
Lung | Large Intestine |
Spleen | Stomach |
Heart | Small Intestine |
Kidneys | Urinary Bladder |
Pericardium | San Jiao (Triple Warmer) |
Liver | Gall Bladder |
Acupuncture points are discrete pin-point areas found along the meridians. There are anywhere from 350 to 400 acupuncture points on the body. Many sources list 361 as the exact number. In Chinese medical theory, placement of needles at these points influences the flow of Qi through the corresponding meridians. In turn, this influences the health or functioning of the corresponding organ. There are meridians corresponding to each organ of the body. In addition, there are two other meridians called Du mai and Ren mai , which do not have corresponding organs. Therefore, there are a total of 14 standard meridians of the body (see Fig. 45.1).
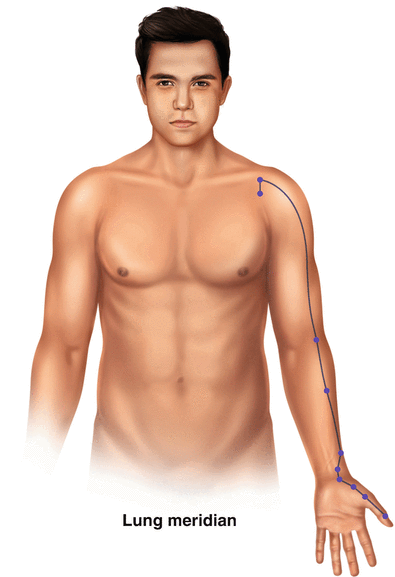
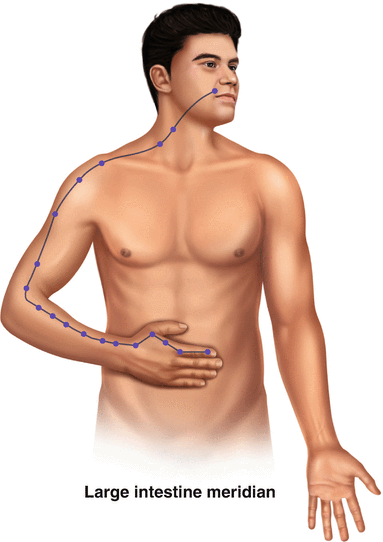


Fig. 45.1
a,b Acupuncture points are discrete pin-point areas found along the meridians . There are anywhere from 350 to 400 acupuncture points on the body. There are meridians corresponding to each organ of the body, totaling 14. A: Lung Meridian. B: Large Intestine Meridian
Western researchers have tried to determine whether there are unique anatomical structures at acupuncture points. Melzac et al. found that 71% of acupuncture points correspond to trigger points. Deung listed structures found in the vicinity of acupuncture points. He found the structures to be as follows: large peripheral nerves; nerves emerging from a deep to a more superficial location; cutaneous nerves emerging from deep fascia; nerves emerging from bone foramina; motor points of neuromuscular attachments ; blood vessels in the vicinity of neuromuscular attachments. Heine found that 80% of acupuncture points correlate with perforations in the superficial fascia of the cadavers he studied [4]. In the majority, acupuncture points correlate with anatomical structures and, in fact, correlate with nerves or fascial layers.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





