2. Achondroplasia (Dwarfism)
Definition
Achondroplasia is a hereditary, congenital autosomal dominant disorder that produces abnormalities in the growth and/or remodeling of cartilage and bone affecting the skull, spine, and extremities. The disorder, commonly known as dwarfism, frequently causes a person to be disproportionately short.
Incidence
The recent estimate for the incidence of achondroplasia in the United States is approximately 1:29,000; internationally, the estimate is approximately 1:40,000.
Etiology
Achondroplasia is an autosomal dominant inherited trait. The defect occurs on the short arm of chromosome 4—specifically, band 4p16.3.
Signs and Symptoms
• Abnormal odontoid
• Atlantoaxial instability
• Cleft lip
• Cleft palate
• Clubfoot
• Congenital heart disease
• Congenital odontoid absence
• Genu varum
• Hydrocephalus
• Kyphosis
• Laryngomalacia
• Micrognathia
• Obstructive sleep apnea
• Pulmonary hypertension
• Scoliosis
• Seizure disorder
• Spinal stenosis
• Tracheomalacia
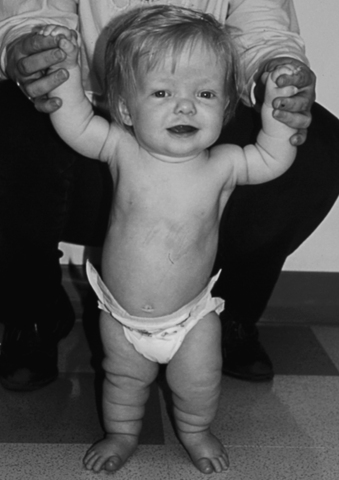 |
| Achrondroplasia (Dwarfism). This girl has short limbs relative to trunk length. She also has a prominent forehead, low nasal root, and redundant skin folds in the arms and legs. |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





