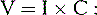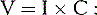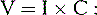2 The theoretical foundation for frequency-specific microcurrent
Biological quantum system
Quantum physics studies the submicroscopic forces that shape our universe at the atomic level. Quantum theory states that energy is not continuous but comes in discrete packets or quanta. These quanta behave like particles having mass at some times but they behave as waves of energy without mass at other times depending on the circumstances. Quantum physics must deal with uncertainty because the position and the momentum of a particle cannot be known at the same time and quantum phenomena, while coherent, are inherently unpredictable. Quantum physics is relevant at the atomic scale describing the behavior of atoms, molecules, electrons and protons. In the new field of quantum biology, electrons from green tea’s anti-oxidant catechins have been observed tunneling instantaneously across a gap between molecules to bind and inactivate a free radical, a process forbidden in classical physics (Anderson 2009).
Four factors operating
1. Current: The microamperage direct current alone produces specific well documented and predictable effects.
2. Frequencies: Two frequencies are used simultaneously, one from each channel, and produce specific effects that are independent of the current applied.
3. The Human Biological Semiconductor: The electromagnetic nature of biological tissue provides a semi-conductor tissue matrix that mediates the response to both the current and the frequencies.
4. Stable State: And finally the patient’s general physical and emotional health, conditioning, diet, hydration and history create an environment that will either support or erode the changes created by the frequencies and the current in any given treatment or any course of treatments.
1 Effects of the current
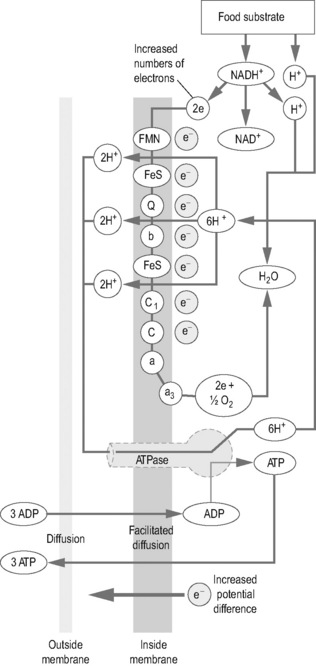
All matter, living and non-living, is ultimately an electromagnetic phenomenon (Becker 1985). All atoms are bonded electrically and all bonds are ultimately electromagnetic because the electrons creating the bonds are in constant motion and moving electrons create a magnetic field. The material world is a collection of atomic structures held together by electromagnetic forces.
Biological tissue is made up of complex combinations of atoms and molecules creating the membranes, organelles and cells that determine physical structure and physiologic function. Every cell and tissue membrane has an electrical potential or charge difference between one side of the membrane and the other (Kirsch 1998). Furthermore, the body as a whole has an electromagnetic field created by charge differentials between one area and another. The human system is more positively charged at the top near the head and along midline at the spine and more negatively charged in the periphery. Becker established that the bioelectric field produced by these linked electrical potentials is responsible for intracellular communication and tissue repair and eventually he proposed that the electromagnetic field controls all life processes (Becker 1985).
Current increases ATP energy
Current flowing through the body fuels all biological process. Gnok Cheng (Cheng et al 1982) and his associates demonstrated that applying additional current to a biological system could increase both protein synthesis and energy production dramatically as long as the current was small enough. Direct current levels of 50 to 1000μamps applied across rat skin increased glycine (amino acid) transport by 75% compared with untreated controls and current levels of 500μamps increased aminoisobutyric acid (amino acid) uptake by 90% indicating a dramatic increase in protein synthesis. But current levels above 1000μamps decreased protein synthesis by as much as 50%.
Cheng and his colleagues hypothesized that the increased number of electrons from the DC current flowing along the mitochondrial membranes increased the proton gradient across the membrane thereby increasing ATP production. Oschman (2009) has proposed that the electron transport chain in mitochondria can become electron-deficient, and that microcurrent provides more electrons that are semiconducted through the living matrix to the mitochondrial membranes. In either case, the additional ATP available is probably responsible for the increase in protein synthesis. There have been no studies that demonstrate increased ATP production in a living system but the increases in healing seen with microamperage current are usually attributed to this increase in ATP production and protein synthesis. Cheng and colleagues did not attempt to explain why current levels over 1000μamps reduced ATP production and protein synthesis. It is worth noting that all electrical stimulation devices except microcurrent use current levels above 1000μamps and may be decreasing ATP production, although that has not been demonstrated.
2 The effects of frequencies
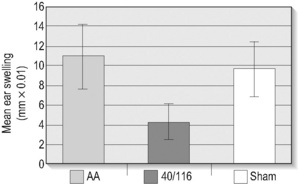
Current flow alone creates some positive effect but the most dramatic effects of FSM occur in response to specific frequencies. The frequency to neutralize a condition is delivered on one channel. The frequency for the tissue being addressed is delivered simultaneously on a second channel. In a blinded placebo controlled trial in mice, one frequency combination, 40Hz on channel A (reduce inflammation), and 116Hz on channel B (the immune system) reduced arachidonic acid induced lipoxygenase (LOX) mediated swelling in the mouse’s ear by 62% in four minutes. The ear swelling was measured with mechanical calipers and recorded in millimeters. Three unrelated frequency combinations (new injury, remove mineral from bone, and .3Hz) tested in the same model had no effect on inflammation or swelling. According to the researcher who performed the tests, no prescription or non-prescription drug has ever reduced inflammation in this animal model by more than 45% (Reilly et al 2004).
In a subsequent trial measuring reductions in COX mediated inflammation, 40Hz (reduce inflammation) and 116Hz (immune system) reduced swelling and inflammation by 30% which is identical to the prescription injectable anti-inflammatory Toridol when it was tested in this same mouse model. But 40Hz on channel A (reduce inflammation) and 355Hz (skin) on channel B had no anti-inflammatory effect and was equivalent to placebo (Reilly 2005). This suggests that the pattern created by both frequencies used is responsible for the anti-inflammatory effect, as long as one of the frequencies is 40Hz. The frequency from the second channel has a definite impact.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


 Box 2.1
Box 2.1