Fig. 17.1
M, 19-year-old Syrian patient. Status after blast injury, open forearm fractures with extensive soft tissue loss. Primary debridement procedure with minimal-invasive stabilization using tubular external fixation frame
The staged treatment protocol with conversion from primary tubular external fixation to finally internal fixation has been well described and accepted for management of patients, who suffered from multiple trauma and from open low-energy fractures, and also by treating of some patients after open high-energy trauma, where there are no present severe tissue loss and relative good coverage of the fracture site may be achieved. The primary benefit for such protocol is the reduction in soft tissue complications compared with immediate open surgery [5].
Extensive soft tissue damage and/or soft tissue loss precludes conversion to internal fixation methods. Poor soft tissue coverage of the bone ends, and fracture site leads to high-rate complications, especially in the presence of implanted internal fixation devices. Dealing these complex patients, we perform conversion of the unilateral external fixation frames to the circular Ilizarov devices (Fig. 17.2). Low morbidity associated with Ilizarov method suited it to the management of complex fractures, when extensive dissection and internal fixation are contraindicated due to comminuting at the fracture site and compromise of the soft tissue [6]. Ilizarov method is not only method of the surgical fracture fixation, but also a unique method of continuous, guided active influence on the tissue healing process and tissue shape. Thus, by treating of the patients, suffered from high-energy trauma with severe tissue damage and loss, this method can be useful tool for limb salvage and reconstruction [7].
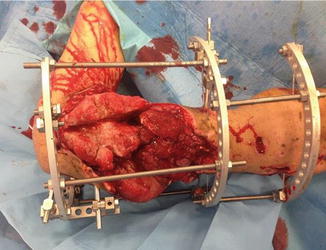

Fig. 17.2
Conversion to Ilizarov circular external frame was performed 2 weeks later after negative pressure wound therapy and repeated debridement
17.1 Damage Control
The method allows shape and function restoration of the injured limb without using of massive implanted devices and traumatic methods of the tissue transfer with attendant donor site morbidity. In unstable polytraumatized patients and those with combined soft tissue injuries (i.e., degloving, burns), stabilization of the fracture by external fixation allows early mobilization of the patient and facilitates nursing care.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree







