26 Sciatic Nerve Block
Anatomy
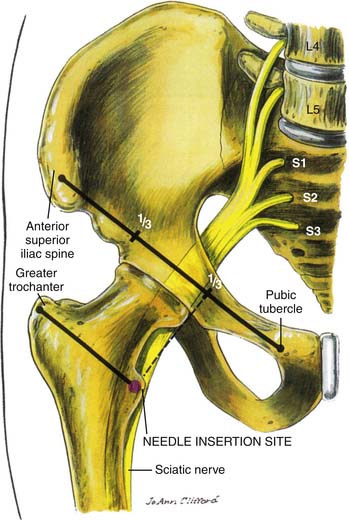
The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the body and is found in the pelvis from the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar to the third sacral spinal nerves.1 It transverses through the sciatic foramen and below the piriformis to enter the lower extremity and then descends between the greater trochanter and the ischial tuberosity (Fig. 26-1). In some cases the common peroneal component may pass through the piriformis, whereas the tibial component passes below the muscle.
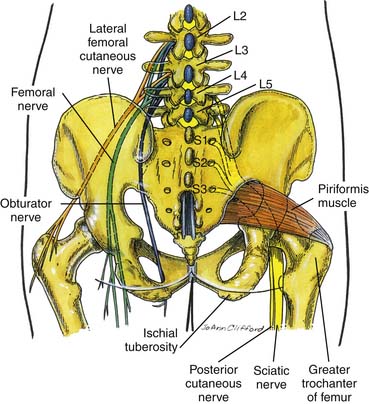
Figure 26-1 Sciatic nerve anatomy.
(From Brown DL: Atlas of Regional Anesthesia, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2005.)
History
Historically, the sciatic nerve block was first described by Victor Pauchet in 1920. In 1923, a similar approach was described by Gaston Labat in his book, Regional Anesthesia: Its Technique and Clinical Application. In 1975, Alon Winnie described the “modified Labat” technique. The anterior approach to the sciatic nerve block was described by Beck. In 1993, Mansour described the parasacral approach to the sacral plexus.2 Di Beneditto and colleagues described the subgluteal approach to the sciatic nerve block in 2001.3
Indications for Sciatic Nerve Block
Sciatic nerve block is indicated for lower limb surgery including surgery on the knee, ankle, and foot. A lumbar plexus block is beneficial for hip surgery. Various studies have demonstrated the benefits of continuous popliteal (sciatic nerve) block for postoperative pain control after painful orthopedic foot surgery. The benefits include decreased pain, reduced opioid requirements and opioid-related adverse effects.4–6 Sciatic nerve block may be a useful adjunct for certain lower extremity chronic pain syndromes such as sciatic neuropathy or piriformis syndrome where there is compression of the sciatic nerve at the piriformis muscle.
Sciatic Nerve Block—Posterior Approach
The needle insertion site is 4 cm below the midpoint of the line joining the posterior superior iliac spine (PSIS) to the ipsilateral greater trochanter (Fig. 26-2). The needle is inserted perpendicular to the skin. A nerve stimulator with a standard setting of 2 Hz and 100 μsec can be used and will initially cause a twitching of the gluteal muscles. On further advancement of the needle and with stimulation of the sciatic nerve, contraction of the hamstrings and calf muscles will be noted. This is observed as dorsiflexion of the ankle and foot. Small adjustments of the needle may become necessary to achieve stimulation at less than 0.5 mA. The stimulation current may be reduced until disappearance of stimulation is noted. This should usually be above 0.2 mA. After initial and intermittent negative aspiration 15 to 30 mL of local anesthetic is injected in increments of 4 to 5 mL. Injection of local anesthetic should be without any resistance and without pain or paresthesia. Triamcinolone (40 to 80 mg) or other corticosteroid with a lower volume of local anesthetic can be added when used for treatment of chronic pain syndromes.
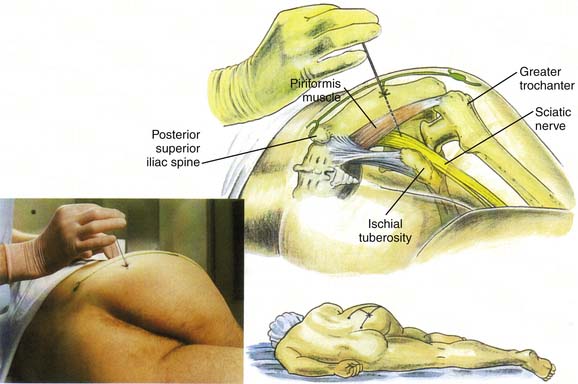
Figure 26-2 Sciatic nerve block: posterior approach.
(From Brown DL: Atlas of Regional Anesthesia, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, Saunders, 2005.)
In situations where prolonged postoperative analgesia is required, a catheter is threaded 5 to 10 cm beyond the needle tip and left in situ. Prior to injecting local anesthetic through the catheter, it should always be aspirated to confirm that the catheter tip is not intravascular.
Sciatic Nerve Block—Anterior Approach
The femoral artery is palpated within the femoral crease. From this point, a line is drawn perpendicular to the femoral crease to identify a point 5 cm distal to the femoral crease (Fig. 26-3). At this point, a needle is inserted perpendicular to the skin plane. A nerve stimulator with a standard setting of 2 Hz and 100 μsec can be used and will initially cause contraction of the quadriceps muscles. On further advancement of the needle and stimulation of the sciatic nerve, contraction of the hamstrings and calf muscles will be noted. Make small adjustments of the needle if necessary to achieve stimulation at less than 0.5 mA. Continue to reduce the stimulation current until the contraction disappears. This should usually be above 0.2 mA. After initial and intermittent negative aspiration of blood 15 to 30 mL of local anesthetic can be injected in increments of 4 to 5 mL. Injection of local anesthetic should be without any resistance and without pain or paresthesia. If bone was contacted prior to obtaining the desired stimulation, the needle can be reinserted medially. Triamcinolone (40 to 80 mg) or other corticosteroid with a lower volume of local anesthetic can be added when used for treatment of chronic pain syndromes.
Lumbar Plexus Block—Parasacral Approach
The parasacral approach to a lumbar plexus block was described by Mansour in 1993.7 This block can be used for anesthesia and analgesia in patients having lower extremity hip, tibia and fibula, knee, ankle, and foot surgery and amputation at the level of the knee.8
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree