Chapter 58 Rheumatologic Disease in the Intensive Care Unit
1 A critically ill patient is seen with an acute hot, swollen joint. What is the next step in management? What are the most common organisms found in a septic joint?
2 List the risk factors for the development of septic arthritis
5 What specific precautions should be taken when performing intubation in a patient with RA?
 Long-term use of corticosteroid
Long-term use of corticosteroid
 Severe peripheral joint deformities from RA
Severe peripheral joint deformities from RA
 Prior cervical spine subluxation
Prior cervical spine subluxation
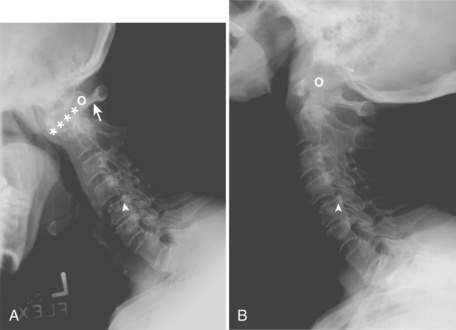
If clinical or radiographic evidence of subluxation exists and intubation is required, an anesthesiologist should be present during the procedure. In patients with AAS, subluxation is worsened with cervical flexion and reduced by cervical extension. Cricoarytenoid arthritis may also complicate endotracheal intubation. These patients may present with symptoms of tracheal pain, stridor, dysphonia, and shortness of breath (see Fig. 58-1).
6 What is scleroderma renal crisis (SRC)? When should this diagnosis be considered, and how is it confirmed?
 Clinical symptoms include headaches, visual disturbances from hypertensive retinopathy, seizures, encephalopathy, fever, general malaise, pulmonary edema. Less commonly, patients may have arrhythmias, myocarditis, and pericarditis.
Clinical symptoms include headaches, visual disturbances from hypertensive retinopathy, seizures, encephalopathy, fever, general malaise, pulmonary edema. Less commonly, patients may have arrhythmias, myocarditis, and pericarditis.
 Laboratory tests typically show an elevated creatinine level, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Urinalysis may show mild proteinuria, hematuria, and granular casts.
Laboratory tests typically show an elevated creatinine level, microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, and thrombocytopenia. Urinalysis may show mild proteinuria, hematuria, and granular casts.
7 Who is at risk for SRC, and what are risk factors indicating poor prognosis? What treatment should be initiated in SRC?
Poor prognosis for recovery from SRC is associated with the following:
9 How do you interpret a positive ANA test? What additional investigations should be ordered if there is a positive ANA test?
10 What clinical findings in a patient whose condition is deteriorating would prompt the consideration of SLE?
 Unexplained neurologic symptoms such as altered mental status, seizures, psychosis (lupus cerebritis)
Unexplained neurologic symptoms such as altered mental status, seizures, psychosis (lupus cerebritis)
 Renal abnormalities with proteinuria and cellular casts (lupus nephritis)
Renal abnormalities with proteinuria and cellular casts (lupus nephritis)
 Hematologic disorders such as hemolytic anemia
Hematologic disorders such as hemolytic anemia
 Serositis such as pericardial effusion and pleural effusion
Serositis such as pericardial effusion and pleural effusion
11 Describe antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)
APS is an acquired cause of hypercoagulability. Fifty percent of patients with APS have SLE. Recurrent venous and arterial thromboses and embolism are the hallmark of this syndrome. See Table 58-2.
Table 58-2 Clinical features and investigations of antiphospholipid syndrome