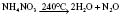CHAPTER 11 Pharmacology
Anaesthetic Gases
Oxygen
Discovered by Joseph Priestley in 1777. Manufactured by:
Nitrous oxide
Entonox
Analgesia is due to release of endogenous opioids and direct effect at opioid receptors.
Side-effects
Banks A., Hardman J.G. Nitrous oxide. Contin Educ Anaesth, Crit Care Pain. 2005;5:145-148.
Harris P.D., Barnes R. The uses of helium and xenon in current clinical practice. Anaesthesia. 2008;63:284-293.
Ma D., Wilhelm S., Maze M., et al. Neuroprotective and neurotoxic properties of the ‘inert’ gas, xenon. Br J Anaesth. 2002;89:739-746.
Maze M., Fujinaga M. Recent advances in understanding the actions and toxicity of nitrous oxide. Anaesthesia. 2000;55:311-314.
O’Driscoll B.R., Howard L.S., Davison A.G. British Thoracic Society: British Thoracic Society guideline for emergency oxygen use in adult patients. Thorax. 2008;63(Suppl VI):vi1-vi68. on behalf of the
Sanders R.D., Franks N.P., Maze M. Xenon: no stranger to anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2003;91:709-717.
Sanders R.D., Weimann J., Maze M. Biologic effects of nitrous oxide: a mechanistic and toxicologic review. Anesthesiology. 2009;109:707-722.
Taneja R., Vaughan R.S. Oxygen. BJA CEPD Rev. 2001;1:104-107.
Drug Interactions
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIS)
Antiplatelet agents
Tricyclics
Therefore tricyclics result in an increased risk of arrhythmias and hypotension.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline, paroxetine)
Anticonvulsants
H2 antagonists
Ranitidine. Causes sinus bradycardia and AV block, especially following i.v. administration.
Cimetidine. Inhibits hepatic cytochrome P450, increasing levels and thus toxicity of lidocaine, nifedipine and propanolol (Table 11.1). Potentiation of action of warfarin and theophyllines. Cimetidine competes with creatinine for renal excretion.
Table 11.1 Drugs affecting hepatic enzymes
| Hepatic enzyme induction | Hepatic enzyme inhibition |
|---|---|
| Alcohol | Cimetidine |
| Barbiturates | Erythromycin |
| Phenytoin | Ciprofloxacin |
| Carbamazepine | |
| Sodium valproate |
Droperidol
Butyrophenone; used for neuroleptic anaesthesia and as an antiemetic. Causes:
Fee J.P.H., McCaughey W. Preoperative preparation, premedication and concurrent drug therapy. In: Nimmo W.S., Rowbotham D.J., Smith G., editors. Anaesthesia. ed 2. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific; 1994:677-703.
Kam P.C.A., Chang G.W.M. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Anaesthesia. 1997;52:982-988.
Licker M., Morel D.R. Inhibitors of the renin angiotensin system: implications for the anaesthesiologist. Curr Opin Anaesth. 1998;11:321-326.
Vuyk J. Drug interactions in anaesthesia. Curr Opin Anaesth. 1997;10:267-270.
Ecstasy
Main problems in the management of these patients are:
Intravenous Induction Agents
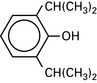
Propofol (di-isopropylphenol)
Emulsified in soya bean oil and egg phosphatide (formerly Cremphor EL).
t½ = 4 h. Induction dose 2–3 mg.kg−1. Highly lipid-soluble.
Metabolized by liver and extrahepatic sites (?lung). Hepatic excretion.