Percutaneous Suprapubic Cystostomy
Antonio Aponte-Feliciano
Jorge D. Yarzebski
Kevin M. Dushay
I. ANATOMY
A. The urinary bladder is anterior and inferior to the peritoneal cavity and posterior to the pubic symphysis.
1. The bladder dome rises above the pubic symphysis when distended (Fig. 16-1).
B. The anterior-superior midline of the external surface of the urinary bladder is generally free of major blood vessels as well as the anterior abdominal wall.
1. Major arterial supply to anterior-superior surface is from internal iliac branches entering lateral walls of the bladder.
2. Venous drainage flows inferiorly and laterally to reach the internal iliac veins.
II. ALTERNATIVES TO PERCUTANEOUS SUPRAPUBIC CYSTOSTOMY
A. Urethral catheterization.
III. INDICATIONS
A. Unsuccessful urethral catheterization in the setting of
1. Acute or chronic urinary retention.
2. Need for accurate urinary output monitoring.
3. Prostatic hyperplasia, cancer, or prior prostate surgery.
4. Loss of or threat to skin integrity due to urinary incontinence.
B. Inability to tolerate urethral catheter.
1. Following prostate or pelvic surgery, urethral pain, excoriation, necrosis, dementia/delirium causing patient to repeatedly remove catheter.
C. Urethral disruption from pelvic trauma/fracture.
D. Bladder drainage in the presence of severe infection: urethral, prostatic, or epididymal.
E. Neurogenic bladder.
F. Spinal cord injury patients.
1. May be easier for patient or caregiver.
2. May reduce frequency of urinary tract infections.
IV. CONTRAINDICATIONS
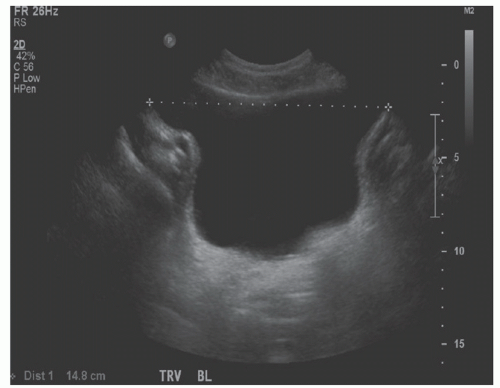
A. Nonpalpable bladder, bowel loops over the anterior bladder wall on sonographic evaluation.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree