Dipty Mangla and Ashish Sinha
1. Correct statement regarding neonatal physiology is
A. Neonates have a greater volume of distribution for water-soluble drugs
B. Total body water is higher in adults
C. Dose of propofol (mg/kg) is lower in neonates than in adults
D. Neonates have a higher body fat content than adults
2. A 4-year-old child weighing 16 kg is scheduled for hernia repair under general anesthesia. Assuming he was NPO for 8 hours, his total fluid deficit will be about _____ (mL):
A. 380
B. 420
C. 460
D. 500
3. The total dose of midazolam that may be given orally as premedication is
A. 0.2 mg/kg, maximum 10 mg
B. 0.2 mg/kg, maximum 20 mg
C. 0.5 mg/kg, maximum 15 mg
D. 0.5 mg/kg, maximum 20 mg
4. A newborn baby of 37 weeks of gestation has a heart rate of 90 bpm, is crying, is pink with blue extremities, and shows some flexion. Her Apgar score would be
A. 6
B. 7
C. 8
D. 9
5. After initial evaluation of the baby described above, the next step in managing her would be
A. Provide positive-pressure ventilation
B. Chest compressions
C. Warming blanket
D. Cardiology consult
6. All of the following drugs can be given through endotracheal tube, except
A. Epinephrine
B. Lidocaine
C. Surfactant
D. Calcium
7. The disease or syndrome with known association with malignant hyperthermia is
A. Huntington chorea
B. Fabry disease
C. King Denborough syndrome (KDS)
D. Burns
8. An 8-year-old child is brought to the emergency room with testicular torsion. The parents tell you he ate a sandwich 6 hours ago. Surgeon wants to operate immediately. Your response should be
A. Take him to the OR, deem it emergent, rapid-sequence intubation
B. Wait for 2 more hours, deem it urgent, rapid-sequence intubation
C. He is adequately fasting, elective, intubation
D. Wait for 2 hours, elective, intubation
9. Which of the following statements about pediatric airway is true?
A. More caudal position of larynx as compared to adult
B. More acute angulation of epiglottis
C. Glottic opening is the narrowest part of airway
D. Longer trachea as compared to adults
10. A 10-week-old baby, who was born prematurely at 30 weeks of gestation, undergoes circumcision uneventfully under general anesthesia. After the baby recovers from anesthetics in postanesthesia care unit, he can/should be
A. Admitted and monitored for 24 hours
B. Discharged home with parents
C. Discharged home if parents live within a 30-minute radius
D. Admitted to the ICU
11. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis is associated with
A. Metabolic acidosis
B. Metabolic alkalosis
C. Hyperkalemia
D. Hyperchloremia
12. A child with which of the following diseases/syndromes should be evaluated for heart disease?
A. Omphalocele
B. Gastroschisis
C. Hypertrophic pyloric stenosis
D. Tracheobronchitis
13. The earliest and the most pathognomic feature of malignant hyperthermia (MH) is
A. Increased temperature
B. Increased end-tidal CO2
C. Increased heart rate
D. Increased respiratory rate
14. The most common type of tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is
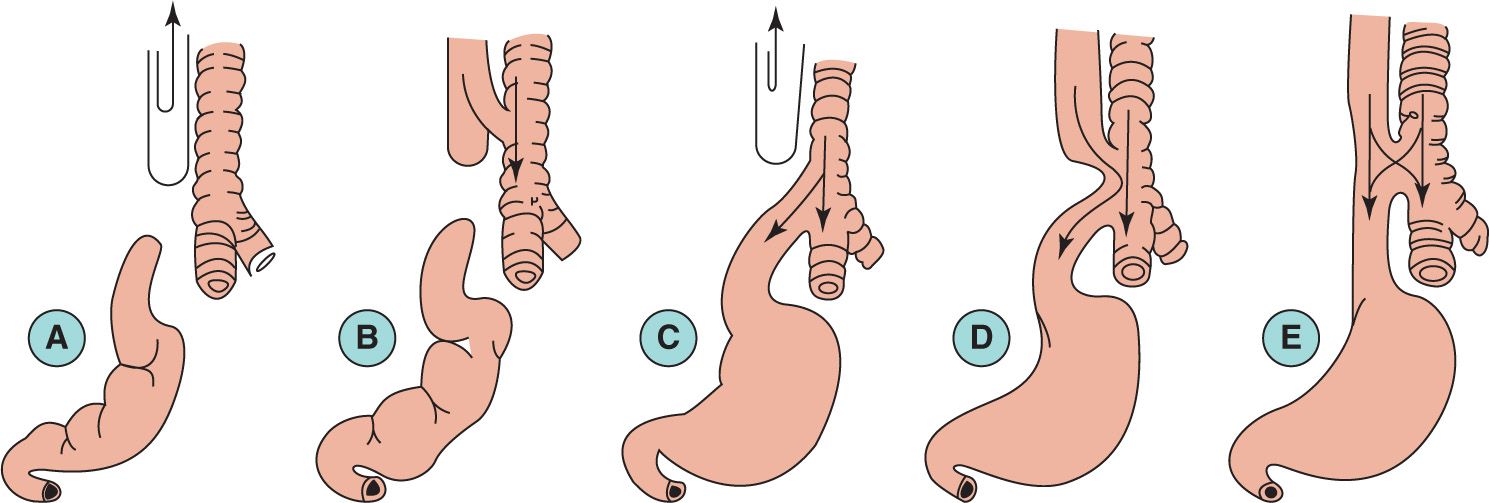
Figure 18-1.
15. Down syndrome is associated with all of the following, except
A. Large tongue
B. Atlantooccipital instability
C. Hyperthyroidism
D. Increased incidence of seizures
16. The first sign of intrathecal injection following the placement of caudal epidural with 0.25% bupivacaine in a 1-year-old child would be
A. Hypotension
B. Bradycardia
C. Falling oxygen saturation
D. Tachycardia
17. A 2-year-old child weighing 13 kg is scheduled for inguinal hernia repair. The calculated dose of 0.25% bupivacaine for a caudal epidural would be approximately ______ (mL):
A. 13
B. 7
C. 10
D. 20
18. All the following are physiologic changes that occur at birth, except
A. Closure of foramen ovale
B. Closure of ductus arteriosus
C. Decreased right-ventricular afterload
D. Decreased left-ventricular afterload
19. Neonates lose heat by all the following mechanisms in the operating room, except
A. Conduction to cold surfaces
B. Exposure to cold operating room
C. Dry airway gases
D. Metabolism of brown fat
20. A 4-year-old child with tetralogy of Fallot is scheduled for incision and drainage of a foot abscess. All the following measures can be used to improve his oxygenation, except
A. Phenylephrine
B. Nitroglycerine
C. Nitric oxide
D. Epinephrine
21. Which of the following heart rates is inappropriate for the age?
A. 50 bpm at 12 years of age
B. 120 bpm for a neonate
C. 100 bpm for a 1-year-old
D. 80 bpm for a 3-year-old
22. The age at which the glomerular filtration rate in a child is same as in adults is
A. 6 months
B. 1 year
C. 1.5 years
D. 2 years
23. Normal blood glucose level in a neonate is ______ (mg/dL):
A. 20 to 40
B. 40 to 60
C. 60 to 70
D. 50 to 80
24. The recommended size of an endotracheal tube for a 1-year-old child is
A. 2.5
B. 3.0
C. 4.0
D. 5.0
25. As compared to a 10-year-old child, a 1-year-old child will have higher
A. Oxygen consumption
B. Functional residual capacity
C. Tidal volume
D. Vital capacity
26. The total blood volume in a preterm is ______ (mL/kg):
A. 90 to 100
B. 70 to 80
C. 50 to 60
D. 80 to 90
27. A 2-year-old is scheduled for elective tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. His mother tells you he has runny nose. Your decision whether to proceed will be based on all the following, except
A. If he is afebrile
B. If he is not actively wheezing
C. Cancel the surgery since it is elective
D. Reluctance of parent for admitting the child, if needed
28. Urine output in a 6-year-old child undergoing surgery under general anesthesia should be ______ (mL/kg/h):
A. 0.5
B. 1
C. 1.5
D. 2
29. Perioperative management of a child with a femur fracture and sickle cell disease includes all of the following, except
A. Hydration
B. Treat infections
C. Transfuse to hemoglobin of 14 mg/dL
D. Avoid metabolic acidosis
30. Anesthetic management of a 12-year-old with Down syndrome includes all of the following, except
A. Continue antiseizure medications
B. Heavy sedation since all such patients are combative
C. Prepare for manual in line neck stabilization
D. Radiographs of the neck should be reviewed to rule out atlantooccipital instability
31. An 8-year-old boy, weighing 30 kg, is undergoing resection of a Wilms tumor in the operating room. His starting hemoglobin is 12 g/dL. If the threshold for transfusion is 8 g/dL, the allowable blood loss is ______ (mL):
A. 820
B. 840
C. 860
D. 880
32. A 5-year-old otherwise-healthy child is undergoing strabismus surgery with a laryngeal mask airway (LMA) in place. Thirty minutes into the procedure, his heart rate is 60 bpm, blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and the pulse oximeter reads 98%. The next step in management should be
A. Replace the LMA with an endotracheal tube
B. Inform surgeon, administer atropine
C. Nothing, this is normal for this child
D. Increase the FIO2 to 1.0
33. The afferent limb for oculocardiac reflex is
A. Vagus nerve
B. Trigeminal nerve
C. Glossopharyngeal nerve
D. Facial nerve
34. Positive-pressure ventilation with a face mask is contraindicated in which of the following condition?
A. Laryngospasm
B. Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
C. Trauma
D. Asthma
35. Treatment of postintubation croup in a child who underwent adenoidectomy is
A. Inhalation of mist
B. Steroids
C. Racemic epinephrine
D. All of the above
36. The most important measure to avoid subglottic edema in children is
A. Use of an appropriate-size endotracheal tube
B. Lubricating the endotracheal tube prior to intubation
C. Administering intravenous lidocaine for all intubations
D. Administering intravenous steroids for all intubations
37. Important difference between epiglottitis and laryngotracheobronchitis (croup) is
A. Croup responds to racemic epinephrine and steroids
B. Croup occurs in older children
C. Higher temperatures are seen in croup patients
D. Etiology of croup is bacterial
38. Anesthesia in a patient with Pierre Robin syndrome can be complicated by
A. Renal failure
B. Tendency to develop malignant hyperthermia
C. Cardiac failure
D. Difficult airway
39. Basic metabolic rate in children is
A. Least at 1 year of age
B. Same as adults
C. Highest till 2 years of age
D. Decreases after puberty
40. The percentage of patients developing malignant hyperthermia (MH) after masseter spasm is
A. 0% to 24%
B. 25% to 49%
C. 50% to 74%
D. 75% to 100%
41. All of the following are true for children with congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH), except
A. Pulmonary hypoplasia may be present
B. Dextrocardia is common
C. Bag and mask ventilation is contraindicated
D. Surgical management takes precedence over medical management
42. To protect lungs in a child with tracheoesophageal fistula, all the following should be done, except
A. Avoid feeding
B. Upright position
C. Intermittent suction of upper blind esophageal pouch
D. Prophylactic intravenous steroids
43. The main factor responsible for physiologic closure of a patent ductus arteriosus is
A. Increased PaCO2
B. Increased PaO2
C. Increased pulmonary artery pressure
D. Administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents
44. The most effective method for maintaining normothermia in an operating room is
A. Warm humidified gases
B. Warm intravenous fluids
C. Warming blankets
D. Increasing the room temperature
45. A 2-year-old child undergoing myringotomy develops laryngospasm in the operating room. The patient is breathing spontaneously with face mask at an FIO2 of 0.6. Next step in the management would be
A. Increasing FIO2 to 1.0
B. Jaw thrust
C. Endotracheal intubation
D. Intramuscular succinylcholine
46. Normal pulmonary dead space in a neonate is ______ (mL/kg):
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
47. Which of the following statements regarding fetal hemoglobin is true?
A. It is composed of two α and two β chains
B. It has more affinity for oxygen than adult hemoglobin
C. Patients with sickle cell disease and high fetal hemoglobin have poor prognosis
D. None of the above
48. Compared to adults, oxygen desaturation is more frequent in pediatric population because of
A. Lower functional residual capacity (FRC) in children
B. Higher oxygen consumption in adult
C. Lower heart rate in adults
D. Lower functional residual capacity in adults
49. The most consistent sign of intravascular injection following caudal epidural with 0.25% bupivacaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine is
A. Tachycardia
B. ST segment changes
C. Bradycardia
D. Hypertension
50. The dose of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants in a neonate is
A. Decreased as compared to adults
B. Increased as compared to adults
C. Same as adults
D. Cannot be predicted
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree






