Treatment of pain should be priority for all clinicians; pain as fifth vital sign
Children often endure unacceptable levels of pain during hospitalization
Children generally receive analgesia less frequently than adults in the emergency setting
When inadequate analgesia is given, children and neonates often experience more distress with subsequent procedures
Pain history: location, intensity, quality, duration, frequency, aggravating, and relieving factors
Regular assessment based on presence and severity of pain: self-report, behavioral observation, and physiologic measures
Self-report is considered “gold standard”:
Children can report degree of pain by 3-4 yrs
Children > 6 yrs can provide detailed descriptions of pain intensity, quality, and location
For infants and children ages 2 months to 7 yrs and cognitively impaired
For children ages 3-7 yrs and older, children unable to use numerical rating scale
Categories: none, a little, medium, a lot
Table 64.1 FLACC Scale | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
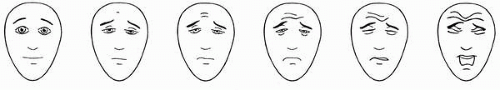 Figure 64.1 Faces Pain Scale Source: With permission from: International Association for the Study of Pain. In: Hicks CL, von Baeyer CL, Spafford P, van Korlaar I, Goodenough B. Faces Pain Scale Revised: toward a common metric in pediatric pain management. Pain. 2001;93:173-183. |
For children > 7 yrs
Numerical scales from 0-10 or 0-100
Uncertainty, anxiety, and fear of procedures
Expectations of pain to be experienced
Previous experiences of pain
Parental anxiety
Avoid using medical jargon
Talk to children using age-appropriate language
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree



