Chapter 9 Paediatrics
General Paediatrics
Physiological changes at birth
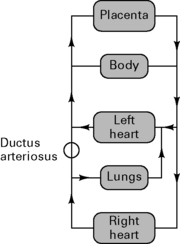
• Tactile stimulus triggers respiratory centre. Inflation of lungs reduces pulmonary vascular resistance.
• Cessation of placental flow increases SVR. Combined with decreased PVR, flow through ductus arteriosus reverses. High PaO2 causes ductal smooth muscle to constrict, and closure occurs (reversible for several days).
Fetal circulation is shown in Figure 9.1.
Neonatal physiology
CVS
• Relatively little contractile tissue in heart (30%), so increased cardiac output achieved by increased heart rate rather than stroke volume. Ventricular thickness equal by 6 months.
• Heart rate at term is 120/min. Rises to 160/min by 1 month and decreases to adult rates by 15 years.
• PNS more developed than SNS. Therefore there is a tendency to bradycardia. Response to adrenergic drugs is diminished.
Respiratory
• Obligatory nasal breathing until 5 months. Nasal passages account for 30–50% of airway resistance. May be unable to convert to mouth breathing if there is nasal obstruction.
• Large tongue obstructs the airway and makes laryngoscopy difficult. Epiglottis is longer, narrower and angled away from the axis of the trachea.
• Narrowest part of upper airway is cricoid cartilage. Even minimal oedema causes a large increase in airway resistance (Hagen–Poiseuille law).
• No bucket handle rib movement, therefore increased minute volume is achieved by increasing respiratory rate.
• Diaphragmatic > intercostal respiration. Fewer type I muscle fibres used in prolonged work so earlier diaphragm fatigue.
Renal
• Immature renal function with reduced GFR; therefore reduced ability to excrete drugs, dependent upon renal clearance.
CNS
• Motor nerve endings differentiate to form end plates at 26–28 weeks, but process still incomplete at term.
• Increased risk of intraventricular haemorrhage, particularly with abrupt fluctuations in cerebral blood flow and CVP, due to underdeveloped perivascular connective tissue.
Blood
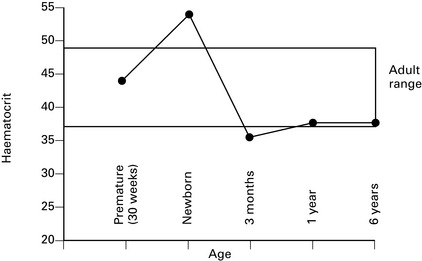
• 70% HbF at term; P50 = 2.7 kPa (3.5–4.0 kPa in adult) with leftward shift of O2 dissociation curve.
Change of haematocrit with age is shown in Figure 9.2.
Temperature
• Noradrenaline > adrenaline released with stress to trigger non-shivering thermogenesis in brown fat. Brown fat stores are limited. Shivering does not occur before 3 months.
General anaesthesia
Preoperative fasting
CONSENSUS GUIDELINE ON PERIOPERATIVE FLUID MANAGEMENT IN CHILDREN, V1.1
Association of Paediatric Anaesthetists of Great Britain and Ireland 2007
Executive summary
1. Children can safely be allowed clear fluids 2 h before surgery without increasing the risk of aspiration.
3. In children under 6 months of age it is probably safe to allow a breast milk feed up to 4 h before surgery.
7. Maintenance fluid requirements should be calculated using the formula of Holliday and Segar
| Body weight | Daily fluid requirement |
|---|---|
| 0–10 kg | 4 mL/kg per h |
| 10–20 kg | 40 mL/h + 2 mL/kg per h above 10 kg |
| >20 kg | 60 mL/h + 1 mL/kg per h above 20 kg |
9. During surgery, all of these requirements should be managed by giving isotonic fluid in all children over 1 month of age.
10. The majority of children over 1 month of age will maintain a normal blood sugar if given non-dextrose containing fluid during surgery.
11. Children at risk of hypoglycaemia if non-dextrose containing fluid is given are those on parenteral nutrition or a dextrose containing solution prior to theatre, children of low body weight (<3rd centile) or having surgery of more than 3 h duration and children having extensive regional anaesthesia. These children at risk should be given dextrose containing solutions or have their blood glucose monitored during surgery.
12. Blood loss during surgery should be replaced initially with crystalloid or colloid, and then with blood once the haematocrit has fallen to 25%. Children with cyanotic congenital heart disease and neonates may need a higher haematocrit to maintain oxygenation.
13. Fluid therapy should be monitored by daily electrolyte estimation, use of a fluid input/output chart and daily weighing if feasible.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree