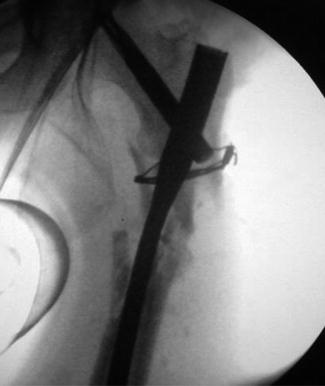
Fig. 19.1
Radiological picture demonstrates fully displaced comminuted proximal left femoral fracture
In the emergency room, he received anti-tetanus vaccination and antibiotic treatment according to our hospital protocol and then was operated 60 min after arrival.
During the operative procedure under general anesthesia, we removed all the sutures, and radical debridement of all in vital tissue and remained foreign bodies was done; cultures were taken from the debrided tissue. Massive washing of wound with 10 L of normal saline was done.
Temporary stabilization of the proximal femur fracture was achieved by fixing his fracture with bridging trans-hip tubular external fixation frame (Fig. 19.2), and we left his wounds unsutured and dressed with vacuum drainage dressings.
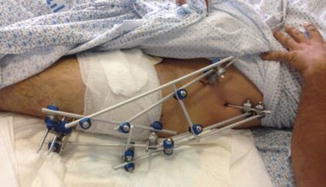

Fig. 19.2
Clinical picture demonstrates primary stabilization by trans-hip tubular external fixation frame
A second look in OR under general anesthesia was performed 3 days after the first operation, and additional thorough debridement was performed; vacuum drainage dressings were applied again.
After 10 days of negative pressure wound therapy, he was stable clinically, without signs of general or local infection, his wound had clean granulation tissue, and we took him back to the operating room for definitive treatment of the femoral fracture—conversion from primary tubular external fixation to proximal femoral intramedullary nail (Fig. 19.3).