 The immunosuppressive effects of the stress response, characterized by catecholamine and glucocorticoid excess, are balanced by the proinflammatory mediators, such as prolactin and vasopressin.
The immunosuppressive effects of the stress response, characterized by catecholamine and glucocorticoid excess, are balanced by the proinflammatory mediators, such as prolactin and vasopressin. In the acute phase of septic shock, inflammation predominates, but during prolonged critical illness, many patients are immune-suppressed.
In the acute phase of septic shock, inflammation predominates, but during prolonged critical illness, many patients are immune-suppressed. Clinically significant immune suppression may result from failure of the neuroendocrine immune (NEI) system or from the immunosuppressive side effects of NEI mediators used as critical care therapy.
Clinically significant immune suppression may result from failure of the neuroendocrine immune (NEI) system or from the immunosuppressive side effects of NEI mediators used as critical care therapy. Catecholamines, glucocorticoids, somatostatin, and opioids have their immunosuppressive side effects and should be tapered as soon as clinical conditions allow.
Catecholamines, glucocorticoids, somatostatin, and opioids have their immunosuppressive side effects and should be tapered as soon as clinical conditions allow. Studies of NEI mediators should include an assessment of their impact on immune function.
Studies of NEI mediators should include an assessment of their impact on immune function.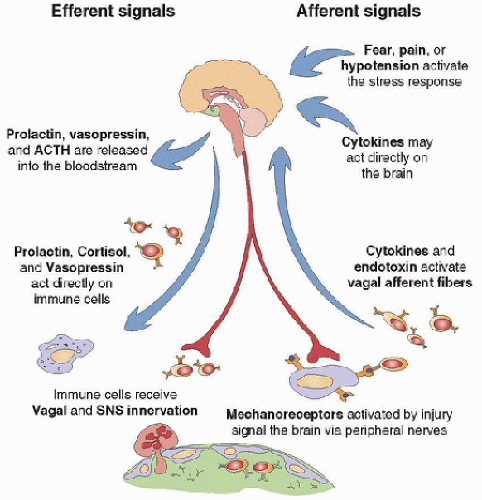 FIGURE 82.1. Bidirectional NEI communication. Stimulation of the acute stress response generates immunosuppressive signals (activation of the HPA axis, the SNS, and endogenous opioids) and immune-supportive signals (release of proinflammatory peptides, such as vasopressin and prolactin). A threat to the homeostatic milieu, in the form of trauma or infection, activates the immune system. Activated immune cells produce cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6), which signal the CNS by stimulating afferent nerves or by circulating directly to the brain. Autonomic nerve activity delivers anti-inflammatory signals in response to immune activation. |
 Although our understanding of NEI interactions is limited, it is still clear that perturbations to any single pathway in this intricate system may have distant reverberations. Because therapies used in critical care interfere with or mimic many of these pathways, it is incumbent on the intensivist to pay attention to developments in the field of NEI interactions. In the past few years, corticosteroids, growth hormone, and vasopressin—all NEI mediators with immunomodulatory effects—have been proposed as therapeutic agents in the treatment of ICU patients.
Although our understanding of NEI interactions is limited, it is still clear that perturbations to any single pathway in this intricate system may have distant reverberations. Because therapies used in critical care interfere with or mimic many of these pathways, it is incumbent on the intensivist to pay attention to developments in the field of NEI interactions. In the past few years, corticosteroids, growth hormone, and vasopressin—all NEI mediators with immunomodulatory effects—have been proposed as therapeutic agents in the treatment of ICU patients.TABLE 82.1 PROINFLAMMATORY AND ANTI-INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
as 36-72 hours impairs macrophage response to monocyte colony-stimulating factor in mice and affects phagocytosis and superoxide production ex vivo (20). In animal models, drugs that potentiate narcotic analgesia, such as clonidine and dexmedetomidine, also have immune suppressive effects (25).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree





